Welcome to the Curious Cat Investing, Economics and Personal Finance Carnival: find useful recent personal finance, investing and economics blog posts and articles.
- Why Financial Literacy Fails (and What to Do About It) by JD Roth – “‘For years, I struggled with money,’ I told my interviewer today. ‘I knew the math, but I still couldn’t seem to defeat debt. It wasn’t until I started applying psychology to the situation that I was able to make changes.’”
- Get ready for the three big financial crises of 2012 by Jim Jubak – “So in 2012 Ireland—and Greece and Portugal—are going to face a huge choice. They can either try to grind out more austerity in the midst of a EuroZone recession or they can try to renegotiate some of that debt. If you remember, the battle over Greek bank debt almost scuttled the euro this year. Well, we’re going to see the same problem again in 2012…”
- How Long Would It Take To Build A $5000/Year Dividend Cash Flow? – John is able to investing $1000 per month in a portfolio now yielding 2.86% and dividends increasing 9% a year (under historical level for the stocks included)… a bit over 7 years…
-
Mark Cuban, invest in yourself. Keep your cash – wait to get a bargin based on the cash your have which allows you to take advantage of market opportunities.
There is an increasing trend to move from the USA to another country to work and live. This is not surprising to me. Recently this has picked up quite a bit; I am surprised by the velocity at which this interest in moving (I figured it would be a long term mega trend but not so drastic, so quickly). Economic changes are often quite surprising in how rapidly they move forward.
An interesting survey shows USA investors have become much more interested in relocating in the last two years (the data they show though has tremendous volatility over time, so I am not really sure this means much). I wonder how much of it can be explained by investors wanting to get a deep understanding of very promising markets. I wouldn’t image the actual number that do this is huge, but maybe the number considering it is significant. Billionaire investor, Jim Rodgers moved to Asia because he sees Asia as key to the future. One of the reasons I moved to Malaysia this year was to get a in depth understanding of what South East Asia is like (it is not a deciding reason, at all but maybe the 4th or 5th reason).
I believe the globalization of the employment market is a long term trend that will continue – especially for “knowledge workers.” The USA rested on the post WW II economic domination for nearly 50 years. The policies also helped this continue: investing in science and engineering, favoring entrepreneurship… But other countries have realized the value of these things (and the USA is slipping – not investing nearly as much in science and engineering and favoring large corporations that give politicians large amounts of cash over innovation – see things like the incredibly outdated “intellectual property” system, SOPA, favoring huge financial institutions…
The combination of long term policy weakness, the inevitable decline in the USA to world ratio of economic wealth, and the financial crisis caused by the policy weaknesses have seemingly greatly accelerated the trend. The next 2 or 3 years will determine if that is a permanent acceleration or if we go back to a slower pace – but on the same path. My guess is that we will stay on this path but the pace will not follow the level surveys might indicate (showing interest in such a big change is far different from actually moving).
There don’t seem to be any decent estimates of Americans living abroad. The US State Department claims releasing their estimates would be a national security risk? And the Census bureau says it would cost too much to try. Wild guesses seem to be between 4 and 6 million.
Related: I want out (subreddit) – Why Investing is Safer Overseas – USA Heath Care System Needs Reform – Copywrong
I am frustrated that we have largely allowed those that don’t believe in capitalism to claim their beliefs are capitalist. I believe capitalism is the best system to provide economic gain to human society. When we allow non-capitalist to claim their ideas are capitalist we often lose by allowing bad policies to be adopted and failing to adopt more capitalist ideas.
Robber barons and their ilk are not capitalists. Those attacked today as capitalists are much more like European nobility that fought to let the nobility take most of the economic profit from everyone else.
Capitalism is a wonderful thing.
The foolish economic policies the politicians we have elected over and over again for decades are idiotic and not capitalist (they are somewhat capitalist but the things people are complaining about are not capitalism but the corruption of the system by those subverting capitalism). They are the result of favoring cronyism and bribery over capitalist regulated markets.
What we need to do is not throw out the capitalists. We need to actually throw out those that say their cronyistic policies are capitalist.
Capitalism is an economic system designed to achieve economic gain for a society. Adam Smith (and others) understood that if those with power to destroy the functioning of markets (for personal gain) were allowed to do so then the benefits capitalism can produce are reduced. And they definitely would try to (according to the believes fundamental to the capitalist model) so a capitalist system has to account for that.
“Free” markets are good. But in capitalism “free” markets means markets where no entity has “market” power – that is the ability to move the market. This is the idea of perfect competition. In the real world this doesn’t happen but capitalist understand the weakness of unfree markets and that has to be dealt with. Things start to get messy here. There is no perfect way to do this and I don’t know of anyone (that I don’t think is naive) that thinks this can be done in some way that avoid economic friction (loss to the society from what is possible in some ideal state).
Now those that like cronyism and letting whoever has the clout do whatever they want have tried to say capitalism means doing whatever you want to get as much capital as you want. It doesn’t. Capitalism isn’t about letting whoever has the gold get more. It is an economic system to provide gain to society by setting up rules that result in market forces brining benefit to society.
Those thinking about setting up the rules for a capitalist system understood that many people are going to try and get away with taking what isn’t theirs. So you have to enforce the rule of law. You have to prevent those that seek to destroy markets and take personal gains they should not be able to (due to being allowed to collude with other market players, collude with politicians to gain political concessions that destroy market functions…).
I happen to believe capitalism is the best economic system we have by far.
I happen to believe those that have increasingly turned out system into one where croynism is destroying markets to give gains to a few parties dominates are creating great damage. But the problem is not that these people show capitalism is bad. Instead these people show the dangers of not putting in the effort to retain capitalist ideas: your economy suffers and people suffer.
Welcome to the Curious Cat Investing and Economics Carnival: find useful recent personal finance, investing and economics blog posts and articles.
- How the Plummeting Price of Cocaine Fueled the Nationwide Drop in Violent Crime – “But it’s not only a growing supply of product that led to the collapse of the cocaine market. Newfound competition in the form of locally-produced methamphetamines and prescription narcotics would continue to drive business away from cocaine… At a certain point the decision matrix for entering a life of drug-related crime collapses for all but those with no other alternate financial sources or for those with a personal interest in the craft.”
- Eight Reasons to be Bullish on the US Dollar by Steen Jakobsen and Michael Shedlock – “58% of the US dollar index is the Euro, and the Euro is a basket case. European banks are in worse shape than their US counterparts, and a breakup of the Eurozone that I expect will certainly exacerbate the problem.”
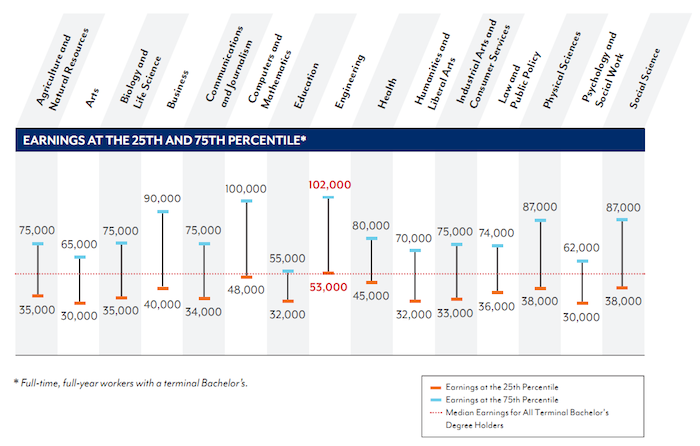
Video: Bogle says Market are About Fairly Valued Today- Investing in an Engineering Degree Provides a Lifetime Advantage of $1,090,000 by John Hunter – “the lifetime advantage ranges from $1,090,000 for Engineering majors to $241,000 for Education majors”
Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce has produced a new report looking at the value of different college degrees in the USA. I have seen a great increase in discussions of the “bubble” in education. Those articles often say a college degree doesn’t assure the success it used to. The data I review seems to show extremely large benefits for those with a college degree (higher salaries but, much more importantly, in my opinion, they also have much lower unemployment rates).
Those benefits are greatest for several majors including science, math and engineering. The problem I see is not so much that significant benefits are lacking for college degrees but the huge increases in costs of getting a degree are so large that for some majors the cost is just so large that even with the benefits it is arguable whether it is worth the cost (while a few decades ago the benefits were universal and so large the economic benefit was not debatable).
The authors of the report found that all undergraduate majors are worthwhile, even taking into account the cost of college and lost earnings. However, the lifetime advantage ranges from $1,090,000 for Engineering majors to $241,000 for Education majors. As I have written frequently on the Curious Cat Science and Engineering blog, engineering degrees are very financially rewarding.
The top 10 majors with the highest median earnings for new graduates are:
- Petroleum Engineer ($120,000)
- Pharmacy/pharmaceutical Sciences and Administration ($105,000)
- Mathematics and Computer Sciences ($98,000)
- Aerospace Engineering ($87,000)
- Chemical Engineering ($86,000)
- Electrical Engineering ($85,000)
- Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering ($82,000)
- Mechanical Engineering, Metallurgical Engineering and Mining and Mineral Engineering (each with median earnings of $80,000)
Related: 10 Jobs That Provide a Great Return on Investment – Mathematicians Top List of Best Occupations – New Graduates Should Live Frugally
The increases in income inequality creates problems and increases serious risks. Some people have a political ideology that drives their thoughts on any economic policy. I instead, look to economic issues if they benefit society. The reason capitalism is great is because society benefits. The policies that create huge income inequality are bad for society and should be changed.
Sadly the strong support for policies to elevate trust fund babies in the USA have created a society where economic wealth in the USA is now greatly defined by how rich your parents are instead of your ability and effort. The USA used to have great social mobility now we have changed society to become more like feudal Europe, while Scandinavia has become more like the USA used to be for social mobility.
Related: Economic Fault, Income Inequality – Middle Class Families from 1970-2005 – Income Inequality in the USA (2006) – The Widening “Marriage Gap” is Breeding Income Inequality
Welcome to the Curious Cat Investing, Economics and Personal Finance Carnival: find useful recent personal finance, investing and economics blog posts and articles. If you want to have an post considered for the next carnival please submit it to quixperito: money.
- How I live on $7,000 per year by Jacob Lund Fisker – “If I had to venture a guess, I’d say I’m more frugal (the way your grandparents were frugal—in fact what I do wouldn’t be considered very extreme by your grandparents or great grandparents—I’d probably be average from their perspective) and I adhere more to a do-it-your-self ethics.”
- Invest in Communities to Advance Capitalism by Howard Schultz (CEO of Starbucks) – “It is no longer enough to serve customers, employees, and shareholders. As corporate citizens of the world, it is our responsibility — our duty — to serve the communities where we do business by helping to improve, for example, the quality of citizens’ education, employment, health care, safety, and overall daily life, plus future prospects.” [similar to Dr. Deming ideas from decades ago on the purpose of organizations, which I share - John].
- My dad taught me cashflow with a soda machine by Rob Fitzpatrick – “The vending machine didn’t magically make me want to be an entrepreneur. I wanted to be a video game designer, then an engineer, then a video game designer again, and then an academic. I get the impression kids are a bit slippery in that regard.
But when I stumbled into the startup world two decades later, the dots began to connect. Cashflow wasn’t a new concept.” - Disability Insurance is Very Important by John Hunter – “When I would have had gaps in coverage from work, I have purchased disability insurance myself. I am all in favor of saving money. About the only 2 things I don’t believe in saving money being very important are health and disability insurance.”
- What Other Dividend Lists Exist Besides the Dividend Aristocrats? – “companies that have increased their annual regular dividends for at least the past 10 consecutive years and have met specific liquidity screening criteria… The members of the Dividend Champions List include, those stocks (not limited to the S&P 500) that have increased their dividend for the past 25 years.”
- Buying a New Home and Converting Your Current Home Into a Rental Property by Philip Taylor – “By refinancing our mortgage, we reduced our mortgage payment by enough to allow us to rent out the property by at least a hundred more per month than all of our expenses: mortgage, property taxes, insurance, home owners association dues, repairs, and property management fees.”
- The perils of near monopoly by Joshua Gans – “Had Qantas had market shares akin to airlines in more competitive markets, the shut down would not have had the external spillovers, publicity and also the ability to shield Qantas — both managers and workers — from personal long-term consequences of such brinkmanship.”

Forest Glen Preserve, Illinois, Illinois by John Hunter
After World War II essentially the only significantly large industrial base was in the USA. The USA was emerging as a national power in the early 1900′s. The wake of World War I and World War II left a very odd situation. You had many formerly very rich countries that were devastated and one rich country that wasn’t. Devastation is not easy to overcome in even 20 years. So for a good 2 decades the USA got wealthier and wealthier even while other formerly rich countries were re-developing there countries rapidly.
This made the USA even richer as selling to all those around the world was pretty easy, just creating enough stuff was the hardest part. Almost none of the current emerging markets were doing much of anything economically. This resulted in the USA being able to live incredibly well and generate enormous wealth.
The main legacy of this is a huge benefit to the USA – enormous wealth and experience. However, it seems to have left people thinking the USA is just suppose to be enormously wealthy always no matter if we throw away hundreds of billions a year on a broken health care system, provide huge benefits to political donors (farmers or bankers or phone oligopolists or robbers of the public domain [preventing innovation through repressive, outdated "intellectual property" regimes]), spending many hundreds of billions yearly on military expenditures far beyond those of any other country… It doesn’t work that way.
You can waste huge amounts of economic benefit when you are the dominant economic power globally. And when you were as rich as the USA was in the 1950s and 1960s more and more people felt they deserved to be favored with economic gifts. So for a a few decades the USA used the excess wealth to pay off all sorts of special interests and still do very well economically. The only thing surprising is how long we have been able to keep this up.
It isn’t rational to base expectations on periods when we were granted economic wealth largely by virtue of the world industrial production, other than ours, being destroyed. This isn’t the only reason we were wealthy, we do many things very well (compared to other countries) entrepreneurship, less corruption (still way too much but less than average), from 1950 to about 1990 an equitable distribution of economic gains, until recently a good advanced education system, a brilliant system to turn science and engineering breakthroughs into economic profit (that in the last few decades other countries are starting to do, but they are still way behind)…
From 1970s until say the 2000s we could use our accumulate wealth to live off and not allow huge inefficiencies to continue (lousy job of regulating banks, lousy job of subsidizing farming, lousy job of subsidizing lousy food [making it cheap to eat unhealthy food and expensive to eat healthy food], lousy job of controlling the costs of higher education, lousy job of getting people to realize they cannot expect to live far beyond most everyone else in the world just because they were born in the USA…
Read more

Manuel De Jesus, miller and farmer in El Salvador, will use his loan to buy parts for this milling euipment.
There is a great deal focus recently on the “99%” (via occupy wall street and the like). The truth is these are mainly about the 5% or 10% (those rich, but not quite as rich as the richest 1% – and much further from the richest than they were a few decades ago). As I have written before, most of those in the USA (also Europe, Japan…) are rich (though this is changing, a greater percentage of the USA is not rich, looking globally, than maybe any point since the 1930s).
We get confused because many near us are even richer and think that means the rest of us are very poor. But those in the USA are often in the 5% or 10% – not the 30% or 60% or 90% they seem to think they are. $50,000 in annual income puts you in the top 1% globally. $25,000 puts you in the top 10%.
I agree with the desire to reduce the political and market corruption, as I have written for years.
For the 99% (or the 90% anyway), I really think the best things are government policies that reduce corruption and increase market forces. Letting actually capitalism work instead of political and corporate cronyism failing to let markets work as they should. Also giving education and the chance to build a better life for yourself are important. Thankfully many countries have been doing very well on this front: Singapore, Korea, Brazil, Ghana, China… That doesn’t mean there are not huge issues to still address for most of the 90%, there are.
Microfinance in general, and Kiva in particular, are one great way to help. Again it isn’t perfect. And those getting the loans are not given an easy life. They are given a chance to try and build there business to improve there economic condition. This isn’t a certain success. And I do worry that taking on too high an interest rate, or loan amount, can leave people worse off than before. But when looking at the system of microfinance I really like the opportunity it gives people, who haven’t been given many.
Those getting loans have to make smart personal finance and business decisions. If they do well they can greatly improve their financial situation. I made several more loans today, using money repaid by previous borrowers. I try to find loans where I am able to help fund a investment that will improve capacity (but that isn’t always possible) – a new machine that makes them more efficient for example. I also try to avoid loans where the interest rate is over 30% (which might seem very high, but rates below 20% are very rare given the economics of these loans – they are very costly to service). What Kiva does is provide the funds people like me lend as interest free loans to the partner banks. The idea is that this allows partner banks to provide more capital for loans (obviously) and at a lower rate because the bank isn’t having to pay interest on the funds.
My loans today went to: Mali, Honduras, Senegal, Ecuador, Togo, Philippines and in the photo above El Salvador. The Curious Cat Kivans group has now lent $12,925 in 320 loans. We now have 11 members, join up and help give people an opportunity to improve their economic condition.
Related: More Kiva Entrepreneur Loans: Kenya, Honduras, Armenia… – Using Capitalism in Mali to Create Better Lives – Funding Entrepreneurs in Nicaragua, Ghana, Viet Nam, Togo and Tanzania
It is very simple. Adam Smith understood it and commented on it. If you allow businesses to have control of the market they will take benefits they don’t deserve at the expense of society. And many business will seek every opportunity to collude with other businesses to stop the free market from reducing their profits and instead instituting anti-competitive practices. Unless you stop this you don’t get the benefits of free market capitalism. Free markets (where perfect competition exists, meaning no player can control the market) distribute the gains to society by allowing those that provide services in an open market efficiently and effectively to profit.
Those that conflate freedom in every form and free markets don’t understand that free markets are a tool to and end (economic well being for a society) not a good in and of themselves. Politically many of these people just believe in everyone having freedom to do whatever they want. Promoting that political viewpoint is fine.
When we allow them to discredit free market capitalism by equating anti-market policies as being free market capitalism we risk losing a great benefit to society. People, see the policies that encourage allowing a few to collude and take “monopoly rents” and to disrupt markets, and to have politicians create strong special interest policies at the expense of society are bad (pretty much anyone, conservative liberal, anything other than those not interested in economics see this).
When people get the message that collusion, anti-competitive markets, political special interest driven policies… are what free market capitalism is we risk losing even more of the benefits free markets provide (than we are losing now). That so few seem to care about the benefit capitalism can provide that they willingly (I suppose some are so foolish they don’t understand, but that can’t be the majority) sacrifice capitalism to pay off political backers by supporting anti-market policies.
Allowing businesses to buy off politicians (and large swaths of the “news media” talking heads that spout illogical nonsense) to give them the right to tap monopoly profits based on un-free markets (where they use market power to extract monopoly rents) is extremely foolish. Yet the USA has allowed this to go on for decades (well really a lot longer – it is basically just a modification of the trust busting that Teddy Roosevelt tried). It is becoming more of an issue because we are allowing more of the gains to be driven by anti-competitive forces (than at least since the boom trust times) and we just don’t have nearly as much loot to allow so much pilfering and still have plenty left over to please most people.
I am amazed and disgusted that we have, for at least a decade or two, allowed talking head to claim capitalist and market support for their special interest anti-market policies. It is an indictment of our educational system that such foolish commentary is popular.
Free Texts Pose Threat to Carriers
This is exactly the type of behavior supported by the actions of the politicians you elect (if you live in the USA).
It is ludicrous that we provide extremely anti-market policies to help huge companies extract monopoly profits on public resources such as the spectrum of the airwaves. It is an obvious natural monopoly. It obviously should be managed as one. Several bandwidth providers provide bandwidth and charge a regulated rate. And let those using it do as they wish. Don’t allowing ludicrous fees extracted by anti-free-market forces such as those supporting such companies behavior at Verizon, AT&T…
Related: Financial Transactions Tax to Pay Off Wall Street Welfare Debt – Extremely Poor Broadband for the USA (brought to us by the same bought and paid for political and commentary class) – Ignorance of Capitalism – Monopolies and Oligopolies do not a Free Market Make