The report, The Dwindling Taxable Share Of U.S. Corporate Stock, from the Brookings Institution Tax Policy Center includes some amazing data.

In 1965 foreign ownership of USA stocks totaled about 2%, in 1990 it had risen to 10% and by 2015 to 26%. That the foreign ownership is so high surprised me. Holdings in retirement accounts (defined benefit accounts, IRAs etc.) was under 10% in 1965, rose to over 30% in 1990 and to about 40% in 2015. The holdings in retirement accounts doesn’t really surprise me.
The combination of these factors (and a few others) has decreased the holding of USA stocks that are taxable in the USA from 84% in 1965 to 24% in 2015. From the report
As with much economic data it isn’t an easy matter to determine what values to use in order to get figures such as “foreign ownership.” Still this is very interesting data, and as the report suggests further research in this area would be useful.
Related: There is No Such Thing as “True Unemployment Rate” – The 20 Most Valuable Companies in the World – February 2016 (top 10 all based in the USA) – Why China’s Economic Data is Questionable – Data provides an imperfect proxy for reality (we often forget the proxy nature of data)
We have tax plans from the major USA Presidential candidates. I don’t like any of them, though I actually like Ted Cruz’s plan more than the others, but it has a huge problem. His plan doesn’t fund the government he wants, not even just as poorly as we have been doing. He would increase the debt substantially.
My plan would have 3 parts. I like a flat tax, I doubt it will ever happen, but if we could get one I would be happy. Cruz proposes that (at 10%). I am fine with his proposal to eliminate all deductions but mortgage interest and charity. I would definitely tweak that some – no more than $50,000 in mortgage interest deduction a year and the same for charity. Basically subsidizing it a bit for the non-rich is fine. Subsidizing these for the rich seems silly so I would cap the deductions in some way. I also wouldn’t mind an almost flat tax, say 12% up to $200,000 and 15% after that (or some such rates).
Cruz’s rate is far too low given the government he wants. The government budget is largely: Social Security, Medicare and Military. Then you also have debt payment which have to be paid. Those 4 things are over 80% of the spending. All the other things are just in the last 20%, you can cut some of that but realistically you can’t cut much (in percentage terms – you can cut hundreds of billions theoretically but it is unlikely and even if you did it isn’t a huge change).
We are piling on more debt than we should. Therefore we should increase revenue, not reduce it. But if we can’t increase it (for political reasons) we definitely should not reduce it until we have shown that we have cut spending below revenue for 2 full years. After that, great, then decrease rates.

The White House, Washington DC by John Hunter. See more of my photos of Washington DC.
The VAT tax on businesses replacing the corporate tax system is in Cruz’s plan and this is the best option for corporate taxes in my opinion. Another decent option is just to pass through all the earnings to the owners (I first heard this proposal from my Economics professor in College) and tax them on the earnings.
Increasing the giveaways to trust-fund baby as Cruz and Trump propose is the single worst tax policy change that can be made. I have explained previously how bad an idea this is: The estate tax is the most capitalist tax that exists. The trust-fund-baby favors should be reduced not increased. I would roll back to the Reagan Administration policy on estate tax rates.
When I lived in Malaysia I learned that the residential electricity rates were very low for the low levels of use and climbed fairly rapidly as you used a lot of electricity (say running your air conditioner a lot). I think this is a very good idea (especially for the not yet rich countries). In rich countries even most of the “poor” have high use of electricity and it isn’t a huge economic hardship to pay the costs.
Effectively the rich end up subsidizing the low rates for the poor, which is a very sensible setup it seems to me. The market functions fairly well even though it is distorted a bit to let the poor (or anyone that uses very little electricity) to pay low rates.
In a country like Malaysia as people become rich they may well decide to use a great deal of electricity for air conditioning (it is in the tropics). But their ancestors didn’t have that luxury and having that be costly seems sensible to me. Allowing the poor to have access to cheap electricity is a very good thing with many positive externalities. And subsidizing the rate seems to be a good idea to me.
Often you get bad distortions in how markets work when you try to use things like subsidies (this post is expanded from a comment I made on Reddit discussing massive bad investments created by free electricity from the power company to city governments – including free electricity to their profit making enterprises, such as ice rinks in Puerto Rico).

View of downtown Johor Bahru from my condo (a small view of Singapore visible is in the background)
With the model of low residential rates for low usage you encourage people to use less electricity but you allow everyone to have access at a low cost (which is important in poor or medium income countries). And as people use more they have to pay higher rates (per kwh) and those rates allow the power company to make a profit and fund expansion. Often in developing countries the power company will be semi-private so the government is involved in providing capital and sharing in profits (as well as stockholders).
The USA mainly uses central air conditioning everywhere. In Malaysia, and most of the world actually, normally they just have AC units in some of the rooms. In poor houses they may well have none. In middle class houses they may have a one or a couple rooms with AC units.
Even in luxury condos (and houses) they will have some rooms without AC at all. I never saw a condo or house with AC for the kitchen or bathrooms. The design was definitely setup to use AC in fairly minimal ways. The hallways, stairways etc. for the “interior” of the high rise condos were also not air conditioned (they were open to the outside to get good air flow). Of course as more people become rich there is more and more use of AC.
Related: Traveling for Health Care – Expectations – Looking at the Malaysian Economy (2013) – Pursuing a Growing Economy While Avoiding the Pitfalls That Befall to Many Middle Income Countries – Singapore and Iskandar Malaysia – Looking at GDP Growth Per Capita for Selected Countries from 1970 to 2010 – Malaysian Economy Continues to Expand, Budget Deficits Remain High (2012) – Iskandar Malaysia Housing Real Estate Investment Considerations (2011)
The USA economy is far from strong. The global economy seems even weaker. Inflation is not an imminent risk. Under such conditions the USA Federal Reserve adding gasoline to the economy via low interest rates makes sense.
The issue I see is that a .25% Fed Funds rate is adding gasoline to the economy via low interest rates. Many people are saying an increase is like taking away the gasoline and taking out a fire extinguisher. But it really isn’t. Raising the rate to .25% is slightly decrease the amount of gas you are adding to the fire. A .25% Federal Funds rate is pouring nearly as much gas on as you are able to but not quite the absolute most you are able to.
It is also true that the Fed bailing out the too-big-to-fail bankers and banks resulted in them not only opening up the gasoline as much as possible (taking rates to 0) they even went far beyond that with new methods of pouring on gasoline that hadn’t even been considered until the bankers’ risk-taking doomed the economy (and bankrupted their institutions – without government bailouts propping them up).
The Federal Reserve has finally turned off the massive extraordinary dumping of gasoline onto the economic fire (via quantitative easing). But they have kept not only dumping lots of gasoline on the economy but doing so to the absolute maximum possible via a 0% Fed Funds rate.
Arguing for slowing the amount of fuel you are dumping into the economy is not the same as saying you are constricting the economy. We have been put into a crazy global economic condition by the too-big-to-fail bankers and the massive amounts of government and personal debt taken out. So simple analogies are not effective in making policy.
The analogies can help explain what the intent and expectation of the policy is. It is true we have created a very tenuous economic foundation (and we haven’t in any way substantial way addressed the risk too-big-to-fail bankers can throw the global economy into and we still have massive debt problems). The main beneficiaries of the central banker’s policies the last nearly 10 years are too-big-to-fail bankers and those borrowing huge amounts of money.
Those suffering from the policy are savers and I fear those that have to cope with the aftermath of this massive intervention with likely bubbles (government debt, personal debt [including education debt in the USA, etc.]). The main reason I believe rates should be raised are to begin the path to stop transferring wealth from savers to too-big-to-fail bankers and those with massive debt problems.
One thing for investors consulting historical data to remember is we may have had fundamental changes in stock valuations over the decades (and I suspect they have). Just to over simplify the idea if lets say the market valued the average stock at a PE of 11 and everyone found stocks a wonderful investment. And so more and more people buy stocks and with everyone finding stocks wonderful they keep buying and after awhile the market is valuing the average stock at a PE of 14.
Within the market there is tons of variation those things of course are not nearly that simple, but the idea I think holds. Well if you look back at historical data the returns will include the adjustment of going from a PE of 11 to a PE of 14. Now maybe the new few decades would adjust from PE of 14 to PE of 17 but maybe not. At some point that fundamental re-adjustment will stop.
And therefore future returns would be expected to be lower than historically due to this one factor. Now maybe other factors will increase returns to compensate but if not the historical returns may well provide an overly optimistic view.
And if there is a short term bubble that lets say pushes the PR to 16 while the “fair” long term value is 14, then there will be a negative impact on the returns going forward bringing the PE from 16 to 14. That isn’t necessarily a drop (though it could be) in stock prices, it could just be very slow increases as earning growth slowly pushes PE back to 14.

Monument to the People’s Heroes with the Shanghai skyline in the background. See more photos by John Hunter
Another thing to consider is another long term macro-economic factor may also be giving long term historical returns an extra boost. The type of economic growth from the end of World War I to 1973 (just to pick a specific time, there was a big economic slowdown after OPEC drastically increased the price of oil). While that period includes the great depression and World War II, which massively distorts figures, from the end of WW I through the 1960s Europe and the USA went through an amazing amount of economic growth.
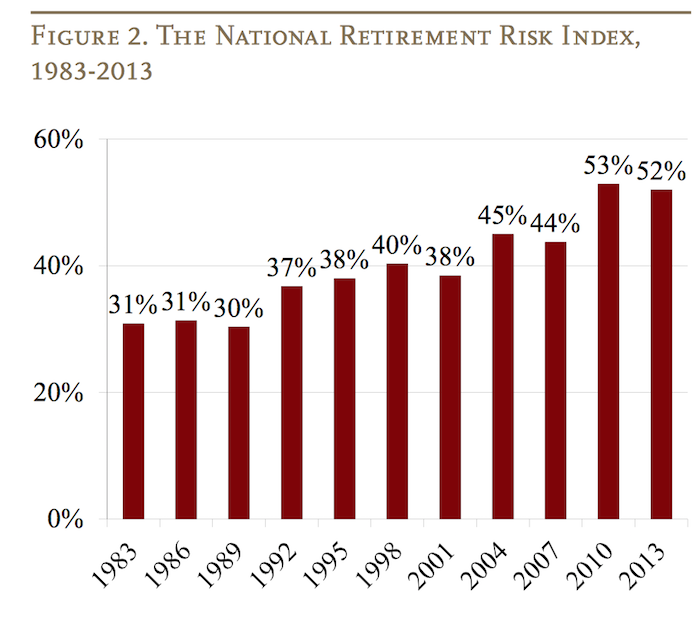
The Center for Retirement Research at Boston College is a tremendous resource for those planning for, or in, retirement. The center created the National Retirement Risk Index (NRRI) to capture a macroeconomic level measure of how those in the USA are progressing toward retirement.
Based on the Federal Reserve’s 2013 Survey of Consumer Finances the Center updated the NRRI results (the entire article is a very good read).
The lower the risk number in the chart the better, so things have not been going well since the 1990s for those in the USA saving for retirement.
As the report discusses their are significant issues with retirement planning that defy easy prediction; this makes things even more challenging for those saving for retirement. The report discusses the difficulty placed on retirees by the Fed’s extremely low interest rate policy (a policy that provides billions each year to too-big-too-fail banks – hardly the reward that should be provided for bringing the world to economic calamity but never-the-less that transfer of wealth from retirees to too-big-to-fail banks is the policy the Fed has chosen).
That exacerbates the problems of too little savings during the working career for those in the USA. The continued evidence is that those in the USA continue to spend too much today and save too little. Also you have to expect the Fed and politicians will continue to make policy that favors their friends at too-big-fail banks and hedge funds and the like. You can’t expect them to behave differently than they have been the last 50 years. That means the likely actions by the government to take from median income people to aid the richest 1% (such as bailing out the bankers with super low interest rate policies and continue to subsidize losses and privatize their winning bets) will continue. You need to have extra savings to support those policies. Of course we could change to do things differently but there is no realistic evidence of any move to do so. Retirement planning needs to be based on evidence, not hopes about how things should be.
Related: How Much of Current Income to Save for Retirement – Save What You Can, Increase Savings as You Can Do So – Don’t Expect to Spend Over 4% of Your Retirement Investment Assets Annually – Retirement Planning: Looking at Assets (2012) – How Much Will I Need to Save for Retirement? (2009)
A reasonable amount of government debt is not a problem in a strong economy. If countries take on debt wisely and grow their economy paying the interest on that debt isn’t a problem. But as that debt grows as a portion of GDP risks grow.
Debt borrowed in other currencies is extremely risky, for substantial amounts. When things go bad they snowball. So if your economy suffers, your currency often suffers and then the repayment terms drastically become more difficult (you have to pay back the debt with your lower valued currency). And the economy was already suffering which is why the currency decreased and this makes it worse and they feed on each other and defaults have resulted in small economies over and over from this pattern.
If a government borrows in their currency they can always pay it back as the government can just print money. They may pay back money not worth very much but they can pay it back. Of course investors see this risk and depending on your economy and history demand high interest to compensate for this risk (of being paid back worthless currency). And so countries are tempted to borrow in another currency where rates are often much lower.
If you owe debts to other countries you have to pay that money outside the system. So it takes a certain percentage of production (GDP) and pays the benefit of that production to people in other countries. This is what has been going on in the USA for a long time (paying benefits to those holding our debt). Ironically the economic mess created by central banks and too-big-to-fail banks has resulted in a super low interest rate environment which is lousy for lenders and great for debtors (of which the USA and Japanese government are likely the 2 largest in the world).
The benefits to the USA and Japan government of super low interest rates is huge. It makes tolerating huge debt loads much easier. When interest rates rise it is going to create great problems for their economies if they haven’t grown their economies enough to reduce the debt to GDP levels (the USA is doing much better in this regard than Japan).
Japan has a much bigger debt problem than the USA in percentage terms. Nearly all their debt is owed to those in Japan so when it is paid it merely redistributes wealth (rather than losing it to those overseas). It is much better to redistribute wealth within your country than lose it to others (you can always change the laws to redistribute it again, if needed, as long as it is within your economy).
Monsters Inc received power from children’s screams. So the company hired monsters to go scare children to get more screams and create more power.
The current political parties in the USA (Republicans and Democrats) seek to scare their donors into providing cash “donations.” It is even worse, in many ways, than if those parties sold favors to get things done. At least then there would be an incentive for the parties to deliver successful prizes to those paying for influence.
But the parties have become like Monsters Inc. They only seek to increase suffering in order to get what they want (in the case of the Republican and Democrats, cash, and in the case of Monsters Inc, screams).
The damage to the economy from decades of two political parties seeking to increase fear so they can get more cash while neither cares about the damage they do is enormous. We really need to throw out those that have been destroying the country for their own petty interests.
Throwing out the parties that have proven they don’t care about the country won’t result in people that agree on tactics but at least we should elect people that seek to aid the country and refuse to destroy the country in order to hope in doing so they can hurt the other political party more than they are hurt. As long as we keep electing the type of people that don’t care about the damage they do we are going to keep paying a high price.
Occasionally (and much more than occasionally at the state level, it is harder to make excuses about failing to deliver on what people paid for at the state and local level) they do give in and give those paying them lots of cash what those that paid thought they bought. But most of the time they try to avoid doing so as that slows down the flow of money.
Related: USA Congress Further Aids Those Giving Them Cash and Risks Economic Calamity Again – Adding More Bailouts for Politicians and Bankers is Not the Correct Strategy – Anti-Market Policies from Our Talking Heads and Politicians – We Need to be More Capitalist and Less Cronyist
In 2013, international migrants sent $413 billion home to families and friends — three times more than the total of global foreign aid (about $135 billion). This money, known as remittances, makes a significant difference in the lives of those receiving it and plays a major role in the economies of many countries.
India received $72 billion and Egypt $18 billion in 2013.
I liked an interesting point he made. These remittences often include business advice to those relatives in the home country.
This is a great talk if you are interested in economics and global development. It is very important to understand the issues we face in helping billions living in poverty. As he says regulation of small remittences must be reduced. Policies forced by countries like the USA have damaged poor people’s lives worldwide with extremely onerous regulation.
Web site of the speaker: Dilip Ratha
Related: International Development Fair: The Human Factor – Creating a World Without Poverty – Supporting Virtual Workers – Solar Power Market Solutions For Hundreds of Millions Without Electricity
My response to a comment by John Green on Reddit
I really really like your work and webcasts (example included below).
This seems to me to make it really difficult on people trying to use judgement. Calling people’s actions “extremely paternalistic” if they are not definitely so, I think impedes debate. And I think debate should be encouraged.
When making Kiva loans I do steer away from loans with rates above 40% (I also prefer loans that are geared toward a capital investment that will increase earning power going forward though this is hard – lots of loans are essentially for inventory that will be sold at a profit so a fine use of loans but not as powerful [in my opinion] and new capital investments – say a new tool, solar power that will be resold to users…).
Just like people anywhere, people taking Kiva loans are capable of getting themselves into trouble. Choosing to allocate my lender toward certain loans does not mean I am being paternalistic.
I am not being paternalistic if I chose not to invest in the stock of some company that vastly overpays executives and uses high leverage to do very well (in good times).
I do like the idea of direct cash to people in need. I give cash that way (and in fact did it a long time ago, 20 years, for several years – before any of this new hipster cachet :-). And I still do like it.