This post lists the 20 publicly traded companies with the largest market capitalization as of today. Since my May 2017 list of the 20 most valuable stocks many of the market caps have increased significantly.
In the 20 most valuable companies list there are 13 USA companies, 4 Chinese companies and 1 each for Korea, Netherlands and Switzerland. The remaining 17 companies with market caps above $200 billion are based in: USA 8, China 5, Switzerland 2, Japan 1 and Taiwan 1.
| Company | Country | Market Capitalization | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apple | USA | $898 billion |
| 2 | Alphabet (GOOGL) | USA | $729 billion |
| 3 | Microsoft | USA | $642 billion |
| 4 | Amazon | USA | $572 billion |
| 5 | USA | $531 billion | |
| 6 | Tencent | China | $506 billion* |
| 7 | Alibaba | China | $492 billion |
| 8 | Berkshire Hathaway | USA | $451 billion |
| 9 | Johnson & Johnson | USA | $371 billion |
| 10 | Exxon Mobil | USA | $345 billion |
Tencent (China) soared $192 billion (61%) since my May 2017 post (after a 85% gain shown in the last post – behind only Samsung for largest percentage gain in that post). That gain pushed Tencent over a $500 billion market cap and moved them from 10th most valuable to 6th. Alibaba also soared $192 billion (64% for them) and moved into the top 10.
Apple gained $73 billion in market cap and is closing in on a market cap over $1 trillion since my May 2017 post. Microsoft, which continues to gain value rapidly even though it is not getting the attention of many of the internet companies, increased by $117 billion. Amazon added $106 billion to their market cap in the last 6 months. Alphabet (Google) gained $77 billion while Facebook increased by $94 billion.
The next ten most valuable companies:
| Company | Country | Market Capitalization | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | JPMorgan Chase | USA | $341 billion |
| 12 | Industrial & Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) | China | $319 billion* |
| 13 | Samsung | Korea | $310 billion |
| 14 | Walmart | USA | $289 billion |
| 15 | China Unicom | China | $281 billion |
| 16 | Bank of America | USA | $277 billion |
| 17 | Wells Fargo | USA | $267 billion |
| 18 | Nestle | Switzerland | $267 billion |
| 19 | Royal Dutch Shell | Netherlands | $260 billion |
| 20 | Visa | USA | $254 billion |
Market capitalization shown are of the close of business November 26th, as shown on Google Finance.
GE continued to collapse, dropping another 62 billion add dropping well out of the top 20 (they were one of the 10 most valuable companies in 2016).
The total value of the top 20 gained $1.2 trillion since my February, 2016 post: growing from $7.2 trillion to $8.4 trillion. Remember, the companies making up the top 20 has changed (China Unicom, Visa and Royal Dutch Shell were added while GE, China Mobile and Roche dropped out).
As I noted in Stock Market Capitalization by Country from 2000 to 2016: Apple, Alphabet, Microsoft, Facebook and Amazon have a combined market capitalization greater than the entire stock market in every country but those in the USA, China and Japan.
Related: Global Stock Market Capitalization from 2000 to 2012 – Stock Market Capitalization by Country from 1990 to 2010 – Historical Stock Returns
A few other companies of interest (based on their market capitalization):
Even if some lobbyists and their friends in Washington DC try to distract from the long term failure of the USA health care system the data continues to pour in about how bad it is.
U.S. Health-Care System Ranks as One of the Least-Efficient
None of these rankings are perfect and neither is this one. But it is clear beyond any doubt that the USA healthcare system is extremely costly for no better health results than other rich countries (and even more expensive with again no better results than most poor countries). It is a huge drain on the economy that we continue to allow lobbyists and special interests to take advantage of the rest of us via the Democrats and Republican parties actions over the last few decades.
We have to improve. The costs imposed on everyone to support those benefiting from this decades old transfer of economic wealth to health care special interests should no longer be accepted.
The top 5 countries are: Hong Kong, Singapore, Spain, South Korea and Japan. The first four have costs about 25% of the USA. Japan costs about 40% of the USA per person cost.
Mylan’s despicable actions with Epi-pen and the direct participation of both political parties in increasing the costs foisted on the health care system by Mylan is just one in hundreds of the individual actions that continue to saddle the rest of USA economy with huge costs.
Related: Out of Pocket “Maximum”, Understanding USA Health Care Costs – Decades Later The USA Health Care System is Still a Deadly Disease for Our Economy – 2015 Health Care Price Report, Costs in the USA and Elsewhere – USA Health Care Spending 2013: $2.9 trillion $9,255 per person and 17.4% of GDP – USA Spends $7,960 Compared to Around $3,800 for Other Rich Countries on Health Care with No Better Health Results (2009 data)
Based on my thoughts on killing the Goose laying golden eggs in Iskandar Malaysia posted on a discussion forum. The government has instituted several several policies to counteract a bubble in luxury real estate prices in the region (new taxes on short term capital gains in real estate [declining amounts through year 6]), increasing limits on purchases by foreigners, new transaction fees (2% of purchase price?) for real estate transactions, requirements for larger down-payments from purchasers…
Iskandar is 5 times the size of Singapore and is in the state of Johor in Malaysia. Johor Bahru is the city which makes up much of Iskandar but as borders are currently drawn Iskandar extends beyond the borders of Johor Bahru.
The prospects for economic growth in Iskandar Malaysia in the next 5, 10 and 15 years remain very strong. They are stronger than they were 5 years ago: investments that produce economic activity (theme parks, factories, hospitals, hotels, retail, film studio…) have come online and more on being built right now.
Cooperation with Singapore is the main advantage Iskandar has (Iskandar is next to the island of Singapore similar to those areas surrounding Manhattan). It provides Iskandar world class advantages that few other locations have (it is the same advantages offered by lower cost areas extremely close to world class cities – NYC, Hong Kong, London, San Francisco etc.). Transportation connections to Singapore are critical and have not been managed as well as they should have been (only 2 bridges exist now and massive delays are common). A 3rd link should be in place today (they haven’t even approved the location yet).
A MRT connection to Singapore (Singapore’s subway system) should be a top priority of anyone with power interested in the future economic well being of Iskandar and Johor. Johor Bahru doesn’t have a light rail system yet this would be the start of it. It has been “announced” as planned for 2018 but not officially designated or funded yet.
Since I am living in Malaysia now, I pay attention to Malaysia’s economy. There are many reasons to be positive but the large consumer and government debt in Malaysia is a serious concern. They do have many administrators that say the right things, the question is going to be whether those statement define policy action or if they are ignored.
Wahid Says Ringgit Too Weak as Growth Improves: Southeast Asia
India and Indonesia have experienced large stock market declines and currency devaluations recently. The Malaysian Ringgit has declines 10% against the US $ in the last 3 months. Malaysia is holding up ok, but is venerable as these international loses of confidence often sweep over countries (and move from country to country).
There is a real risk that the current account could slip into a deficit for the first time since the fourth quarter of 1997, Macquarie Group Ltd. analysts said in a report this month.
“We are aware of this situation and we are aware of some of the measures to be undertaken to make sure that Malaysia remains in a surplus position,” Abdul Wahid said, without elaborating on the steps. “It is still a surplus and we are managing it.”
The surplus is narrowing on increased overseas investment and property buying, higher imports for infrastructure projects, lower palm oil and rubber export prices and the acquisition of new aircraft by Malaysian Airline System Bhd., the minister said.
The main foreign exchange earner recently seems to be selling property, that isn’t a good way to be earning foreign currency (selling assets). It is ok to do this to some extent, but relying on large inflows this way is very risky (and self defeating over the long term if it is too large). Even though palm oil and rubber exports are declining a bit, I believe they are still strong sources of foreign currency so that is good.
I decided to take a look at some historical economic data to see if some of my beliefs were accurate (largely about how well Singapore has done) and learn a bit more while I was at it.
| country |
|
1970** |
|
2010*** |
|
% increase |
| Korea | 1,320 | 20,200 | 1,430 | |||
| China | 325 | 4,280 | 1,217 | |||
| Singapore | 4260 | 42,650 | 901 | |||
| Indonesia | 460 | 2,960 | 543 | |||
| Brazil | 1900 | 10,500 | 453 | |||
| Thailand | 850 | 4,600 | 441 | |||
| Portugal | 3,970 | 21,000 | 429 | |||
| Japan | 9,000 | 42,300 | 370 | |||
| Malaysia | 1,900 | 7,755 | 308 | |||
| Germany | 11,550 | 40,500 | 251 | |||
| UK | 10,400 | 36,300 | 249 | |||
| France | 13,600 | 40,600 | 199 | |||
| Mexico | 4,160 | 9,200 | 121 | |||
| Panama | 3,480 | 7,700 | 121 | |||
| India | 555 | 1,180 | 113 | |||
| USA | 23,350 | 47,100 | 102 | |||
| South Africa | 3,930 | 7,100 | 81 | |||
| Venezuela | 8,280 | 9,770 | 18 |
I just picked countries that interested me and seemed worth looking at. I looked for some around the starting position of Singapore and close to Singapore geographically. And looked at Panama as the closest match to Singapore (for Singapore’s main 1970 asset, convenient for shipping lanes, and very close for GDP per capita).
Malaysia and Singapore were 1 country after independence (from 1963-1965).
I can’t imagine more than a couple countries could reasonably be argued to have had better economic performance from 1970 to 2010 than Singapore (Korea? China? Who else?). Singapore had very little going for it in 1970. They had a good location for shipping and that is about it macro-economically. No natural resources. No huge storage of wealth. No preeminence in science, technology or business.
It seems to me that Singapore actually did have 1 other thing. A government that was to preside over a fantastic economic growth success. You won’t find many textbooks talking about the way to economic success is a very well run government. And there is good reason for that, I believe. Relying on a very well run government will nearly always fail. In some ways Singapore was like Japan but with significantly more government influence on the way economic development played out.
I was surprised how poorly the USA has faired. It isn’t so surprising that we lagged. People forget how rich the USA was in 1970. The USA is still very rich but bunched together with lots of other rich countries instead of way out ahead as they were in 1970. And in 1970 the lead was already contracting, for what it had been earlier. But even knowing the relative performance of the USA had lagged, I was surprised by how much it under-performed.
I was also surprised with India. I knew they have done poorly but I didn’t realize it had been this poor. The failures to greatly improve infrastructure, education and the stifling effect of their bureaucracy have been causing them great harm. They have been doing some good things in the last 10 years especially but still have a long way to go. Their premier education is actually pretty decent. The problem is the other 90% of the education is often poor and many people (especially women) hardly have any education at all. It is very hard to get ahead when you fail to take advantage of the talents of so many of your people.
Related: Singapore and Iskandar Malaysia – Chart of Largest Petroleum Consuming Countries from 1980 to 2010 – Chart of Nuclear Power Production by Country from 1985-2009 – Top Countries For Renewable Energy Capacity
There is an increasing trend to move from the USA to another country to work and live. This is not surprising to me. Recently this has picked up quite a bit; I am surprised by the velocity at which this interest in moving (I figured it would be a long term mega trend but not so drastic, so quickly). Economic changes are often quite surprising in how rapidly they move forward.
An interesting survey shows USA investors have become much more interested in relocating in the last two years (the data they show though has tremendous volatility over time, so I am not really sure this means much). I wonder how much of it can be explained by investors wanting to get a deep understanding of very promising markets. I wouldn’t image the actual number that do this is huge, but maybe the number considering it is significant. Billionaire investor, Jim Rodgers moved to Asia because he sees Asia as key to the future. One of the reasons I moved to Malaysia this year was to get a in depth understanding of what South East Asia is like (it is not a deciding reason, at all but maybe the 4th or 5th reason).
I believe the globalization of the employment market is a long term trend that will continue – especially for “knowledge workers.” The USA rested on the post WW II economic domination for nearly 50 years. The policies also helped this continue: investing in science and engineering, favoring entrepreneurship… But other countries have realized the value of these things (and the USA is slipping – not investing nearly as much in science and engineering and favoring large corporations that give politicians large amounts of cash over innovation – see things like the incredibly outdated “intellectual property” system, SOPA, favoring huge financial institutions…
The combination of long term policy weakness, the inevitable decline in the USA to world ratio of economic wealth, and the financial crisis caused by the policy weaknesses have seemingly greatly accelerated the trend. The next 2 or 3 years will determine if that is a permanent acceleration or if we go back to a slower pace – but on the same path. My guess is that we will stay on this path but the pace will not follow the level surveys might indicate (showing interest in such a big change is far different from actually moving).
There don’t seem to be any decent estimates of Americans living abroad. The US State Department claims releasing their estimates would be a national security risk? And the Census bureau says it would cost too much to try. Wild guesses seem to be between 4 and 6 million.
Related: I want out (subreddit) – Why Investing is Safer Overseas – USA Heath Care System Needs Reform – Copywrong

Manuel De Jesus, miller and farmer in El Salvador, will use his loan to buy parts for this milling euipment.
There is a great deal focus recently on the “99%” (via occupy wall street and the like). The truth is these are mainly about the 5% or 10% (those rich, but not quite as rich as the richest 1% – and much further from the richest than they were a few decades ago). As I have written before, most of those in the USA (also Europe, Japan…) are rich (though this is changing, a greater percentage of the USA is not rich, looking globally, than maybe any point since the 1930s).
We get confused because many near us are even richer and think that means the rest of us are very poor. But those in the USA are often in the 5% or 10% – not the 30% or 60% or 90% they seem to think they are. $50,000 in annual income puts you in the top 1% globally. $25,000 puts you in the top 10%.
I agree with the desire to reduce the political and market corruption, as I have written for years.
For the 99% (or the 90% anyway), I really think the best things are government policies that reduce corruption and increase market forces. Letting actually capitalism work instead of political and corporate cronyism failing to let markets work as they should. Also giving education and the chance to build a better life for yourself are important. Thankfully many countries have been doing very well on this front: Singapore, Korea, Brazil, Ghana, China… That doesn’t mean there are not huge issues to still address for most of the 90%, there are.
Microfinance in general, and Kiva in particular, are one great way to help. Again it isn’t perfect. And those getting the loans are not given an easy life. They are given a chance to try and build there business to improve there economic condition. This isn’t a certain success. And I do worry that taking on too high an interest rate, or loan amount, can leave people worse off than before. But when looking at the system of microfinance I really like the opportunity it gives people, who haven’t been given many.
Those getting loans have to make smart personal finance and business decisions. If they do well they can greatly improve their financial situation. I made several more loans today, using money repaid by previous borrowers. I try to find loans where I am able to help fund a investment that will improve capacity (but that isn’t always possible) – a new machine that makes them more efficient for example. I also try to avoid loans where the interest rate is over 30% (which might seem very high, but rates below 20% are very rare given the economics of these loans – they are very costly to service). What Kiva does is provide the funds people like me lend as interest free loans to the partner banks. The idea is that this allows partner banks to provide more capital for loans (obviously) and at a lower rate because the bank isn’t having to pay interest on the funds.
My loans today went to: Mali, Honduras, Senegal, Ecuador, Togo, Philippines and in the photo above El Salvador. The Curious Cat Kivans group has now lent $12,925 in 320 loans. We now have 11 members, join up and help give people an opportunity to improve their economic condition.
Related: More Kiva Entrepreneur Loans: Kenya, Honduras, Armenia… – Using Capitalism in Mali to Create Better Lives – Funding Entrepreneurs in Nicaragua, Ghana, Viet Nam, Togo and Tanzania
The chart shows the oil production over the last decade by the top oil producing countries. Production totals include crude oil, shale oil, oil sands and NGLs (the liquid content of natural gas where this is recovered separately). Excludes liquid fuels from other sources such as biomass and coal derivatives.
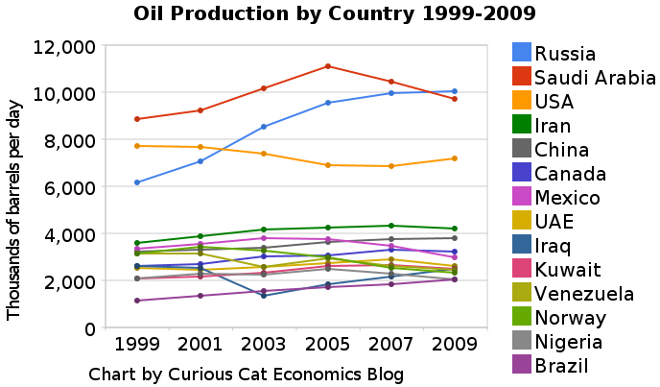 The chart shows the leading oil producing countries from 1999-2009. The chart created by Curious Cat Investing and Economics Blog may be used with attribution.
The chart shows the leading oil producing countries from 1999-2009. The chart created by Curious Cat Investing and Economics Blog may be used with attribution.___________________
The chart show 3 clear leaders in production Russia, Saudi Arabia and the USA (with the USA firmly in 3rd place). Those 3 were responsible for approximately a third of the total oil production in 2009. Russia greatly increased production. During the last decade world production increased from 72 million barrels a day to 80 million barrels a day. Russia accounted for 51% of the increase, close to 4 million barrels a day.
The next 11 countries are pretty closely grouped, with slightly increasing production over the period as a group. Brazil, the last country with over 2 million barrels of production a day in 2009, has the largest percentage increase in the period, producing 79% more in 2009 than they did in 1999. Russia increase production 62% over the period. The other countries ranged from a 23% increase (Canada) to a 25% decrease (Norway). The USA increased production 7% and China increased production 18%. World production increased 11%.
Last year I posted a chart showing oil consumption by the top oil consuming countries over the last 2 decades; showing all countries using over 2 million barrels of oil a day. The USA consumed 18.7 million barrels a day in 2009. Only China was also over 5 million barrels, using 8.2 million in 2009. Japan was next at 4.4 million.
Read more
Countries that can still be travelled on the cheap
If you’re keen to surf or lie on the beach you’re all set to have an adventure for peanuts. As long as you steer clear of tourist-trap resorts, you’ll struggle to spend more than $23.50 a day. Nourish your inner cheapskate and buy souvenirs away from the tourist areas; head to the central market in Denpasar or Ubud’s Pasar Sukowati.
…
Eastern Europe used to be dirt cheap back in the good old days of the Cold War. Now that peace has broken out, costs are on the up. Poland, though, is still at the inexpensive end: a daily budget of $29 will easily get you around the country.
Poland is a nation that’s been run over so many times by invading forces that it’s become bulletproof. Now this EU member is on the rise, so get in quick before the prices go up for good. Rural towns are picturesque and cheap to visit; tiny towns like Krasnystaw in the Lubelskie region are a miser’s wonderland.
…
If you’re looking for a scuba-diving destination where you can put your entire budget into going under, Honduras is the place to be. With sleeping budgets as low as $12 a night and meals available for even less you can really stretch out the funds.
Sitting pretty next door to the Caribbean Sea, you’ll have plenty of time to count your pennies as you sun yourself on the golden beaches. The developers haven’t invaded quite yet, but you’d better get in quick, before the good old days slip into the past.
After snorkelling and kayaking around Roatan’s West Beach, splurge on a visit to the Unesco-listed Archaeological Park of Copan; entry is $18.
Related: Great Time for a Vacation – Travel guide books – Traveling To Avoid USA Health Care Costs – Travel Photo blog
In previous posts I have shown data for global manufacturing output by country. One of the things those posts have showed is that manufacturing output in China is growing tremendously, but it is also growing in the United States. The chart below shows manufacturing production by country as a percent of GDP. China dominates again, with over 30% of the GDP from manufacturing.
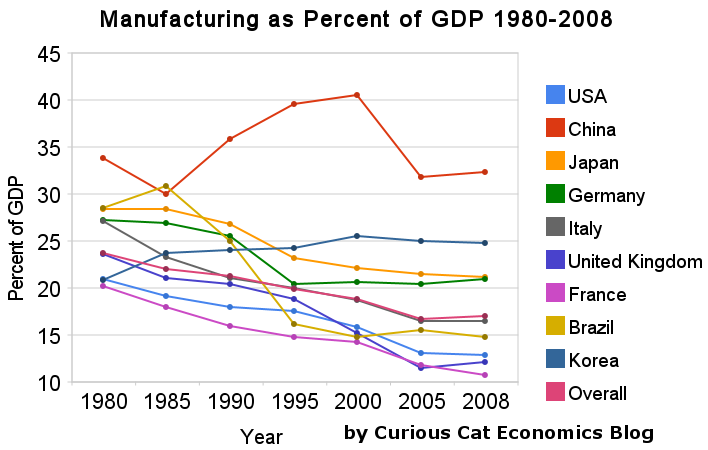
Chart showing manufacturing output, as percent of GDP, by country was created by the Curious Cat Economics Blog based on UN data* (based on current USA dollars). You may use the chart with attribution.
For the 14 biggest manufacturing countries in 2008, the overall manufacturing GDP percentage was 23.7% of GDP in 1980 and dropped to 17% in 2008. I left India (15% in 1980, 15% in 2008), Mexico (20%, 18%), Canada (17%, 13%), Spain (25%, 14%) and Russia (21% in 1990 [it was part of USSR in 1980], 15%) off the chart.
Over the last few decades Korea, and to some extent China, are the only countries that have increased the percent of GDP from manufacturing. China has not only grown manufacturing activity tremendously but also other areas of the economy (construction, mining, information technology). The countries with the largest manufacturing portions of their economies in 2008 were: China 32%, South Korea 25%, Japan and Germany at 21%. The next highest is Mexico at 18% which declined slightly over the last 15 years (with NAFTA in place). Globally, while manufacturing has grown, other areas of economic activity have been growing faster than manufacturing.
The manufacturing share of the USA economy dropped from 21% in 1980 to 18% in 1990, 16% in 2000 and 13% in 2008. Still as previous posts show the USA manufacturing output has grown substantially: over 300% since 1980, and 175% since 1990. The proportion of manufacturing output by the USA (for the top 14 manufacturers) has declined from 31% in 1980, 28% in 1990, 32% in 2000 to 24% in 2008. The proportion of USA manufacturing has declined from 33% in 1980, 29% in 1990, 36% in 2000 to 30% in 2008. While manufacturing output has grown in the USA it has done so more slowly than the economy overall.
Related: The Relative Economic Position of the USA is Likely to Decline – Manufacturing Data, Accuracy Questions – Top 12 Manufacturing Countries in 2007 – Manufacturing Employment Data: 1979 to 2007 – USA Manufacturing Output Continues to Increase (over the long term)
* I made edits to the 1980 Brazil manufacturing data and 1980, 1985 and 2008 China manufacturing data because the UN data only showed manufacturing data combined with mining and utility data. And I am using older UN data that had manufacturing separated from mining and utility figures for China in the other years.