When 2 year US government bonds yield more than the 10 year US government bonds a recession is likely to appear soon. This chart shows why this is seen as such a reliable predictor.
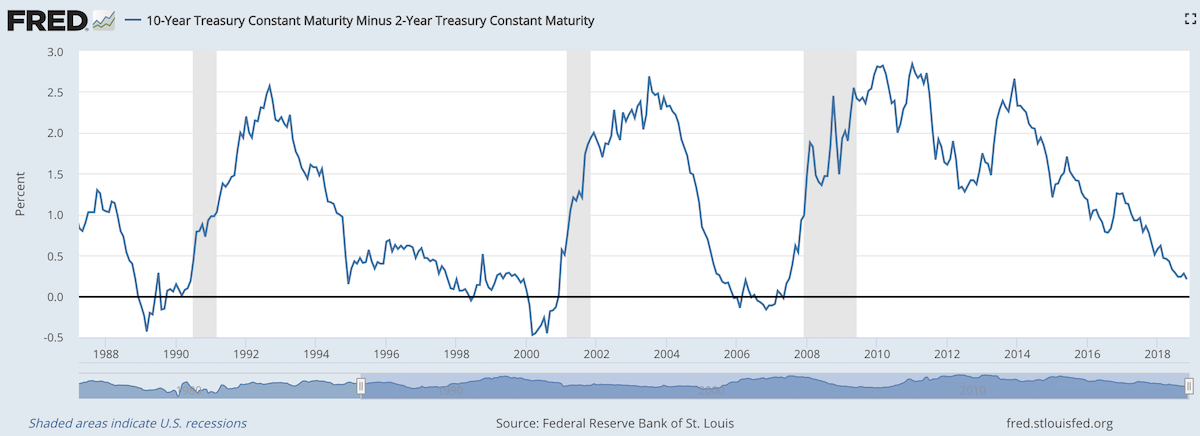
The chart shows the 10 year yield minus the 2 year yield. So when the value falls below 0 that means the 2 year yield is higher. Each time that happened, since 1988, a recession has followed (the grey shaded areas in the chart).
Do note that there were very small inversions in 1998 and 2006 that did not result in a recession in the near term. Also note that in every case the yield curve was no longer inverted by the time a recession actually started.
The reason why this phenomenon is getting so much attention recently is another thing that is apparent when looking at this chart, the 2 and 10 year yields are getting close to equal. But you can also see we are no closer than 1994 and the USA economy held off a recession for 7 more years.
Since 1970 the average length of time from the inversion of the 10 to 2 year yield curve has been 12 months (with a low of 6 months in 1973 and a high of 17 months, before the great recession of 2008).
In addition to a possibly impending yield curve inversion it has been a long time since the last recession which makes many investors and economists nervous that one may be due.
Related: 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates are not correlated with the Fed Funds Rate – Bond Yields Stay Very Low, Treasury Yields Drop Even More (2010) – Looking for Dividend Stocks in the Current Extremely Low Interest Rate Environment (2011) – Stock Market Capitalization by Country from 2000 to 2016
Another thing to note about yield curves at this time is that the US Federal Reserve continues to hold an enormous amount of long term government debt (trillions of dollars) which it has never done before the credit crisis of 2008. This reduces the long term yield since if they sold those assets that would add a huge amount of supply. How this impacts the predictive value of this measure will have to be seen. Also, one way for the Fed to delay the inversion would be to sell some of those bonds and drive up long term rates.
Abuse of the credit system by 3rd party collection agencies (and credit reporting agencies) in the USA has been a long term problem.
An attempt to partially address some of the abuses was a change in the required reporting practices that impacted collections accounts specifically, known as the National Consumer Assistance Plan (NCAP), which rolled into effect during the second half of 2017. The plan has many components, including: (1) a requirement for more frequent, detailed, and accurate reporting of collections accounts, including reflecting when those accounts have been paid; (2) a prohibition against reporting debts that did not arise from an agreement to pay, or from, medical collections less than 180 days old; (3) the removal of collections accounts that did not arise from a contract or agreement to pay; and (4) permission to report any account only when there is sufficient information to link the account with an individual’s credit files (requiring a name, address, and some other personally identifying information such as a Social Security number or date of birth).
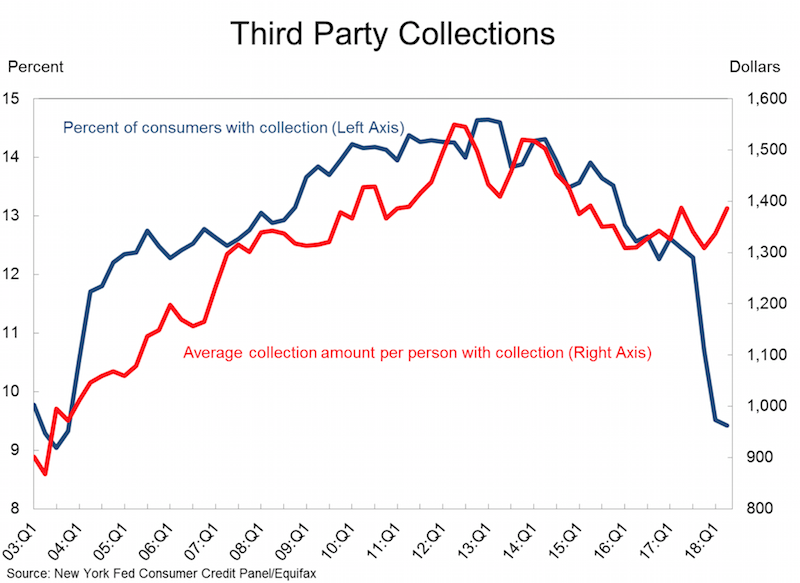
All in all, the changes in credit reporting prompted by the National Consumer Assistance Plan have resulted in an $11 billion reduction in the collections accounts balances being reported on credit reports. A total of 8 million people had collections accounts completely removed from their credit report. However, collections accounts do indeed align with other negative events and the cleanup of collections accounts had the largest impact on the borrowers with the lowest scores.
These borrowers will certainly benefit in the long run from the cleanup of their credit reports, since higher scores are associated with better access to credit, to the job market, and even to the rental housing market. But the immediate impact of the removal of collections will be muted for most of those affected (other items are also impacting their current credit score).
In the longer-term there may be a rebound in collections account reporting because creditors will likely begin collecting the newly required personally identifying information as they adjust to this reporting change.
This was a small good step in protecting consumers from the bad behavior of credit reporting companies and their customers. But much more must be done to protect us from having our financial lives negatively impacted by bad practices of the credit reporting companies.
Related: Cleaning Up Collections – Avoiding the Vicious Cycle of Credit Problems – Truly Free Credit Report – USA Household Debt Jumps to Record $13.15 Trillion
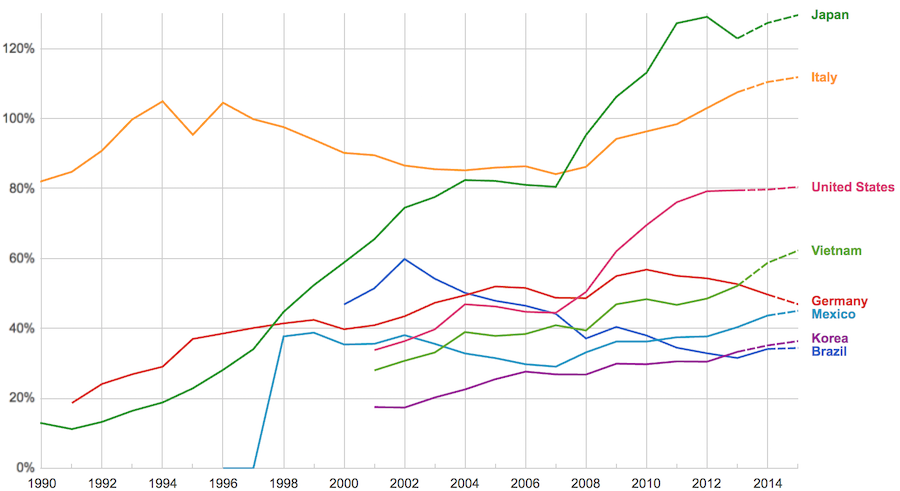
The data, from IMF, does not include China or India.
The chart shows data for net debt (gross debt reduced by certain assets: gold, currency deposits, debt securities etc.).
Viewing our post on the data in 2014 we can see that the USA improved on the expectations, managing to hold net debt to 80% instead of increasing to 88% as expected. Nearly every country managed to take on less debt than predicted (Vietnam took on more, but is very low so this is not a problem).
Taking on debt to invest in valuable resources (building roads, mass transit, internet infrastructure, education, environmental regulation and enforcement, health care, renewable energy…) that will boost long term economic performance can be very useful. The tricky part is knowing the debt levels doesn’t tell you whether the debt was taken on for investment or just to let current taxpayers send the bills for their consumption to their grandchildren.
Also government debt can become a huge burden on the economy (especially if the debt is owed outside the country). The general consensus today seems to be that 100% net debt level is the maximum safe amount and increasing beyond that gets riskier and riskier.
Solar energy capacity has been growing amazingly quickly the last few years. Part of the reason for this is the starting point was so low, making it easy to have large gains.
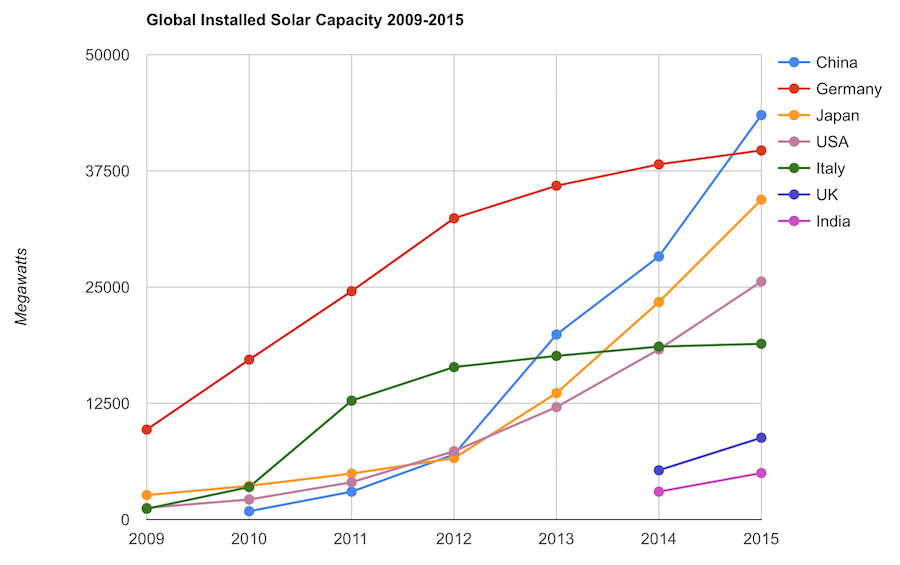
Chart by Curious Cat Economics Blog using data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the US Department of Energy. Chart may be used with attribution as specified here.
The 2014 and 2015 data on this chart is from IAE report for total installed photovoltaic (PV) solar capacity. See previous post on chart of Solar Energy Capacity by Country from 2009 to 2013. Different data sources for different year (and/or countries in the same year) is not ideal but for the purposes of this data in this post is sufficient.
Installed PV capacity is even more questionable that much other economic data. Economic data are always approximations of reality but with PV you have additional questions. The same plant located outside London or Rome have different capability to produce (and there are many factors that contribute not just the most obvious such as how much sun shines in a particular geography). Installed PV data is based on the capability of the equipment regardless of the solar potential of the location.
So even with the same investment it is likely Italy gets more production than Germany. The IAE report attempted to determine what was the likely ability of the solar PV capacity to produce for each country as a percentage of total electricity needs. They estimate Italy has the largest percentage of electricity needs capable of being produced by installed PV systems at 8%, with Greece at 7.4% and Germany at 7.1%. Japan is ranked 5th at just under 4%, UK is 12th at 2.5%, China is 22nd at 1%, India 24th and the USA 25th at close to .9%. They estimate the total global percentage at 1.3%.
These figures also show the huge power needs of China and the USA. Even with huge investments in Solar they us so much electricity that it is slow to make large gains in the percentage of total power generated by solar.
In the USA in 2013 solar energy capacity was under 1% USA total electrical capacity. In 2013 hydropower was 6.8%, wind was 5.3% and biomass was 1.3%. The increase in solar capacity should continue to grow rapidly and is making significant contributions to the macroeconomic energy picture (even if it doesn’t appear dramatic).
Related: Chart of Global Wind Energy Capacity by Country from 2005 to 2015 – Leasing or Purchasing a Solar Energy System For Your House – Nuclear Power Generation by Country from 1985-2010 – Manufacturing Output by Country 1999-2011: China, USA, Japan, Germany
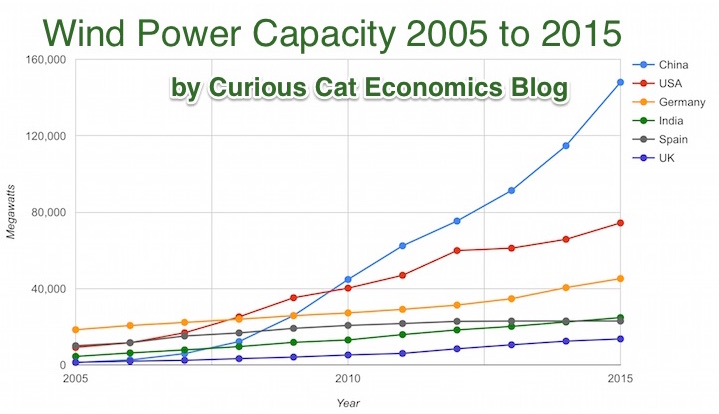
Chart by Curious Cat Economics Blog using data from the Wind Energy Association, data for 2014 and 2015. Chart may be used with attribution as specified here.
After a slowing of additional capacity added in 2013, both 2014 and 2015 saw a bit of a rebound in additions to global wind energy capacity. In 2013 capacity increased only 13% while in both 2014 and 2015 it increased 17%. Still 17% is less than any year in the last 10, except 2013.
At the end of 2013 China had 29% of global capacity (after being responsible for adding 62% of all the capacity added in 2013). In 2005 China had 2% of global wind energy capacity.
At the end of 2015 China accounted for 34% of global capacity, the only country in the top 8 increasing their share of global capacity. The USA now has 17% of capacity. Germany has 10%.
Europe moved first in adding large scale wind energy capacity but has added capacity very slowly in the last 5 years. Germany had 31% of global capacity in 2005. Spain had 17% in 2005 and now has just 5% (during that time Spain has more than doubled their wind energy capacity).
The 6 countries shown on the chart account for 76% of total wind energy capacity globally. From 2005 to 2015 those 8 countries have accounted for between 74 and 77% of total capacity – which is amazingly consistent.
Wind power now accounts for approximately 4 to 5% of total electricity used.
Related: Chart of Global Wind Energy Capacity by Country 2005 to 2013 – Solar Energy Capacity by Country (2005 to 2013) – Nuclear Power Generation by Country from 1985-2010 – Chart of Largest Petroleum Consuming Countries from 1980 to 2010
This chart shows that the percentage of millionaire families by highest education level is dramatically different by education level. The data is looking at USA family income for household headed by a person over 40. For high school dropouts, fewer than 1% are millionaires; all families it is about 5%; high school graduates about 6%; 4 year college degree about 22% and graduate or professional degree about 38%.

Interesting chart based on Federal Reserve data (via the Wall Street Journal)
While the costs of higher education in the USA have become crazy the evidence still suggests education is highly correlated to income. Numerous studies still show that the investment in education pays a high return. Of course, simple correlation isn’t sufficient to make that judgement but in other studies they have attempted to use more accurate measures of the value of education to life long earnings.
Related: The Time to Payback the Investment in a College Education in the USA Today is Nearly as Low as Ever, Surprisingly – Looking at the Value of Different College Degrees – Engineering Graduates Earned a Return on Their Investment In Education of 21%
The blog post with the chart, Why Wealth Inequality Is Way More Complicated Than Just Rich and Poor has other very interesting data. Go read the full post.
Average isn’t a very good measure for economic wealth data, is is skewed horribly by the extremely wealthy, median isn’t a perfect measure but it is much better. The post includes a chart of average wealth by age which is interesting though I think the $ amounts are largely worthless (due to average being so pointless). The interesting point is there is a pretty straight line climb to a maximum at 62 and then a decline that is about as rapid as the climb in wealth.
That decline is slow for a bit, dropping, but slowly until about 70 when it drops fairly quickly. It isn’t an amazing result but still interesting. It would be nice to see this with median levels and then averaged over a 20 year period. The chart they show tells the results for some point in time (it isn’t indicated) but doesn’t give you an idea if this is a consistent result over time or something special about the measurement at the time.
They also do have a chart showing absolute wealth data as median and average to show how distorted an average is. For example, median wealth for whites 55-64 and above 65 is about $280,000 and the average for both is about $1,000,000.
Related: Highest Paying Fields at Mid Career in USA: Engineering, Science and Math – Wealthiest 1% Continue Dramatic Gains Compared to Everyone Else – Correlation is Not Causation: “Fat is Catching” Theory Exposed
Solar energy capacity has been growing amazingly quickly the last few years. Part of the reason for this is the starting point was so low, making it easy to have large gains.
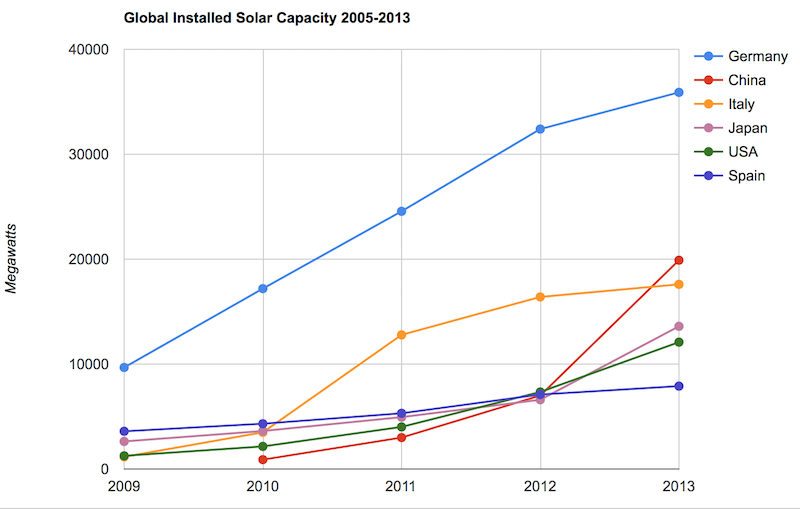
Chart by Curious Cat Economics Blog using data from the US Department of Energy. Chart may be used with attribution as specified here.
As with so many macro economic measures China has made enormous investments in solar energy the last few years. China’s increase in 2013 was larger than the USA’s total capacity at the end of 2013. Since solar energy use on a large scale is still small investments are quickly ramping up. Europe was a few years ahead of others putting countries like Germany, Spain and Italy far in the lead. China, the USA and Japan have been investing huge amounts the last few years and will likely leave those other than Germany (which already has such a large capacity) far behind very shortly.
In the USA, even after growing 60% in 2008, 53% in 2009, 71% in 2010, 86% in 2011, 83% in 2012 and 64% in 2013 solar energy capacity only totaled 1% of USA total electrical capacity. In 2013 hydropower was 6.8%, wind was 5.3% and biomass was 1.3%. The increase in solar capacity should continue to grow rapidly and is starting to make significant contributions to the macroeconomic energy picture.
When you look at total electricity generation solar only represented .5% (compared to 6.6% for hydropower 4.1% for wind and 1.5% for biomass).
USA data based on only solar capacity that is connected to the grid (and my guess would be that is the measure used in other countries too). Data is largely from that Department of energy report, with historical data for other countries pulled from previous editions.
The US Energy Information Agency (USEIA) expects the USA to add (net) 9,841 MW of wind capacity; 4,318 MW of natural gas capacity and 2,235 MW of solar in 2015. In 2015 they also predict a net decline of 12,922 MW of coal capacity. They also share that nuclear plants and natural gas combined-cycle generators having utilization factors 3 to 5 times those of wind and solar generators, which means capacity measures are significantly different from actually produced electricity measures.
The USEIA has predicted “global solar PV capacity seen rising from 98 GW in 2012 to 308 GW in 2018.” They predicted in 2018 China would have the most solar PV capacity followed by Germany, Japan and the USA.
The Solar Energy Industries Association (USA) states that 5,000 MW of solar capacity was added in the USA in 2013 and 7,000 MW in 2014. They forecast 8,000 MW to be added in 2015 and 12,000 MW in 2016.
Related: Solar Direct Investing Bonds – Chart of Global Wind Energy Capacity by Country 2005 to 2013 – Leasing or Purchasing a Solar Energy System For Your House – Nuclear Power Generation by Country from 1985-2010 – Google Invests $168 million in Largest Solar Tower Power Project (2011) – Molten Salt Solar Reactor Approved by California (2010) – 15 Photovoltaics Solar Power Innovations (2008)
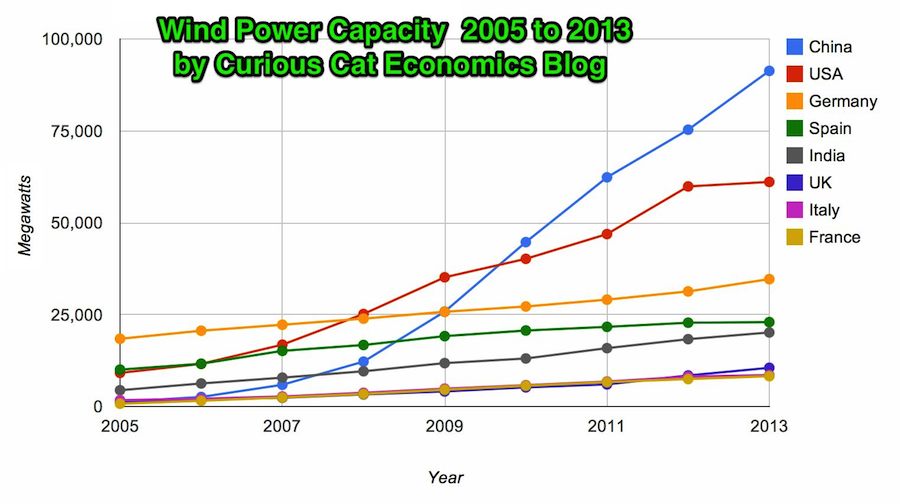
Chart by Curious Cat Economics Blog using data from the Wind Energy Association. Chart may be used with attribution as specified here.
In 2013 the addition to wind power capacity slowed a great deal in most countries. Globally capacity was increased just 13% (the increases in order since 2006: 26%, 27%, 29%, 32%, 25%, 19% and again 19% in 2012). China alone was responsible for adding 16,000 megawatts of the 25,838 total added globally in 2013.
At the end of 2013 China had 29% of global capacity (after being responsible for adding 62% of all the capacity added in 2013). In 2005 China had 2% of global wind energy capacity.
The 8 countries shown on the chart account for 81% of total wind energy capacity globally. From 2005 to 2013 those 8 countries have accounted for between 79 and 82% of total capacity – which is amazingly consistent.
Wind power now accounts for approximately 4% of total electricity used.
Related: Chart of Global Wind Energy Capacity by Country 2005 to 2012 – In 2010 Global Wind Energy Capacity Exceeded 2.5% of Global Electricity Needs – Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment – Nuclear Power Generation by Country from 1985-2010
Looking at stock market capitalization by country gives some insight into how countries, and stocks, are doing. Looking at the total market capitalization by country doesn’t equate to the stock holdings by individuals in a country or the value of companies doing work in a specific country. Some countries (UK and Hong Kong, for example) have more capitalization based there than would be indicated by the size of their economy.
It is important to keep in mind the data is in current USA dollars, so big swings in exchange rates can have a big impact (and can cause swings to be exacerbated when they move in tandem with stock market movements – if for example the market declines by 15% and the currency declines by 10% against the US dollar those factors combine to move the result down).

The chart shows the top four countries based on stock market capitalization, with data from 200 to 2012. The chart created by Curious Cat Investing and Economics Blog may be used with attribution. Data from the World Bank.
As with so much recent economic data China’s performance here is remarkable. China grew from 1.8% of world capitalization in 2000 to 6.9% in 2012. And Hong Kong’s data is reported separately, as it normally is with global data sets. Adding Hong Kong to China’s totals would give 3.7% in 2000 with growth to to 8.9% in 2012 (Hong Kong stayed very stable – 1.9% in 2000, 2% in 2012). China alone (without HK) is very slightly ahead of Japan.
The first chart shows the largest 4 market capitalizations (2012: USA $18.6 trillion, China and Japan at $3.7 trillion and UK at $3 trillion). Obviously the dominance of the USA in this metric is quite impressive the next 7 countries added together don’t quite reach the USA’s stock market capitalization. I also including the data showing the global stock market capitalization divided by 3 (I just divide it by three to have the chart be more usable – it lets us see the overall global fluctuations but doesn’t cram all the other data in the lower third of the chart).
Canada is the 5th country by market capitalization (shown on the next chart) with $2 trillion. From 2000 to 2012 China’s market capitalization increased by $3.1 trillion. The USA increased by $3.6 trillion from a much larger starting point. China increased by 536% while the USA was up 23.5%. The world stock market capitalization increased 65% from 2000 to 2012.
Related: Stock Market Capitalization by Country from 1990 to 2010 – Government Debt as Percent of GDP 1998-2010 – Manufacturing Output by Country 1999-2011: China, USA, Japan, Germany
Global wind power capacity has increased 391% from 2005 to 2012. The capacity has grown to over 3% of global electricity needs.
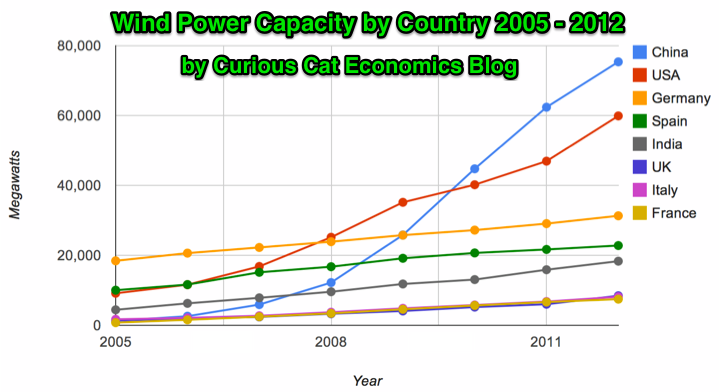
Chart by Curious Cat Economics Blog using data from the Wind Energy Association. Chart may be used with attribution as specified here.
The 8 countries shown on the chart account for 82% of total wind energy capacity globally. From 2005 to 2012 those 8 countries have accounted for between 79 and 82% of total capacity – which is amazingly consistent.
Japan and Brazil are 13th and 15th in wind energy capacity in 2012 (both with just over one third of France’s capacity). Japan has increased capacity only 97% from 2005 to 2012 and just 13% from 2010 to 2012. Globally wind energy capacity increased 41% from 2010 to 2012. The leading 8 countries increased by 43% collectively lead by China increasing by 68% and the USA up by 49%. Germany added only 15% from 2010 through 2012 and Spain just 10%.
Brazil has been adding capacity quickly – up 170% from 2010 through 2012, by far the largest increase for a county with significant wind energy capacity. Mexico, 24th in 2012, is another country I would expect to grow above the global rate in the next 10 years (I also expect Brazil, India and Japan to do so).
In 2005 China accounted for 2% of wind energy capacity globally they accounted for 30% in 2012. The USA went from 15% to 24%, Germany from 31% to 12%, Spain from 17% to 9% and India from 8% to 7%.
Related: Global Wind Energy Capacity Exceeds 2.5% of Global Electricity Needs (2011) – Nuclear Power Generation by Country from 1985-2010 – Chart of Wind Power Generation Capacity Globally 2005 to 2012 (through June)