When 2 year US government bonds yield more than the 10 year US government bonds a recession is likely to appear soon. This chart shows why this is seen as such a reliable predictor.
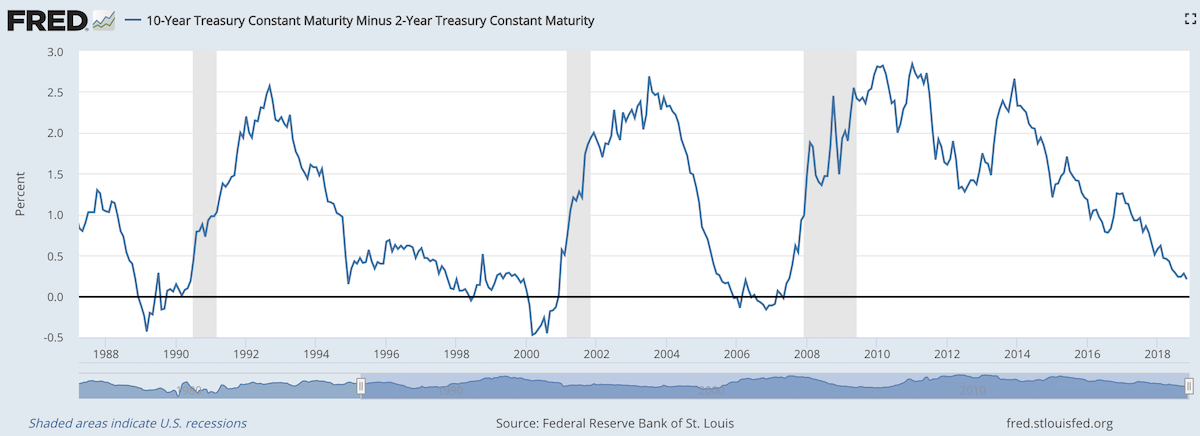
The chart shows the 10 year yield minus the 2 year yield. So when the value falls below 0 that means the 2 year yield is higher. Each time that happened, since 1988, a recession has followed (the grey shaded areas in the chart).
Do note that there were very small inversions in 1998 and 2006 that did not result in a recession in the near term. Also note that in every case the yield curve was no longer inverted by the time a recession actually started.
The reason why this phenomenon is getting so much attention recently is another thing that is apparent when looking at this chart, the 2 and 10 year yields are getting close to equal. But you can also see we are no closer than 1994 and the USA economy held off a recession for 7 more years.
Since 1970 the average length of time from the inversion of the 10 to 2 year yield curve has been 12 months (with a low of 6 months in 1973 and a high of 17 months, before the great recession of 2008).
In addition to a possibly impending yield curve inversion it has been a long time since the last recession which makes many investors and economists nervous that one may be due.
Related: 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates are not correlated with the Fed Funds Rate – Bond Yields Stay Very Low, Treasury Yields Drop Even More (2010) – Looking for Dividend Stocks in the Current Extremely Low Interest Rate Environment (2011) – Stock Market Capitalization by Country from 2000 to 2016
Another thing to note about yield curves at this time is that the US Federal Reserve continues to hold an enormous amount of long term government debt (trillions of dollars) which it has never done before the credit crisis of 2008. This reduces the long term yield since if they sold those assets that would add a huge amount of supply. How this impacts the predictive value of this measure will have to be seen. Also, one way for the Fed to delay the inversion would be to sell some of those bonds and drive up long term rates.
I created a 10 stocks for 10 years portfolio in April of 2005 which I shared on this blog. It did very well.
Over the years I adjusted the portfolio occasionally. Unfortunately the website I used to track results stopped doing that (and it is much more difficult to track results – with dividends, stock splits, spinoff… than you might suppose). I estimate I beat the S&P 500 by maybe 300 basis points annually (for the portfolio with slight adjustment over time, which is the one I tracked).
With this post I have created a new 10 stocks for 10 years portfolio.
The 10 stocks I came up with are (closing price on 22 April 2005 – % of portofilo invested):
- Tencent (TCEHY) – $43 and 15% (using the USA ADR). A phenomenal company with incredible global prospects for the long term. As the stock price has been hampered by concerns about China it has great potential for appreciation from the current price.
- Alibaba (BABA) – $175 and 15% (using USA ADR). Another phenomenal company with incredible global prospects that has performed poorly this year due to China concerns.
- Alphabet (GOOGL) – $1,254 and 11% (in the original 2005 portfolio the price was $216 and it started at 12% of the portfolio. The prospects are great long term, the stock price reflects that so it isn’t cheap but over the long term I expect it to do very well).
- Apple (AAPL) – $225 and 11% (I added Apple to the original 10 for 10 portfolio in 2010. The biggest mistake in the original portfolio was leaving off Apple, I considered it but chose not to include it. It has been my largest stock holding for years. It has been very cheap even just a few years ago, though today I think the price is much more reasonable so it isn’t the great bargin it has been. Still the long term prospects are great.)
- Abbvie (ABBV) – $97 and 10% (I added Abbive to the original portfolio in 2014. I would select a couple other healthcare stocks in a real invested portfolio for balance but Abbvie is the company I am most comfortable with so I include it here.)
- Toyota (TM) $125 and 9% (in the 2005 portfolio the price was $72 and it made up 12% of the portfolio). I believe the company is very well managed and the long term prospects are good though I am a bit worried about autonomous cars and the future of transportation. A potential new market for Toyota is robotics but they have not been as aggressive with software development innovation as I would hope on that front. The companies I am most interested in are very internet focused and I don’t like how concentrated that makes this portfolio so adding Toyota and Abbive adds a bit of diversity, though obviously not much)
- Amazon (AMZN) – $2,002 and 8% (in the 2005 portfolio the price was $33 a share, it was by far the best performer. It started as 8% of the original 2005 portfolio. I am very high on the prospects for the company, the stock price is what leads me to limit it to 8% of the new portfolio.)
- Naspers (NPSNY) – $33 and 8% (bought 30 October 2018, the company is largely a proxy for Tencent but also has many other significant investments in internet companies, the decline in Tencent, along with the Chinese market decline, and therefore the decline in Naspers just makes it too good an opportunity to pass up)
- Vanguard Health Care Index Fund (VHT) – $177 and 8% (I can’t decide on what other health care stock to hold for 10 years but I believe strongly in global growth of health care investments over the next 10 years so I settled on this low expense ETF.)
- Danaher (DHR) – $103 and 5% (I like this company but honestly the biggest reason for including it is to get some more diversity in the portfolio. I added it to the 2005 portfolio in 2008.)
I strongly believe that 10 years from now the Chinese stock market will have performed extremely well. There are of course numerous substantial worries about Chinese investments (the real estate bubble, high debt levels, “Great Firewall”, difficult government regulatory environment, restrictions on the press, restrictions on open debate…) but there are many reasons to be very optimistic about the long term prospects for China’s economic growth and the very promising leading companies prospects: such as Tencent, Alibaba, Baidu, Ctrip….
At this time it seems to me that the stock prices of leading Chinese companies are being held down compared to other leading companies (Apple, Google, Amazon…). Either the USA companies are overvalued or the Chinese ones are very under-valued or the global economy outside the USA is going to do very poorly in the next 10 years. Google, Apple etc. make a huge amount overseas but they have more earnings in the USA than Tencent and Alibaba (which still have almost none in the USA though their global business, outside China, is growing extremely rapidly).
One very big factor that I believe will support Chinese stock prices over the next 10 to 20 years is an large increase in the holdings of stocks by those in China. The current distribution of savings in China has extremely limited stock investments (and much larger bank savings accounts and real estate investments than in other countries). I expect that to change with a large increase in stock investing in China over the next 10 to 20 years.
Two other companies that are interesting are Naspers (which owns a huge amount of Tencent) and Softbank (which owns a large amount of Alibaba). Softbank has a large portfolio of investments in leading technology companies globally though much of it is held in a somewhat complicated manner. Naspers is more focused but also has a strong global portfolio. One of the very important aspects of Alibaba and Tencent is their huge portfolio of technology company investments made at the venture capital stage mostly (Google also has quite a few more investments than most people realize). I also believe Vanguard Emerging Market ETF (VWO) is a very good long term investment.
I wouldn’t be surprised if Chinese stocks had difficulty in the next year or two but long term stocks such as Alibaba and Tencent offer the best prospects considering realistic expectations for possible rewards compared to the risk investing in them poses today.
This portfolio is not meant to be a complete personal financial portfolio (at most it would be a portion of the portfolio allocated to equity holdings). Previous posts on portfolio allocation: Investment Risk Matters Most as Part of a Portfolio, Rather than in Isolation, Investment Options Are Much Less Comforting Than Normal These Days (2013) and Investing Return Guesses While Planning for Retirement.
Factfulness by Hans Rosling (of TED talks and Gapminder charts fame) is an exceptionally good book. It provides great insight into how to think more effectively and how to understand the reality of the world we live in (versus the large distortions so common in most people’s vision of the world). You can take a quick quiz to see how well you understand the world
The truth of the very widespread increase in wealth around the globe has influenced my investing strategy for decades. It should be influencing yours, is it?
Data is extremely valuable in helping us make decisions and evaluating the effectiveness of policy. However it is critical to be careful. It is very easy to focus on meeting targets that seem sensible – increasing the number of hospital beds – but that lead to less effective policy.
Dollar street provides photos of people at all 4 income levels from around the globe. This illustrates Hans’ point that what determines how people live and what their circumstances look like is mostly a matter of income not the country they live in. It is simple idea but one that runs counter to much of the economic discussion focused so much on national boundaries. National boundaries do matter and the laws and economic reality of the national economy has a large impact but the issues for people at each level of income are much more tied to those in their level of income anywhere in the world than they are tied to their nation.

The book relentlessly points out the great progress that has been made globally over the last 50 years and how that progress continues today and looks to be set to continue in the future. We have plenty of areas to work on improving but we should be aware of how much progress we have been making. As he points out frequently he has continually seen huge underestimation of the economic conditions in the world today. This book does a great job of presenting the real success we have achieved and the progress we can look forward to in the future.
* In 2017
Level 1 has 0.75 billion people living on less than $2 per day.
Level 2 has 3.3 billion people living on incomes between $2 to $8 per day.
Level 3 has 2.5 billion people living on $8 to $32 per day.
Level 4 has 0.9 billion people living on more than $32 per day.
Related: GDP Growth Per Capita for Selected Countries from 1970 to 2010 (Korea, China, Singapore, Brazil) – Stock Market Capitalization by Country from 2000 to 2016 – Ignorance of Capitalism Leads us Astray – Wealthiest 1% Continue Dramatic Gains Compared to Everyone Else
We have tax plans from the major USA Presidential candidates. I don’t like any of them, though I actually like Ted Cruz’s plan more than the others, but it has a huge problem. His plan doesn’t fund the government he wants, not even just as poorly as we have been doing. He would increase the debt substantially.
My plan would have 3 parts. I like a flat tax, I doubt it will ever happen, but if we could get one I would be happy. Cruz proposes that (at 10%). I am fine with his proposal to eliminate all deductions but mortgage interest and charity. I would definitely tweak that some – no more than $50,000 in mortgage interest deduction a year and the same for charity. Basically subsidizing it a bit for the non-rich is fine. Subsidizing these for the rich seems silly so I would cap the deductions in some way. I also wouldn’t mind an almost flat tax, say 12% up to $200,000 and 15% after that (or some such rates).
Cruz’s rate is far too low given the government he wants. The government budget is largely: Social Security, Medicare and Military. Then you also have debt payment which have to be paid. Those 4 things are over 80% of the spending. All the other things are just in the last 20%, you can cut some of that but realistically you can’t cut much (in percentage terms – you can cut hundreds of billions theoretically but it is unlikely and even if you did it isn’t a huge change).
We are piling on more debt than we should. Therefore we should increase revenue, not reduce it. But if we can’t increase it (for political reasons) we definitely should not reduce it until we have shown that we have cut spending below revenue for 2 full years. After that, great, then decrease rates.

The White House, Washington DC by John Hunter. See more of my photos of Washington DC.
The VAT tax on businesses replacing the corporate tax system is in Cruz’s plan and this is the best option for corporate taxes in my opinion. Another decent option is just to pass through all the earnings to the owners (I first heard this proposal from my Economics professor in College) and tax them on the earnings.
Increasing the giveaways to trust-fund baby as Cruz and Trump propose is the single worst tax policy change that can be made. I have explained previously how bad an idea this is: The estate tax is the most capitalist tax that exists. The trust-fund-baby favors should be reduced not increased. I would roll back to the Reagan Administration policy on estate tax rates.
This richest 1% continue to take advantage of economic conditions to amass more and more wealth at an astonishing rate. These conditions are perpetuated significantly by corrupt politicians that have been paid lots of cash by the rich to carry out their wishes.
One thing people in rich countries forget is how many of them are in the 1% globally. The 1% isn’t just Bill Gates and Warren Buffett. 1% of the world’s population is about 72 million people (about 47 million adults). Owning $1 million in assets puts you in the top .7% of wealthy adults (Global Wealth Report 2013’ by Credit Suisse). That report has a cutoff of US $798,000 to make the global 1%. They sensibly only count adults in the population so wealth of $798,000 puts you in the top 1% for all adults.
$100,000 puts you in the top 9% of wealthiest people on earth. Even $10,000 in net wealth puts you in the top 30% of wealthiest people. So while you think about how unfair it is that the system is rigged to support the top .01% of wealthy people also remember it is rigged to support more than 50% of the people reading this blog (the global 1%).
I do agree we should move away from electing corrupt politicians (which is the vast majority of them in DC today) and allowing them to continue perverting the economic system to favor those giving them lots of cash. Those perversions go far beyond the most obnoxious favoring of too-big-to-fail banking executives and in many ways extend to policies the USA forces on vassal states (UK, Canada, Australia, France, Germany, Japan…) (such as those favoring the copyright cartel, etc.).
Those actions to favor the very richest by the USA government (including significantly in the foreign policy – largely economic policy – those large donor demand for their cash) benefit the global 1% that are located in the USA. This corruption sadly overlays some very good economic foundations in the USA that allowed it to build on the advantages after World War II and become the economic power it is. The corrupt political system aids the richest but also damages the USA economy. Likely it damages other economies more and so even this ends up benefiting the 38% of the global .7% that live in the USA. But we would be better off if the corrupt political practices could be reduced and the economy could power economic gains to the entire economy not siphon off so many of those benefits to those coopting the political process.
The USA is home to 38% of top .7% globally (over $1,000,000 in net assets).
| country | % of top .7% richest | % of global population |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 38.3% | 4.5% |
| Japan | 8.6% | 1.8% |
| France | 7.5% | .9% |
| UK | 6.1% | .9% |
| Germany | 5.9% | 1.1% |
| other interesting countries | ||
| China | 3.4% | 19.2% |
| Korea | 1% | .7% |
| Brazil | .6% | 2.8% |
| India | .5% | 17.5 |
| Indonesia | .3% | 3.5% |
Oxfam published a report on these problems that has some very good information: Political capture and economic inequality
Business should not be allowed to store credit card numbers that can be stolen and used. The credit card providers should generate a unique credit card number for the business to store that will only work for the purchaser at that business.
Also credit card providers should let me generate credit card numbers as I wish for use online (that are unique and can be stopped at any time I wish). If I get some customer hostile business that makes canceling a huge pain I should just be able to turn off that credit card “number.”
Laws should be adjusted to allow this consumer controlled spending and require that any subscription service must take the turning off of the payments as cancellation.
For some plan where the consumer agrees up front to say 12 months of payments then special timed numbers should be created where the potentially convoluted process used now remain for the first 12 months.
Also users should be able to interact with there credit reports and do things like turn on extra barriers to granting credit (things like they have to be delayed for 14 days after a text, email [to as many addresses and the consumer wants to enter] and postal notification are sent to the user. Variations on how these work is fine (for example, setting criteria for acceptance of the new credit early at the consumers option if certain conditions are met (signing into the web site and confirming information…).
Better security on the cards themselves are also needed in the USA. The costs of improvement are not just the expenses credit card and retailers face but the huge burden to consumers from abuse of the insecure system in place for more than a decade. It is well past time the USA caught up with the rest of the world for on-card security.
The providers have done a lousy job of reducing the enormous burden of fraud on consumers. As well as failing to deal adequately with customer hostile business practices (such as making canceling very cumbersome and continuing to debit the consumer’s credit card account).
Related: Protect Yourself from Credit Card Fraud – Personal Finance Tips on the Proper use of Credit Cards – Continued Credit Card Company Customer Dis-Service – Banks Hoping they Paid Politicians Enough to Protect Billions in Excessive Fees
I like charity that provides leveraged impact. I like charity that is aimed at building long term improvement. I like entrepreneurship. I like people having work they enjoy and can be proud of. And I like people having enough money for necessities and some treats and luxuries.
I think sites like oDesk provide a potentially great way for people to lead productive and rewarding lives. They allow people far from rich countries to tap into the market demand in rich counties. They also allow people to have flexible work arrangements (if someone wants a part time job or to work from home that is fine).
These benefits are also true in the USA and other rich countries (even geography – there are many parts of the USA without great job markets, especially many rural areas). The biggest problem with rich country residents succeeding on something like oDesk is they need quite a bit more money than people from other countries to get by (especially in the USA with health care being so messed up). There are a great deal of very successful technology people on oDesk (and even just freelancing in other ways), but it is still a small group that is capable and lucky enough to pull in large paychecks (it isn’t only technology but that is the majority of high paying jobs I think on oDesk).
But in poor countries with still easily 2 billion and probably much more there is a huge supply of good workers. There is a demand for work to be done. oDesk does a decent job of matching these two but that process could use a great deal of improvement.
I think if I became mega rich one of the projects I would have would be to create an organization to help facilitate those interested in internet based jobs in poor countries to make a living. It takes hard work. Very good communication is one big key to success (I have repeatedly had problems with capable people just not really able to do what was expected in communications). I think a support structure to help with that and with project management would be very good. Also to help with building skills.
If I were in a different place financially (and I were good at marketing which I am not) I would think about creating a company to do this profitably. The hard part for someone in a rich country to do this is that either they have to take very little (basically do it as charity) or they have to take so much cash off the top that I think it makes it hard to build the business.
But building successful organizations that can grow and provide good jobs to those without many opportunities but who are willing to work is something I value. I did since I was a kid living in Nigeria (for a year). I didn’t see this solution then but the idea of economic well being and good jobs and a strong economy being the key driver to better lives has always been my vision.
This contrast to many that see giving cash and good to those in need as good charity. I realize sometimes that is what is needed – especially in emergencies. But the real powerful change comes from strong economy providing people the opportunity to have a great job.
I share Dr. Deming’s personal aim was to advance commerce, prosperity and peace.
Related: Commerce Takes More People Out of Poverty Than Aid – Investing in the Poorest of the Poor – I am a big fan of helping improve the economic lives of those in the world by harnessing appropriate technology and capitalism – A nonprofit in Queens taught people to write iPhone apps — and their incomes jumped from $15k to $72k
Fed Continues Adding to Massive Quantitative Easing
In fact, while the Fed has pumped about $2.8 trillion into the financial system through nearly five years of asset buying.
Bank excess reserves deposited with the New York Fed have mushroomed from less than $2 billion before the financial crisis to $2.17 trillion today. In essence, roughly two-thirds of the money the Fed pumped into the banking system never left the building.
The Fed now pays banks for their deposits. These payment reduce the Fed’s profits (the Fed send profits to the treasury) by paying those profits to banks so they can lavish funds on extremely overpaid executives that when things go wrong explain that they really have no clue what their organization does. It seems very lame to transfer money from taxpayers to too-big-to-fail executives but that is what we are doing.
Quantitative easing is an extraordinary measure, made necessary to bailout the too-big-to-fail institutions and the economies they threatened to destroy if they were not bailed out. It is a huge transfer payment from society to banks. It also end up benefiting anyone taking out huge amounts of new loads at massively reduced rates. And it massively penalizes those with savings that are making loans (so retirees etc. planing on living on the income from their savings). It encourages massively speculation (with super cheap money) and is creating big speculative bubbles globally.
This massive intervention is a very bad policy. The bought and paid for executive and legislative branches that created, supported and continue to nurture the too-big-to-fail eco-system may have made the choice – ruin the economy for a decade (or who knows how long) or bail out those that caused the too-big-to-fail situation (though only massively bought and paid for executive branch could decline to prosecute those that committed such criminally economically catastrophic acts).
The government is saving tens of billions a year (maybe even hundred of billions) due to artificially low interest rates. To the extent the government is paying artificially low rates to foreign holders of debt the USA makes out very well. To the extent they are robbing retirees of market returns it is just a transfer from savers to debtors, the too-big-to-fail banks and the federal government. It is a very bad policy that should have been eliminated as soon as the too-big-to-fail caused threat to the economy was over. Or if it was obvious the bought and paid for leadership was just going to continue to nurture the too-big-to-fail structure in order to get more cash from the too-big-to-fail donors it should have been stopped as enabling critically damaging behavior.
It has created a wild west investing climate where those that create economic calamity type risks are likely to continue to be rewarded. And average investors have very challenging investing options to consider. I really think the best option for someone that has knowledge, risk tolerance and capital is to jump into the bubble created markets and try to build up cash reserves for the likely very bad future economic conditions. This is tricky, risky and not an option for most everyone. But those that can do it can get huge Fed created bubble returns that if there are smart and lucky enough to pull off the table at the right time can be used to survive the popping of the bubble.
Maybe I will be proved wrong but it seems they are leaning so far into bubble inflation policies that the only way to get competitive returns is to accept the bubble nature of the economic structure and attempt to ride that wave. It is risky but the supposedly “safe” options have been turned dangerous by too-big-to-fail accommodations.
Berkshire’s Munger Says ‘Venal’ Banks May Evade Needed Reform (2009)
Related: The Risks of Too Big to Fail Financial Institutions Have Only Gotten Worse – Is Adding More Banker and Politician Bailouts the Answer? – Anti-Market Policies from Our Talking Head and Political Class
A report by the Dallas Federal Reserve Bank, Assessing the Costs and Consequences of the 2007–09 Financial Crisis and Its Aftermath, puts the costs to the average household of the great recession at $50,000 to $120,000.
The worst downturn in the United States since the 1930s was distinctive. Easy credit standards and abundant financing fueled a boom-period expansion that was followed by an epic bust with enormous negative economic spillover.
…
Our bottom-line estimate of the cost of the crisis, assuming output eventually returns to its pre-crisis trend path, is an output loss of $6 trillion to $14 trillion. This amounts to $50,000 to $120,000 for every U.S. household, or the equivalent of 40 to 90 percent of one year’s economic output.
They say “misguided government incentives” much of which are due to payments to politicians by too-big-to-fail institution to get exactly the government incentives they wanted. There is a small bit of the entire problem that is likely due to the desire to have homeownership levels above that which was realistic (beyond that driven by too-big-to-fail lobbyists).
“Were safer” says a recent economist. Which I guess is true in that it isn’t quite as risky as when the too-big-to-fail-banks nearly brought down the entire globally economy and required mass government bailouts that were of a different quality than all other bailouts of failed organizations in the past (not just a different quantity). The changes have been minor. The CEOs and executives that took tens and hundreds of millions out of bank treasures into their own pockets then testified they didn’t understand the organization they paid themselves tens and hundreds of a millions to “run.”
We left those organizations intact. We bailed out their executives. We allowed them to pay our politicians in order to get the politicians to allow the continued too-big-to-fail ponzie scheme to continue. The too-big-to-fail executives take the handouts from those they pay to give them the handouts and we vote in those that continue to let the too-big-to-fail executives to take millions from their companies treasuries and continue spin financial schemes that will either work out in which case they will take tens and hundreds of millions into their person bank accounts. Or they won’t in which case they will take tens of millions into their personal bank accounts while the citizens again bail out those that pay our representatives to allow this ludicrous system to continue.
Printing money (and the newer fancier ways to introduce liquidity/capital) work until people realize the money is worthless. Then you have massive stagflation that is nearly impossible to get out from under. The decision by the European and USA government to bail out the too big to fail institutions and do nothing substantial to address the problem leaves an enormous risk to the global economy unaddressed and hanging directly over our heads ready to fall at any time.
The massively too big to fail financial institutions that exist on massive leverage and massive government assistance are a new (last 15? years) danger make it more likely the currency losses value rapidly as the government uses its treasury to bail out their financial friends (this isn’t like normal payback of a few million or billion dollars these could easily cost countries like the USA trillions). How to evaluate this risk and create a portfolio to cope with the risks existing today is extremely challenging – I am not sure what the answer is.
Of the big currencies, when I evaluate the USA $ on its own I think it is a piece of junk and wouldn’t wan’t my financial future resting on it. When I look at the other large currencies (Yen, Yuan, Euro) I am not sure but I think the USD (and USA economy) may be the least bad.
In many ways I think some smaller countries are sounder but smaller countries can very quickly change – go from sitting pretty to very ugly financial situations. How they will wether a financial crisis where one of the big currencies losses trust (much much more than we have seen yet) I don’t know. Still I would ideally place a bit of my financial future scattered among various of these countries (Singapore, Australia, Malaysia, Thailand, Brazil [maybe]…).
Basically I don’t know where to find safety. I think large multinational companies that have extremely strong balance sheets and businesses that seem like they could survive financial chaos (a difficult judgement to make) may well make sense (Apple, Google, Amazon, Toyota, Intel{a bit of a stretch}, Berkshire Hathaway… companies with lots of cash, little debt, low fixed costs, good profit margins that should continue [even if sales go down and they make less they should make money – which many others won’t]). Some utilities would also probably work – even though they have large fixed costs normally. Basically companies that can survive very bad economic times – they might not get rich during them but shouldn’t really have any trouble surviving (they have much better balance sheets and prospects than many governments balance sheets it seems to me).
In many ways real estate in prime areas is good for this “type” of risk (currency devaluation and financial chaos) but the end game might be so chaotic it messes that up. Still I think prime real estate assets are a decent bet to whether the crisis better than other things. And if there isn’t any crisis should do well (so that is a nice bonus).
Basically I think the risks are real and potential damage is serious. Where to hide from the storm is a much tricker question to answer. When in that situation diversification is often wise. So diversification with a focus on investments that can survive very bad economic times for years is what I believe is wise.
Related: Investing in Stocks That Have Raised Dividends Consistently – Adding More Banker and Politician Bailouts in Not the Answer –
Failures in Regulating Financial Markets Leads to Predictable Consequences – Charlie Munger’s Thoughts on the Credit Crisis and Risk – The Misuse of Statistics and Mania in Financial Markets
