This is a continuation of my previous post: Investing in Peer to Peer Loans
LendingClub suggest a minimum of 100 loans (of equal size) to escape the risk of your luck with individual loans causing very bad results. Based on this diversity the odds of avoiding a loss have been very good (though that obviously isn’t a guarantee of future performance), quote from their website (Nov 2015):
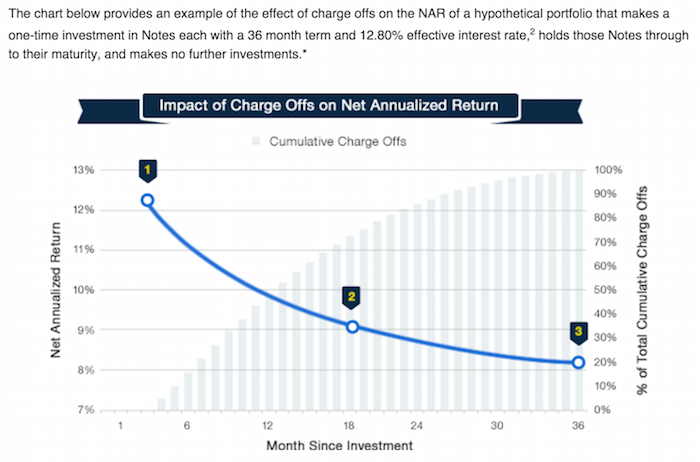
This chart, from LendingClub, shows a theoretical (not based on past performance) result. The basic idea is that as the portfolio ages, more loans will default and thus the portfolio return will decline. This contrasts with other investments (such as stocks) that will show fluctuating returns going up and down (over somewhat dramatically) over time.
For portfolios of personal loans diversity is very important to avoid the risk of getting a few loans that default destroying your portfolio return. For portfolios with fewer than 100 notes the negative returns are expected in 12.8% of the cases (obviously this is a factor of the total loans – with 99 loans it would be much less likely to be negative, with 5 it would be much more likely). I would say targeting at least 250 loans with none over .5% would be better than aiming at just 100 loans with none over 1% of portfolio.
There are several very useful sites that examine the past results of Lending Club loans and provide some suggestions for good filters to use in selecting loans. Good filters really amount to finding cases where Lending Club doesn’t do the greatest job of underwriting. So for example many say exclude loans from California to increase your portfolio return. While this may well be due to California loans being riskier really underwriting should take care of that by balancing out the risk v. return (so charging higher rates and/or being more stringent about taking such loans.
So I would expect Lending Club to adjust underwriting to take these results into account and thus make the filters go out of date. Of course this over simplifies things quite a bit. But the basic idea is that much of the value of filters is to take advantage of underwriting weaknesses.
This chart (for 36 month loans) is an extremely important one for investors in peer to peer loans. It shows the returns over the life of portfolios as the portfolio ages. And this chart (for LendingClub) shows the results for portfolios of loans issued each year. This is a critical tool to help keep track to see if underwriting quality is slipping.
In a very good result for LendingClub the worst performances are the first 2 years (2008 and 2009). Investing is challenging and trying to examine historical data and draw conclusions is not simple. The conclusion that LendingClub learned from their initial efforts in 2008 and 2009 and improved seems reasonable to me.
2010, 2011 and 2012 all have the loans completed (or nearly so, fro 2012) and the truth about peer to peer lending (or really any lending) can be seen from the chart. The return of the portfolio declines as it ages (as loans default).
What you should keep an eye on if you invest in peer to peer loans is if the lines for new years started to look much worse over time than previous years (for example if they started to look like 2008 or 2009). If that happened, ask why. If the economy entered a deep recession that may well explain it. But if there is not a macroeconomic explanation then you need to worry about underwriting quality.
If I decided the risk was real that underwriting quality had declined what I would likely do it stop reinvesting my payments in new loans (or reduce the amount of that I was doing). It is possible with LendingClub to sell your fractions of loans to other investors. I doubt I would bother with this but it is another option. Of course, unless you correctly determine underwriting quality declined faster than the other investors do their bids for those loans are going to be low (you will likely lose money on the sales).
In 2010 and 2011 returns started in the 11% to 12% range and by the time the loans closed the return was a bit above 6%. This is the type of decline you can expect (and it will be worse if there are bad macroeconomic conditions).
2012 started above 12% and is on track (with 2 months left) to slightly exceed the final returns for 2010 and 2011. The chart (and these comments) are based on all 36 month loans of all grades made in those years. LendingClub lets you show view the chart of 36 or 60 month loans and for all loans or looking at a specific grade. Remember in looking at all loans the returns are going to be impacted by the makeup of the loans (how many are A, B, C, D etc.). But you can also look at it directly for each grade to see if issues are cropping up in more specific areas.
An example of a site that examine past loan results to guess about future: How Will P2P Lending Perform During a National Recession?
it’s amazing to note that banks still did not lose money on credit cards during the 2008 recession. The stock market fell 57% in six months, yet major banks kept earning and earning.
What we see is the average return of 8.8% steadily dropping after each recession:
After the 2000 recession, avg. credit card returns fell 20% to an ROI of 7%
After the 2008 recession, avg. credit card returns fell 40% to an ROI of 5.2%
…
If this is equally felt in peer to peer lending, it could mean:A more typical recession may also drop a peer lending return by 20% – say from 6% to 4-5%.
A more serious recession may also drop a peer lending return by 40% – say from 6% to 3-4%.
Of course, these losses will be easier if investors hold more A-grade loans, and more ugly if investors hold more E-grade loans.
100m deep is another useful resource. It provides an interactive tool to let you look at the past results based on characteristics (employment length, purpose of loan, home ownership, income, loan term, etc.) you chose.
My investigation so far makes me think peer to peer lending is a sensible place for a sophisticated investor to put a portion of their fixed income investments. I would go slowly and not commit a large amount to such investments but taking a small stake with a couple percent of a portfolio may well be wise for investors that know what they are doing. I will have more posts looking at peer to peer loans, including more on filters and automated investing with LendingClub.
Related: Investment Risk Matters Most as Part of a Portfolio, Rather than in Isolation
– Corporate and Government Bond Yields (2008) – All-weather Portfolio
Comments
3 Comments so far

[…] Peer to Peer Portfolio Returns and The Decline in Returns as Loans Age […]
[…] post continues our series on peer-to-peer lending (and LendingClub): Peer to Peer Portfolio Returns and The Decline in Returns as Loans Age, Investing in Peer to Peer Loans. LendingClub, and other peer-to-peer lenders let you use filters […]
[…] Peer to Peer Portfolio Returns and The Decline in Returns as Loans Age (2015) – Investing in Peer to Peer Loans – Looking for Yields in Stocks and Real Estate (2012) […]