When critics say that Europe is running out of time to deal with the financial crisis I wonder if they are not years too late. Both in Europe responding and those saying it is too late.
It feels to me similar to a situation where I have maxed out 8 credit cards and have a little bit left on my 9th. You can say that failing to approve my 10th credit card will lead to immediate pain. Not just to me, but all those I owe money to. That is true.
But wasn’t the time to intervene likely when I maxed out my 2nd credit card and get me to change my behavior of living beyond my means then? If you only look at how to avoid the crisis this month or year, yeah another credit card to buy more time is a decent “solution.”
But I am not at all sure that bailing out more bankers and politicians for bad financial decisions is a great long term strategy. It has been the primary strategy in the USA and Europe since the large financial institution caused great recession started. And, actually, for long before that the let-the-grandkids-pay-for-our-high-living-today has been the predominate economic “strategy” of the last 30 years in the USA and Europe.
That has not been the strategy in Japan, Korea, China, Singapore, Brazil, Malaysia… The Japanese government has adopted that strategy (with more borrowing than even the USA and European government) but for the economy overall in Japan has not been so focused on living beyond what the economy produces (there has been huge personal savings in Japan). Today the risks of excessive government borrowing in Japan and borrowing in China are potentially very serious problems.
I can understand the very serious economic problems people are worried about if bankers and governments are not bailed out. I am very unclear on how those wanting more bailout now see the long term problem being fixed. Unless you have some system in place to change the long term situation I don’t see the huge benefit in delaying the huge problems by getting a few more credit cards to maintain the fiction that this is sustainable.
We have seen what bankers and politicians have done with the trillions of dollars they have been given (by governments and central banks). It hardly makes me think giving them more is a wonderful strategy. I would certainly consider it, if tied to some sensible long term strategy. But if not, just slapping on a few more credit cards to let the bankers and politicians continue their actions hardly seems a great idea.
Related: Is the Euro Going to Survive in the Long Run? (2010) – Which Currency is the Least Bad? – Let the Good Times Roll (using Credit) – The USA Economy Needs to Reduce Personal and Government Debt (2009 – in the last year this has actually been improved, quite surprisingly, given how huge the federal deficit is) – What Should You Do With Your Government “Stimulus” Check? – Americans are Drowning in Debt – Failure to Regulate Financial Markets Leads to Predictable Consequences
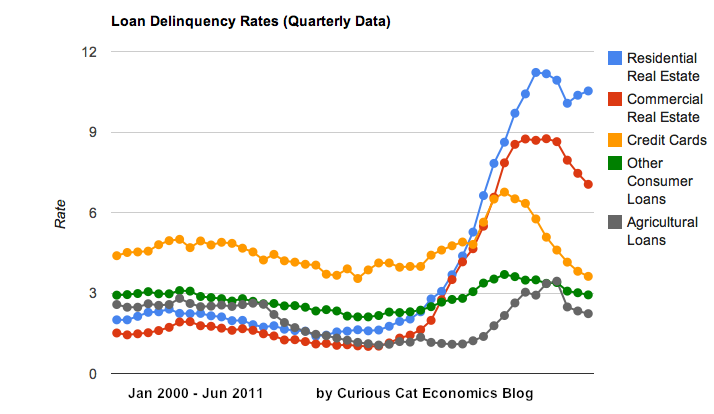
Chart showing loan delinquency rates from 2000-2011, shows seasonally adjusted data for all banks for consumer and real estate loans. The chart is available for use with attribution. Data from the Federal Reserve.
Residential real estate delinquency rates increased in the first half of 2011 in the USA. Other debt delinquency rates decreased. Credit card delinquency rates have actually reached a 17 year low.
While the job market remains poor and the serious long term problems created by governments spending beyond their means (for decades) and allowing too big to fail institutions to destroy economic wealth and create great risk for world economic stability the USA economy does exhibit positive signs. The economy continues to grow – slowly but still growing. And the reduction in delinquency rates is a good sign. Though the residential and business real estate rates are far far too high.
Related: Consumer and Real Estate Loan Delinquency Rates 2000-2010 – Real Estate and Consumer Loan Delinquency Rates 1998-2009 – Government Debt as Percent of GDP 1998-2010 for OECD
For the first time ever average 30 year fixed mortgage rates have fallen under 4%. My guess about interests rates have not been very good the last decade or so. I can’t believe people actually want to lend at these rates but obviously I have been wrong. The risks of lending at these rates over the long term just seem way too high to take a paltry 4%. But obviously I have been wrong.
So if you didn’t refinance when I suggested it (and refinance, myself), previously, you may want to look at doing so now. Or you may believe that listen to me about interest rates doesn’t seem very wise.
I have even read that banks are reducing fees in order to encourage refinancing. Seems crazy to me, but what do I know.
You do need to have a decent loan to value ratio (certainly no more than 90%, and probably 80% would be better). That can be difficult for those that have had large decreases in their homes value. Also you need a great credit rating and a stable job situation. But if you qualify refinancing at these rates should be a great financial move for many. I’m perfectly happen to have done so earlier, I didn’t quite pick the bottom but I still think over 30 years these rates (the current rates and earlier rates of 4 1/4% or 4 3/8%) will seem like a dream.
Related: Fixed Mortgage Rates Reach New Low (August 2010) – Lowest 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates in 37 Years (Dec 2008) – The Impact of Credit Scores and Jumbo Size on Mortgage Rates (Jan 2009)
Bill Gates is really doing some great stuff the last few years. He takes a look at the enormous problem with state government’s failure do deal with the very long term health care failure in the USA (this has been going on for the last few decades) and the financial games them play. His Twitter quote is: Enron would blush at the financial untruth State governments engage in.
I have written about these problems before, including in: USA State Governments Have $1,000,000,000,000 in Unfunded Retirement Obligations. One small (compared to the problem for the whole country) He notes is that California has a $62.5 billion health care liability and $3 billion set aside for it.
We have been doing a very bad job of electing people to honest manage budgets. We, or our children and grandchildren are going to pay for those failures. The longer we fail to elect people that will deal with the real decisions that need to be made for government spending and taxing the greater those bills for our mistakes will be.
Related: Are Municipal Bonds Safe? – USA Heath Care System Needs Reform – USA Spends Record $2.5 Trillion, $8,086 per person 17.6% of GDP on Health Care in 2009 – The USA Pays Double for Worse Health Results – The Long-Term USA Federal Budget Outlook
Consumers debt decreasing very slowly. In the 3rd quarter it decreased at an annual rate of 1.5%, after decreasing at a 3.25% rate in the second quarter. Revolving credit (credit card debt) decreased at an annual rate of 8.5% (compared to 9.5% in the second quarter), and nonrevolving credit (car loans…, not including mortgages) was up 2.5% (versus essentially unchanged).
Revolving consumer debt now stands at $814 billion down $52 billion this year. That is on top of a $92 decline in 2009. Hopefully we can increase the size of the decrease going forward. As individuals we should aim to have no consumer debt and build up cash reserves instead (the way the debt figures are calculated though, even if you don’t really have any debt, say you pay off your credit card bill each month, I believe your balance is still seen as “debt”, it is credit extended to you).
On September 30, 2010 total outstanding consumer debt was $2,411 billion (a decline of just $8 billion in the 3rd quarter, after a decline of $21 billion in the 2nd quarter). This still leaves over $8,000 in consumer debt for every person in the USA and $20,000 per family.
Consumer debt grew by about $100 billion each year from 2004 through 2007. In 2009 consumer debt declined over $100 billion: from $2,561 billion to $2,449 billion. For the first 3 quarters of 2010 it has declined just $38 billion.
The huge amount of outstanding consumer and government debt remains a burden for the economy. At least some progress is being made to decrease consumer debt. Credit card delinquency rates have actually been decreasing the last couple of year (from a high of 6.75% in the 2nd quarter of 2009 to 5% in the 2nd quarter of 2010 (I would guesstimate the average for the decade was 4.5%).
Those living in USA have consumed far more than they have produced for decades. That is not sustainable. You don’t fix this problem by encouraging more spending and borrowing: either by the government or by consumers. The long term problem for the USA economy is that people have consuming more than they have been producing.
We can’t afford to seek even more short term spending powered by more debt. Government debt has been exploding so unfortunately that problem has continued to get worse.
Data from the federal reserve.
Related: Consumers Continue to Slowly Reduce Their Debt Level – The USA Economy Needs to Reduce Personal and Government Debt – Consumer debt needs to decline much more.
The world today has a much different economic landscape than just 20 years ago. China’s amazing economic growth is likely the biggest story. But the overwhelming success of many other countries is also a huge story. Today it is not the developing world that has governments spending taxes they promise their grandchildren will pay, but instead the richest countries on earth that choose to spend today and pay tomorrow. While “developing” countries have well balanced government budgets overall.
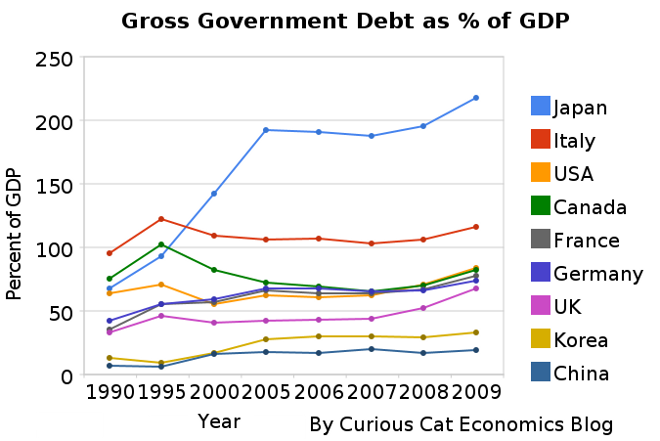 The chart shows gross government debt as percentage GDP from 1990-2009. By Curious Cat Investing and Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution. Data source: IMF
The chart shows gross government debt as percentage GDP from 1990-2009. By Curious Cat Investing and Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution. Data source: IMF___________________________
There are plenty of reasons to question this data but I think it gives a decent overall picture of where things stand. It may seem like government debt should be an easy figure to know but even just agreeing what would be the most reasonable figure for one country is very difficult, comparing between countries gets even more difficult and the political pressures to reduces how bad the data looks encourages countries to try and make the figures look as good as they can.
The poster child for irresponsible spending is Japan which has gross government debt of 218% of GDP (Japan’s 2009 figure is an IMF estimate). Greece is at 115%. Gross debt is not the only important figure. Government debt held within the country is much less damaging than debt held by those outside the country. Japan holds a large portion of its own debt. If foreigners own your debt then debt payments you make each year are paid outside your country and it is in essence a tax of a portion of your economic production that must be paid. If the debt is internal it mean taxpayers have to support bond holders each year (but at least when those bondholders spend the money it stays within your economy).
Read more
I made several more Kiva loans to entrepreneur in Kenya, Lebanon, Nicaragua, Kenya, Honduras and Armenia (brining my total loans to 251). It really is great to see real people using capitalism to improve their lives. And being able to help by lending some money is wonderful. When looking for loans I give preference to loans that improve productivity and increasing capacity of the entrepreneur. If they use the proceeds of the loan to increase their capacity to produce they can pay off the loan and find themselves much better off.
 Douglas Osusu, Kisii, Kenya, in front of his posho mill (used for grinding maize into flour).
Douglas Osusu, Kisii, Kenya, in front of his posho mill (used for grinding maize into flour).A nice example of this is the loan to Douglas Osusu (pictured). He has requested this loan of 80,000 KES to purchase a dairy cow and a posho mill. This loan also has a portfolio yield (Kiva’s equivalent of an annual percentage rate) of 19%. 19% is very loan for loans on Kiva (remember there are significant costs to servicing micro-loans) – I like the rate to be under 30% but sometimes accept rates up to 40% (or even higher occasionally). I also give great preference to low rates, as the lower the rate the better for the entrepreneur. The 3rd factor I consider is the history of the field partner bank (default rate, delinquency rate and currency exchange loss rate). In this case the field partner is new and carries risk because of that. Still in this case I really like the loan and I like that this lender is charging low rates so I want to take the risk and see how they can do. The amount I lend is based on the combination of these factors – I lend more when I have several reasons to really like the loan.
Join other readers by making loans and joining the Curious Cats Lending Team: 8 members, 213 loans totaling $8,775. Comment with the link to your Kiva page and I will add a link on Curious Cat Kivans.
My current default rate is 1.39% and the delinquency rate is 8.49% (see chart of USA general delinquency rates). The delinquency rate is exaggerated due to technical details (some difficulties in reporting in various countries and such things). Agricultural loans often become delinquent on Kiva but still are paid in full (in my experience). While the defaulted loan rate is 1.39% if you look at the percent of dollars lost I have a rate of 1.2% (this is nearly all due to a bank that failed over a year ago to which I had 2 loans where I lost $87.50 of $100 – there are also 2 other losses for under $5). I add to my total loan amount a couple times a year but also I get to keep relending as money is paid back.
Some of my favorite ways to help reduce extreme poverty are Trickle Up, Kiva and using Global Giving to find small organizations.
Related: 100th Entrepreneur Loan – More Kiva Entrepreneur Loans: Kenya, El Salvador (June 2010) – Kiva Opens to USA Entrepreneur Loans – MicroFinance Currency Risk – Kiva Fellows Blog: Nepalese Entrepreneur Success
The chart shows the total percent of delinquent loans by commercial banks in the USA.
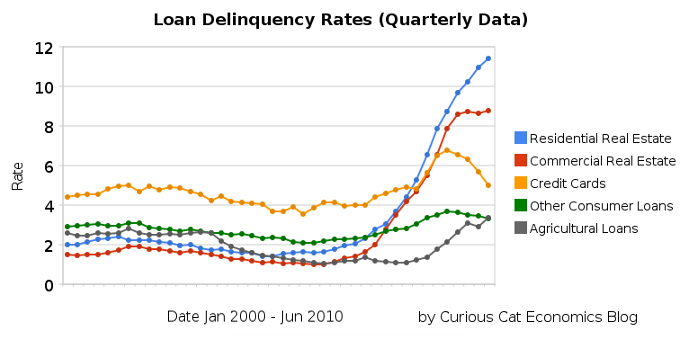
The first half of 2010 saw residential real estate delinquencies continue to increase and other consumer loan delinquencies decreasing (both trends continue those of the last half of 2009). Residential real estate delinquencies increased 118 basis points to 11.4%. Commercial real estate delinquencies increased just 7 basis points to 8.79%. Agricultural loan delinquencies also increased (25 basis points) though to just 3.35%. Consumer loan delinquencies decreased, with credit card delinquencies down 131 basis points to 5.01% and other consumer loan delinquencies down 15 basis points to 3.34%.
Related: Real Estate and Consumer Loan Delinquency Rates 1998-2009 – Bond Rates Remain Low, Little Change in Late 2009 – Government Debt as Percentage of GDP 1990-2008 – USA, Japan, Germany… –posts with charts showing economic data
Read more
U.S. Investors Regain Majority Holding of Treasuries
Mutual funds, households and banks have boosted the domestic share of the $8.18 trillion in tradable U.S. debt to 50.2 percent as of May, according to the most recent Treasury Department data.
…
The biggest jump in demand this year among domestic buyers of Treasuries has been commercial lenders. Bank holdings of Treasury and agency securities increased 5 percent to $1.57 trillion last month, according to the latest data available from the Fed.
…
The Fed’s decision to hold its target for the overnight lending rate at a record low has made it possible for banks to borrow at near-zero interest rates to finance purchases of longer-term and higher-yielding Treasuries while lending less.
I must say, unless you are getting special government interest free loans to invest in treasuries (like those that caused the credit crisis are) it seems crazy to me to invest at these low rates. In retirement, it probably does make sense to have some just as a diversification measure but other than that I would certainly reduce my holdings from what they would have been 10 years ago.
If politicians or the fed would just give special favors to me to borrow billions and essentially 0% and then lend it back for more I would take that deal.
But if I am not granted the welfare Chase, Goldman Sachs, Citibank and the rest are (with huge amounts of free money and bailouts if their bets fail) buying extremely low yield government debt is not an investment I want. I don’t think betting on deflation is not a bet I want to take. Inflation seems a bigger risk to me. But people get to make their own decisions, and we will see which investors are right.
Related: Paying Back Direct Cash from Taxpayers Does not Excuse Bank Misdeeds – Can Bankers Avoid Taking Responsibility Again? – What the Financial Sector Did to Us
Consumer debt decreased at an annual rate of 3.25% in the second quarter. Revolving credit (credit card debt) decreased at an annual rate of 9.5%, and nonrevolving credit (car loans…) was about unchanged.
Revolving consumer debt now stands at $827 billion down $39 billion this year. That is on top of a $92 decline in 2009. Hopefully we can continue this success.
Through June of 2010 total outstanding consumer debt was $2,419 billion, a decline of $30 billion ($21 billion of the decline was in the 2nd quarter). This still leaves over $8,000 in consumer debt for every person in the USA and $20,000 per family.
Consumer debt grew by about $100 billion each year from 2004 through 2007. In 2009 consumer debt declined over $100 billion so far: from $2,561 billion to $2,449 billion.
The huge amount of outstanding consumer and government debt remains a burden for the economy. At least some progress is being made to decrease consumer debt.
Those living in USA have consumed far more than they have produced for decades. That is not sustainable. You don’t fix this problem by encouraging more spending and borrowing: either by the government or by consumers. The long term problem for the USA economy is that people have consuming more than they have been producing.
Thankfully over the last year at least consumer debt has been declining, but it needs to decline more. I disagree with those that want to see short term improvement in the economy powered by consumer debt. It would be nice to see improvement to the current economy. But we can’t afford to achieve that with more debt. Government debt has been exploding so unfortunately that problem has continued to get worse.
Data from the federal reserve.
Related: Consumer Debt Declined a Record $21.5 Billion in July – The USA Economy Needs to Reduce Personal and Government Debt