I’m really too lazy for any ongoing budgeting. This is the model I have used: write down your big expense (rent, car payment, required student loan payment…). Get the total take home pay each month subtract your big expenses. If that is negative you better do something else (make more money, get rid of big expenses).
Big monthly expenses:
- Rent: $900
- Car payment + insurance: $300
- Cash (miscellaneous spending food, gas, cloths, books…): $450
- Utilities+ (heat, electricity, phone, internet…): $250
Take home pay: $2,800.
That leaves $900/month ($2,800 – $1,900). Decide how to allocate that – toward your IRA, saving to buy a house or take a vacation, eating out (above what was allocated above for cash), pay off debt (if you have it…), build up an emergency fund, save to buy a new MacBook Pro with Retina display…
If I decided to allocate $300 to my IRA (or increase my 401k) I would just set that up automatically each month. Then say I decided to put $400 toward other savings I would have that go to my savings account each month. And I decided I could use the $200 to pamper myself I just leave that in my checking account and what is in checking is what I have to spend.
I just don’t spend more than that. Just like when I was in college I had little spending money. I could spend that. I couldn’t spend any more, I didn’t have it. If I were to go over (I never did), but if I were to have (say my credit card bill exceeded my checking account balance), I would have had to reduce my cash the next month. I reality I would have something like $2,000 extra in the checking account so no bills would be a problem (and just view $2,000 as 0).
In 6 months see where things stand. Is it really working? Did you mess up and forget some expenses… If you need to adjust, do so. Re-examine every 6 months (or every year, if you are doing pretty well).
Take a portion of each raise (50% maybe) and devote it to personal finance goals (paying off debt, retirement savings, building up emergency fund, saving for big purcahse, investing, give more to charity…); don’t just use it to increase spending. Use no more than half (or whatever level you set) of the raise to increase your current spending.
Related: Personal Finance Basics: Avoid Debt – Investing in Stocks That Have Raised Dividends Consistently
Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2012
…
renewable power (excluding large hydro) accounted for 44% of new generation
capacity added worldwide in 2011, up from 34% in 2010 [and 10% in 2004]. The $237 billion invested in building these green power plants compares with $223 billion of net new expenditure annually on building additional fossil-fuelled power plants globally last year.
…
Current predictions are that total installed capacity in non-hydro renewable power will rise ninefold to 2.5Tw by 2030, with investment in assets rising from $225 billion in 2011 to $395 billion-a-year by 2020 and $460 billion-a-year by 2030
Total investment in solar in 2011 increased 52% to $147 billion, driven by a drop of 50% in photovoltaic module prices. Investment in wind dropped 12% to $84 billion, while onshore wind turbine prices fell between 5 and 10%. Biomass and waste to energy was the 3rd largest renewable sector at $11 billion in investments (down 12% from 2010).
USA investment surged 51% to $51 billion just behind China at $52 billion (China increased investment in renewable energy by 17% from 2010). German investment dropped 12% to $31 billion.
In 2011 renewable energy power capacity (excluding large hydropower), as a percentage of total system capacity, reached 9%, up from 4% in 2004. Total renewable energy generation (excluding large hydro) reached 6%, up from 4% in 2004.
Related: Top Countries For Renewable Energy Capacity – Wind Energy Capacity Exceeds 2.5% of Global Electricity Needs – Leasing or Purchasing a Solar Energy System For Your Home
When critics say that Europe is running out of time to deal with the financial crisis I wonder if they are not years too late. Both in Europe responding and those saying it is too late.
It feels to me similar to a situation where I have maxed out 8 credit cards and have a little bit left on my 9th. You can say that failing to approve my 10th credit card will lead to immediate pain. Not just to me, but all those I owe money to. That is true.
But wasn’t the time to intervene likely when I maxed out my 2nd credit card and get me to change my behavior of living beyond my means then? If you only look at how to avoid the crisis this month or year, yeah another credit card to buy more time is a decent “solution.”
But I am not at all sure that bailing out more bankers and politicians for bad financial decisions is a great long term strategy. It has been the primary strategy in the USA and Europe since the large financial institution caused great recession started. And, actually, for long before that the let-the-grandkids-pay-for-our-high-living-today has been the predominate economic “strategy” of the last 30 years in the USA and Europe.
That has not been the strategy in Japan, Korea, China, Singapore, Brazil, Malaysia… The Japanese government has adopted that strategy (with more borrowing than even the USA and European government) but for the economy overall in Japan has not been so focused on living beyond what the economy produces (there has been huge personal savings in Japan). Today the risks of excessive government borrowing in Japan and borrowing in China are potentially very serious problems.
I can understand the very serious economic problems people are worried about if bankers and governments are not bailed out. I am very unclear on how those wanting more bailout now see the long term problem being fixed. Unless you have some system in place to change the long term situation I don’t see the huge benefit in delaying the huge problems by getting a few more credit cards to maintain the fiction that this is sustainable.
We have seen what bankers and politicians have done with the trillions of dollars they have been given (by governments and central banks). It hardly makes me think giving them more is a wonderful strategy. I would certainly consider it, if tied to some sensible long term strategy. But if not, just slapping on a few more credit cards to let the bankers and politicians continue their actions hardly seems a great idea.
Related: Is the Euro Going to Survive in the Long Run? (2010) – Which Currency is the Least Bad? – Let the Good Times Roll (using Credit) – The USA Economy Needs to Reduce Personal and Government Debt (2009 – in the last year this has actually been improved, quite surprisingly, given how huge the federal deficit is) – What Should You Do With Your Government “Stimulus” Check? – Americans are Drowning in Debt – Failure to Regulate Financial Markets Leads to Predictable Consequences
The expenses for long term care is exactly the type of financial risk insurance is best for. The problem is the whole area is so uncertain that what you buy may not provide the coverage you planned on (the health care system is so broken that it is not certain insurance will cover the costs, companies can go bankrupt, change coverage rules drastically…).
The questions about long term care insurance are not about the sensibility of the coverage abstractly, it is very wise. But the complexities, today, in the real world make the question of buying more a guess about what coverage you will actually receive if you need it.
Many of my posts here are focused on the USA but applicable elsewhere, or just applicable wherever you are. This post is mainly focused on the USA, long term care insurance options in other locations will be very different and have different considerations (in many countries it may not even apply, mainly due to a less broken health care system than the USA has).
Long-Term-Care Insurance: Who Needs It? by Marilyn Geewax
Such care can be crushingly expensive: Just one hour of home-health-aide care costs roughly $20, while the average private nursing home room costs $87,000 a year. Neither routine employer-based medical insurance nor Medicare will pay for extended periods of custodial care.”
…
Also, some people pay their premiums for years, and then get hit with rate hikes they can’t afford.
Insurance has a transaction cost. Paying that transaction cost for expenses you can afford is just waste. You should pay the cost directly. This is why higher deductibles are most often wise. It doesn’t make sense to cover pay insurance costs every year to pay for a $500 risk you can afford to absorb yourself.
But huge expenses are exactly what you want coverage for. Long term care expenses are huge. However, long term care insurance is still in flux, which isn’t good for something you want to provide long term protection. A huge risk is paying premiums for years, and then getting hit with rate hikes that may well be designed primarily just to get people to drop coverage (or be so expensive that those that stay pay enough that the insurance company makes money).
Ideally such insurance would be set so maybe the cost rose at some preset limit when you signed up. The problem is the USA health care system is so broken this won’t work. No one can predict how much more excessively expensive long term coverage will be in 30 years so the insurance companies can’t predict. It leaves consumers in a risky place.
Insurance is regulated by the states. There are huge differences in which states do a good job regulating long term care insurance and those that don’t. The majority don’t.
This is one of the more important areas of personal finance. Unfortunately there is no easy answer. If the system were stable, reliable and predictable, long term care insurance would be a definite requirement for a sound financial plan. Today it is wise to insure yourself from those risks, the problem is determining whether any of the options available are worth it. The risk of needing this insurance is high: it is both likely and costly. So getting coverage is definitely wise if you can find some you think is reliable over the long term. Because of the uncertain nature of the options, this will require much more effort on your part than many personal finance actions (I included several links below to help your research).
Also look at how long the coverage is for. This is another limitation insurance companies have put in place that makes it much less worthwhile.
Related: Personal Finance Basics: Long-term Care Insurance – National Clearinghouse for Long-Term Care Information – AARP advice – Disability Insurance is Very Important – How to Protect Your Financial Health
3 Economic Misconceptions That Need to Die
…
Just 6.4% of nondurable goods — things like food, clothing and toys — purchased in the U.S. are made in China; 76.2% are made in America. For durable goods — things like cars and furniture — 12% are made in China; 66.6% are made in America.
Those numbers are significantly less than I expected but the concept matches my understanding – that we greatly underestimate the purchasing of USA goods and services.
We have an inflated notion of how large the China macro economic numbers are for the USA (both debt and manufacturing exports to us). The China growth in both is still amazingly large: we just overestimate the totals today. We also forget that 25 years ago both numbers (imports from China and USA government debt owned by China) were close to 0.
We also greatly underestimate how much manufacturing the USA does, as I have been writing about for years. In fact, until 2010, the USA manufactured more than China.
Who owns the rest? The largest holder of U.S. debt is the federal government itself. Various government trust funds like the Social Security trust fund own about $4.4 trillion worth of Treasury securities. The Federal Reserve owns another $1.6 trillion.
Ok, this figure is a bit misleading. But even if you thrown out the accounting games 1.13/8.9 = 12.7%. That is a great deal. But it isn’t a majority of the debt or anything remotely close. Other foreign investors own $3.5 trillion trillion in federal debt (Japan $1 trillion, UK $500 billion). The $4.6 trillion of federal debt owned by foreigners is a huge problem. With investors getting paid so little for that debt though it isn’t one now. But it is a huge potential problem. If interest reates increase it will be a huge transfer of wealth from the USA to others.
The oil figure is a bit less meaningful, I think. Oil import are hugely fungible. The USA cutting back Middle East imports and pushing up imports from Canada, Mexico, Nigeria… doesn’t change the importance of Middle East oil to the USA in reality (the data might seem to suggest that but it is misleading due to the fungible nature of oil trading). Whether we get it directly from the Middle East or not our demand (and imports) creates more demand for Middle East oil. It is true the USA has greatly increased domestic production recently (and actually decreased the use of oil in 2009). So while I believe the data on Middle East oil I think that it is a bit misleading. If we had 0 direct imports from there we would still be greatly dependent on Middle East oil (because if France and China and India… were not getting their oil there they would buy it where we buy ours… Still the USA uses far more oil than any other country and is extremely dependent on imports. Several other countries are also extremely dependent on oil imports, including the next two top oil consuming countries: China, Japan.
Related: Oil Production by Country 1999-2009 – Government Debt as Percentage of GDP 1990-2009: USA, Japan, Germany, China… – Manufacturing Output as a Percent of GDP by Country – The Relative Economic Position of the USA is Likely to Decline
Very interesting USA federal tax data via the tax foundation. Top 1% has adjusted gross income of $343,000; over $154,000 puts you in the top 5%; $112,000 puts you in the top 10% and $66,000 puts you in the top 25%.
The chart only shows federal income tax data. So the costly social security tax (which is directly based on earned income* so in reality is federal income tax but is handled in a separate account so is consistently not classified as income tax data) for outside the top 5% (income above $106,800 [for 2011] does not have to pay the social security tax) is not reflected in the rates paid here.
Looking at the data excluding social security is fine, but it is very important to remember the social security (plus medicare) tax is the largest tax for, I would guess, most people in the USA. Social security tax is 6.2% paid by the employee plus 6.2% paid by the company – a total of 12.4%. That part of the tax was capped at $106,800 in income for 2011. The medicare tax is 1.45% of income paid by the employee and 1.45% paid by the employer (and it has no cap). So that totals 2.9% (for the employee and employer tax) and brings the total to 15.3%** for most earned income.
|
|
Number of Returns with Positive AGI |
AGI ($ millions) |
Income Taxes Paid ($ millions) |
Group’s Share of Total AGI |
Group’s Share of Income Taxes |
Income Split Point |
Average Tax Rate |
|
All Taxpayers |
137,982,203 |
$7,825,389 |
$865,863 |
100.0% |
100.0% |
– |
11.06% |
|
Top 1% |
1,379,822 |
$1,324,572 |
$318,043 |
16.9% |
36.7% |
$343,927.00 |
24.01% |
|
1-5% |
5,519,288 |
$1,157,918 |
$189,864 |
14.8% |
22.0% |
|
16.40% |
|
Top 5% |
6,899,110 |
$2,482,490 |
$507,907 |
31.7% |
58.7% |
$154,643.00 |
20.46% |
|
5-10% |
6,899,110 |
$897,241 |
$102,249 |
11.5% |
11.8% |
|
11.40% |
|
Top 10% |
13,798,220 |
$3,379,731 |
$610,156 |
43.2% |
70.5% |
$112,124.00 |
18.05% |
|
10-25% |
20,697,331 |
$1,770,140 |
$145,747 |
22.6% |
17.0% |
|
8.23% |
|
Top 25% |
34,495,551 |
$5,149,871 |
$755,903 |
65.8% |
87.3% |
$ 66,193.00 |
14.68% |
|
25-50% |
34,495,551 |
$1,620,303 |
$90,449 |
20.7% |
11.0% |
|
5.58% |
|
Top 50% |
68,991,102 |
$6,770,174 |
$846,352 |
86.5% |
97.7% |
> $32,396 |
12.50% |
|
Bottom 50% |
68,991,102 |
$1,055,215 |
$19,511 |
13.5% |
2.3% |
< $32,396 |
1.85% |
Source: Internal Revenue Service. Table via the tax foundation.
Other interesting data shows that the top 1% earn 16.9% of the total income and pay 36.7% of the total federal income taxes. Those in the top 1-5% earn 14.8% of the total income and pay 22% of the income taxes. Those in the top 5-10% earn of the income 11.5% of the income and pay 11.8% of the federal income taxes. So once you exclude the main tax on income (social security) and use adjusted gross income the tax rates are slightly progressive (higher rates for those that are making the most – and presumably have benefited economically the most from the economic system we have).
Given that this is skewed by excluding the regressive (higher taxes paid by those earning less – social security is the same rate for everyone except those earning the very most who don’t have to pay it on their income above $106,800 [in 2011]) social security tax I believe we should have a more progressive tax system. But that is mainly a political debate. There are good economic arguments for the bad consequences of too unequal a distribution of wealth (which the USA has been moving toward the last few decades – unfortunately).
In addition to the other things I mention there are all sorts of games played by those that desire a royalty type system (where wealth is just passed down to the children of those who are rich, instead of believing in a capitalist system where rewards are given not to the children of royalty but to those that are successful in the markets). A good example of the royalty model is Mitch Romney giving his trust fund children over $100 million each. These schemes use strategies to avoid paying taxes at all. Obviously these schemes also make the system less progressive (based on my understanding of the tax avoidance practiced by these trust fund babies and those that believe it is ethical to give such royalty sized gifts to their royal heirs).
I don’t like the royalty based model of behavior. I much prefer the actions of honorable capitalist such as Warren Buffett and Bill Gates that give their children huge benefits that any of us would be thrilled with, but do not treat them as princes and princesses who should live in a style of luxury that few kings have every enjoyed based solely off their birthright. Both Bill Gates and Warren Buffett have honorably refused to engage in royal seeking behavior that many of their less successful business peers have chosen to engage in. Those that favor trust fund babies are welcome to their opinion and have managed to get most of congress to support their beliefs instead of a capitalist model that I would prefer so they are free to engage in their desire to parrot royalty and honor the royalty model of behavior.
* earned income – you also don’t have to pay social security or medical tax on unearned income (dividends, capital gains, rental income…). Again this by and large favors wealthy taxpayers. Everyone is eligible for the same favorable tax treatment but only those that have the wealth to make significant amounts of unearned income get this advantage.
** the social security tax has been reduced by 200 basis points (this relief was recently extended) as part of dealing with the results of the too big to fail banking caused credit crisis. So under the temporary reduction the personal tax rate is 4.2% and the total cost is 13.2%.
Related: Taxes – Slightly or Steeply Progressive? – Taxes per Person by Country – USA State Governments Have $1,000,000,000,000 in Unfunded Retirement Obligations – Retirement: Roth IRA Earnings and Contribution Limits
The latest data from the commonwealth fund report confirms the status quo. The USA spends twice as much on their health care system for no better results. It is easier to argue the USA is below average in performance that leading. And for double the cost that is inexcusable.
Globally the rich countries citizens are not tremendously happy with health care systems overall. It seems likely not only does the USA cost twice and much as it should and perform poorly compared to countries doing an excellent job but the USA performs that poorly compared to countries that themselves have quite a bit of improvement to make. Which makes the state of the USA system even worse.
Data from the Commonwealth fund report published in 2011 with data for 2009, International Profiles of Health Care Systems, 2011:
Table showing, percent of GDP spent and total spending per capita in USD on health care by country.
| Country | 2007 | Spending |
|
2009 | Spending |
| Australia | 9.5% | $3,128 | 8.7% | $3,445 | |
| Canada | 9.8% | $3,326 | 11.4% | $4,363 | |
| Germany | 10.7% | $3,287 | 11.6% | $4,218 | |
| Japan | 8.5% | $2,878 | |||
| New Zealand | 9.0% | $2,343 | 10.3% | $2,983 | |
| UK | 8.3% | $2,724 | 9.8% | $3,487 | |
| USA | 16.0% | $6,697 | 17.4% | $7,960 |
| Survey of population, showing % that chose each statement (no data available for Japan) | |||||||
| Australia | Canada | Germany | New Zealand | UK | USA | ||
| 2007 – 2010 | 2007 – 2010 | 2007 – 2010 | 2007 – 2010 | 2007 – 2010 | 2007 – 2010 | ||
| Overall health system views | |||||||
| Only minor changes needed, system works well | 24 – 24 | 26 – 38 | 20 – 38 | 26 – 37 | 26 – 62 | 16 – 29 | |
| Fundamental changes needed | 55 – 55 | 60 – 51 | 51 – 48 | 56 – 51 | 57 – 34 | 48 – 41 | |
| Rebuild completely | 18 – 20 | 12 – 10 | 28 – 14 | 17 – 11 | 15 – 3 | 34 – 27 | |
| Percent uninsured | 0 – 0 | 0 – 0 | <1 – 0 | 0 – 0 | 0 – 0 | 16 – 16 | |
Under currently law in the USA by 2020 the uninsured rate should decline to under 5% by 2020 (still far more than any rich country – nearly all of which are at 0%).
On many performance measures in the report the USA is the worst performing system (in addition to costing twice as much). Such as Avoidable Deaths, 2006–07, the USA had 96 per 100,000, the next highest was the UK at 83, Australia was the lowest at 57. And Diabetes Lower Extremity Amputation Rates per 100,000 population, the USA had 36 the next highest was New Zealand at 12, the lowest was the UK at 9. For experiencing a medical, medication or lab test rrror in past 2 years, the USA was at 18%, next worst was Canada at 17%, best was UK at 8%. The USA was top performer in breast cancer five-year survival rate, 2002–2007. And sometimes the USA was in the middle, able to get same/next day appointment when sick: the USA was at 57%, New Zealand achieved 78% while Canada only reached 45%.
It is possible to argue the USA provides mediocre results, which is consistent with most global health care performance measures. Unless you directly benefit from the current USA system it is hard to see how you can argue it is not the worst system of any rich country. Costing twice as much and achieving middling performance. All that doesn’t even factor in the cost in anguish and bankruptcies and restricting individual freedom (when you have to stay tied to a job you would rather leave, just because of health insurance) caused by the difficulty getting coverage and fighting with the insurance companies for payment and coverage for treatment expenses.
Related: Measuring the Health of Nations – USA Paying More for Health Care – Traveling for Health Care – resources for improvement health system performance
Apple has been performing amazingly well for years. They keep producing blockbuster hits over and over. Not only are these hits enormously popular they are enormously profitable.
The only real objections to Apple’s stock I can see are: the overall market value is so huge it just has to collapse (over $400 billion – the largest in the world) or it has to be time for a huge reversal of fortunes.
The problem with the view that it will fall is that the stock is very cheap by any rational measure. You are not paying much for all the earnings. Even if Apple does not continue the trend of the last 5 years, if it just stopped growing altogether, it is still cheap (if it does continue that trend it will break $1 trillion by 2014 – but I don’t think it will). The biggest risk is the profit margin shrinks drastically. That is possible. It is even somewhat likely to shrink a fair amount. But there isn’t much reason to think revenues will not grow. And to me, the current price makes sense only if revenues fall and profit margins fall. It takes the worst case scenario to make this stock seem overpriced.
The data on the last quarter (and for 2011 overall) are impossible (except they actually happened).
- record quarterly revenue of $46.33 billion ($26.74 billion in 2010)
- record quarterly net profit of $13.06 billion ($6 billion in 2010)
- Gross margin was 44.7 percent compared to 38.5 percent in the year-ago quarter
- $17.5 billion in cash flow from operations during the quarter (and $38 billion in the last year)
- $100 billion in cash now ($97.6 billion to be exact but since the data was gathered they probably passed $100 billion anyway). That is more than the market cap of all but 52 companies in the world.
You can’t grow quarterly sales from $26.7 billion to $46.3 billion. $26 million to $46 million, fine that is possible, billions however – not possible. Except Apple did. You can’t grow a $6 billion quarterly profit to $13 billion in 1 year. Except Apple did. You can’t generate a cash flow of $17.5 billion in a quarter. Except Apple did. You can’t have a stockpile of $100 billion in cash. Except Apple does. These figures would not have been seen as unlikely just 3 years ago. They were impossible. But Apple achieved them.
These figures are not short term blips. They are the latest in a long stream of amazingly results.
Related: How Apple Can Grow from $200 Billion to $300 Billion In Market Cap – Apple Tops Google (August 2008)
Apple has numerous, incredibly strong businesses. Each could be the linchpin of an extremely valuable company.
- iPhone initial sales and reoccurring income (over 50% of Apple’s revenue)
- app sales (for iPhones, iPads and Macs)
- iPads
- iTunes
- Macs
- Their retail store business – selling all their products
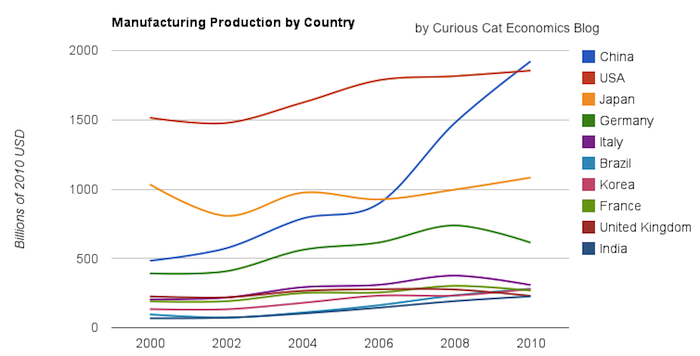
Chart of manufacturing production by the top 10 manufacturing countries (2000 to 2010). The chart was created by the Curious Cat Economics Blog. You may use the chart with attribution. All data is shown in 2010 USD (United States Dollar).
In my last post I looked at the output of the top 10 manufacturing countries with a focus on 1980 to 2010. Here I take a closer look at the last 10 years.
In 2010, China took the lead as the world’s leading manufacturing country from the USA. In 1995 the USA was actually very close to losing the lead to Japan (though you wouldn’t think it looking at the recent data). I believe China will be different, I believe China is going to build on their lead. As I discussed in the last post the data doesn’t support any decline in Chinese manufacturing (or significant moves away from China toward other South-East Asian countries). Indonesia has grown quickly (and have the most manufacturing production, of those discussed), but their total manufacturing output is less than China grew by per year for the last 5 years.
The four largest countries are pretty solidly in their positions now: the order will likely be China, USA, Japan, Germany for 10 years (or longer): though I could always be surprised. In the last decade China relentlessly moved past the other 3, to move from 4th to 1st. Other than that though, those 3 only strengthened their position against their nearest competitors. Brazil, Korea or India would need to increase production quite rapidly to catch Germany sooner. After the first 4 though the situation is very fluid.
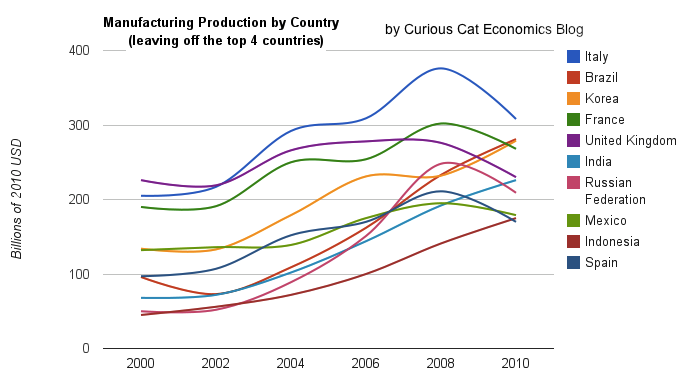
Taking a closure look at the large group of countries after top 4. Chart of manufacturing production from 2000-2010.
Chart of manufacturing production by the leading manufacturing countries (2000 to 2010). The top 4 countries are left off to look more closely at history of the next group. The chart was created by the Curious Cat Economics Blog based on UN data. You may use the chart with attribution.
Removing the top 4 to take a close look at the data on the other largest manufacturing countries we see that there are many countries bunched together. It is still hard to see, but if you look closely, you can make out that some countries are growing well, for example: Brazil, India and Indonesia. Other countries (most in Europe, as well as Mexico) did not fare well in the last decade.
The UK had a particularly bad decade, moving from first place in this group (5th in the world) to 5th in this group and likely to be passed by India in 2011. Europe has 4 countries in this list (if you exclude Russia) and they do not appear likely to do particularly well in the next decade, in my opinion. I would certainly expect Brazil, India, Korea and Indonesia to out produce Italy, France, UK and Spain in 2020. In 2010 the total was $976 billion by the European 4 to $961 billion by the non-European 4. In 2000 it was $718 billion for the European 4 to $343 billion (remember all the data is in 2010 USD).
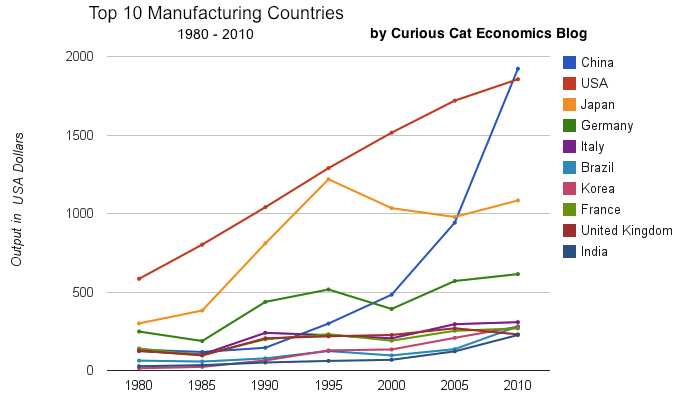
Chart of output by top 10 manufacturing countries from 1980 to 2010. The chart was created by the Curious Cat Economics Blog based on UN data. You may use the chart with attribution.
China has finally actually taken the lead as the largest manufacturer in the world. Reading many news sources and blogs you may have thought the USA lost the lead a couple of decades ago, but you would be wrong. In 1995 it looked like Japan was poised to take the lead in manufacturing production, but they have slumped since then (still they are solidly the 3rd biggest manufacturer). China has been growing manufacturing output enormously for 20 years, and they have now taken the lead from the USA.
As I have been saying for years the biggest economic story about manufacturing is the dramatic and long term increase of productive capacity in China. The next is the continuing global decline in manufacturing employment: increased productivity has seen production rise year after year and employment fall. What is the next most interesting stories is debatable: I would say the continuing failure to appreciate the continuing strong manufacturing production increases by the USA. Another candidate is the the decline in Japan. Another is the increase in several other counties: Korea, Brazil, India, Indonesia…
Looking more closely at some of the long term data shows how much China stands out. From 1980 to 2010 China increased output 1345%. The total top 10 group increased output 302% (all data is in current USD so inflation accounts for most of the gain, 100 1980-USD equal 280 2010-USD). From 1995 to 2010 China increased output 543%. The group increased 64%. For 1980-2010, the results for the other 3 largest manufacturing countries are: USA up 218%, Japan up 261% and Germany up 148% (other countries doing very well are Korea up 1893% and India up 737%). Looking at the last half of that period, from 1995-2010 the: USA up 44%, Japan down 11% and Germany up 19%.
One thing to remember about adjusting manufacturing data for inflation is that often the products created in later years are superior and cost less. So that a computer manufactured in 1990 which added $5,000 to the manufacturing total is far inferior to one in 2010 that added just $1,000. This point is mainly to say that while the increase in manufacturing in real (not inflated dollars) is not as high as it might seem the real value of manufacturing good did likely increase a great deal. But the economic data is based on price so manufacturing increases are reduced by cost decreases. Computers are the most obvious example, but it is also true with many other manufactured goods.
You can that the other largest manufacturing countries fail to keep up with the increases of the entire group of the top 10. China’s gains are just too large for others to match. If you remove China’s results (just to compare how the non-China countries are doing) from 1980-2010 the increase was 216% (so compared to the other 9 top manufacturers over this period the USA was even and Japan better than the average and Germany was worse). And from 1995-2010 the top 9 group (top 10, less China) increased just 28%: so the USA beat while Japan and Germany did worse than the other 9 as a group.