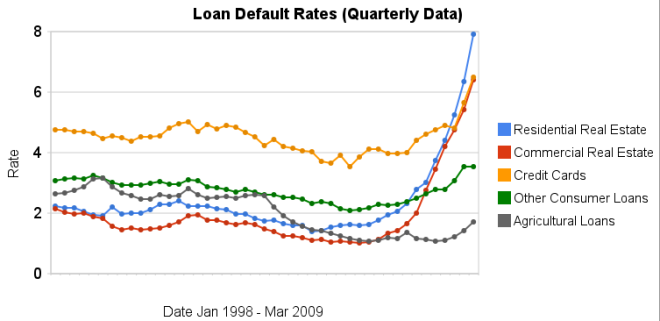
 Chart showing loan default rates for real estate, consumer and agricultural loans for 1998 to 2009 by the Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.
Chart showing loan default rates for real estate, consumer and agricultural loans for 1998 to 2009 by the Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.As you can see real estate default rates exploded in 2008. In the 4th quarter of 2007 residential default rates were 3.02% by the 4th quarter of 2008 they were 6.34% and in the 1st quarter of this year they were 7.91% (471 basis points above the 4th quarter of 2007). Commercial real estate default rates were at 2.74 in the 4th quarter of 2007, 5.43% in the fourth quarter of 2008 and 6.5% in the 1st quarter of 2009 (a 366 basis point increase).
Credit card default rates were much higher for the last 10 years (the 4-5% range while real estate hovered above or below 2%). In the last 2 quarters it has increased sharply. From 4.8% in the 3rd quarter 2008 to 5.66% in the 4th and 6.5% in the 1st quarter of 2009. The default rate on other consumer loans are up but nowhere near the amounts of real estate or credit cards.
Agricultural loan default rates are actually about as low now as they have every been 1.71%. That is up a bit from the 1.06% low the default rate hit in the 1st quarter of 2009 but actually lower than it was for half of the last decade (the last 5 years it has been lower but prior to that it was higher – in fact with higher default rates than either real estate loan category).
Related: Mortgage Rates: 6 Month and 5 Year Charts – Jumbo Loan Defaults Rise at Fast Pace – Continued Large Spreads Between Corporate and Government Bond Yields – Nearly 10% of Mortgages Delinquent or in Foreclosure
The Society for Actuaries has published a good resource: Managing post-retirement risks.
…
Many investors try to own some assets whose value may grow in times of inflation. However, this sometimes will trade inflation risk for investment risk.
• Common stocks have outperformed inflation in the long run, but are
poor short-term hedges. The historically higher returns from stocks
are not guaranteed and may vary greatly during retirement years.
…
Retirement planning should not rely heavily on income from a bridge job. Many retirees welcome the chance to change careers and move into an area with less pay but more job satisfaction, or with fewer demands on their time and energy.
Terminating employment before age 65 may make it difficult to find a source of affordable health insurance before Medicare is available.
…
Insurance for long-term care covers disabilities so severe that assistance is needed with daily activities such as bathing, dressing and eating. Some policies require a nursing home stay; others do not. The cost of long-term care insurance is much less if purchased at younger ages, well before anticipated need.
The full document is well worth reading.
Related: Many Retirees Face Prospect of Outliving Savings – How to Protect Your Financial Health – Financial Planning Made Easy – personal finance tips
Surging U.S. Savings Rate Reduces Dependence on China
…
Nouriel Roubini, an economics professor at New York University and chairman of RGE Monitor, forecasts that the savings rate will ultimately reach 10 percent to 11 percent. What’s critical, he said in a Bloomberg Television interview on June 24, is how quickly it increases.
A rapid rise in the next year because of a collapse in consumption would push the economy, already in its deepest contraction in 50 years, further into recession, he said. If it occurs over a few years, the economy may grow.
…
From 1960 until 1990, households socked away an average of about 9 percent of their after-tax income, government figures show. Americans got out of the habit in the 1990s as they saw their wealth build up in other ways, first through surging stock prices and then soaring home values, Gramley said.
That process has now gone into reverse. U.S. household wealth fell by $1.3 trillion in the first quarter of this year, with net worth for households and nonprofit groups reaching the lowest level since 2004, according to a Fed report. Wealth plunged by a record $4.9 trillion in the last quarter of 2008.
Edmund Phelps, winner of the Nobel Prize in economics in 2006 and a professor at Columbia University in New York, said it may take as long as 15 years for households to rebuild what they lost in the recession.
As I have been saying the living beyond our means must stop. Those that think health of an economy is only the GDP forget that if the GDP is high due to spending tomorrows earnings today that is not healthy. Roubini correctly indicates the speed at which savings increases could easily determine the time we crawl out of the recession. I hope the savings rate does increase to over 10 percent.
If we do that over 3 years that would be wonderful. But it is more important we save more. If that means a longer recession to pay off the excessive spending over the last few decades so be it. And it is going to take a lot longer than a few years to pay off those debts. It is just how quickly we really start to make a dent in paying them off that is in question now (or whether we continue to live beyond our means, which I think it still very possible – and unhealthy).
Related: Will Americans Actually Save and Worsen the Recession? – Can I Afford That? – $2,540,000,000,000 in USA Consumer Debt (April 2008) – Paying for Over-spending
The economic clout of the USA has been huge since the end of World War II. The relative position has been decreasing recently with the rise of not only Europe and Japan but Korea, China, India, Brazil and many more. This means the risks to the USA of failing to deal with perennial problems (the most costly but not most effective health care system, spending beyond our means, weak diplomacy, excessive legal costs, poor management practices…) is higher today than it has been.
Fareed Zakaria’s Post American World is a good explanation of some of the current global economic forces in play. He comes to the same conclusion I do that the USA is still in the strongest position today. But the world is changing and the relative position of the United States is declining. The new world requires working with others and the USA needs to adjust to this reality. Too many think the USA can continue to act as though the rest of the world must comply with the wishes of the USA.
…
The litigation system is now routinely referred to as a huge cost of doing business, but no one dares propose any reform of it. Our mortgage deduction for housing costs a staggering $80 billion a year, and we are told it is crucial to support home ownership. Except that Margaret Thatcher eliminated it in Britain, and yet that country has the same rate of home ownership as the United States. We rarely look around and notice other options and alternatives, convinced that “we’re number one.”
…
America has become a nation consumed by anxiety, worried about terrorist and rouge nations, Muslims and Mexicans, foreign companies and free trade, immigrants and international organizations. The strongest nation in the history of the world now sees itself as besieged by forces beyond its control.
The book focuses quite a bit on the USA, China and India and provides good overviews of the economic strength and weaknesses of those countries. The USA is in a leadership position but the future requires an understanding that others deserve to be treated as partners not allies to be dictated to. If not they will just partially disengage with the USA and create stronger relationships with others. That would not be in the interests of the USA.
Related: Best Research University Rankings (2008) – Dr. Deming’s 7 Deadly Diseases of Western Management – Science leadership and economic growth – Easiest Countries for Doing Business (2008) – Top 12 Manufacturing Countries in 2007 – Why America Needs an Economic Strategy – Country H-index Rank for Science Publications – USA Spent $2.2 Trillion, 16.2% of GDP, on Health Care in 2007
Starting next Monday GM and Citigroup will no longer be in the list of 30 companies making up the Dow Jones Industrial Average. I posted in 2005 that GM should be dropped from the DJIA. GE has lasted in the Dow for more than 100 years. 12 of the 30 stocks have been added since 1997. Cisco and Travelers are the companies that are joining the Dow on June 8th.
The 30 stocks of the Dow Jones Industrial Average, as of June 8th, 2009:
| Stock | Market Capitalization | Year Added |
|---|---|---|
| Exxon (XOM) | $347 Billion | 1928 |
| Walmart (WMT) | 195 | 1997 |
| Microsoft | 189 | 1999 |
| Proctor & Gamble (PG) | 155 | 1932 |
| Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) | 153 | 1997 |
| GE | 147 | 1896 |
| AT&T (T) | 145 | 1999 |
| IBM | 143 | 1979 |
| JPMorgan Chase (JPM) | 141 | 1991 |
| Chevron (CVX) | 138 | 2008 |
| Coca-Cola (KO) | 113 | 1987 |
| Cisco (CSCO) | 112 | 2009 |
| Pfizer (PFE) | 100 | 2004 |
| Intel (INTC) | 91 | 1999 |
Debt Negotiators May Give Little Relief to Consumers
Credit-card delinquencies are at record highs, according to Fitch Ratings, and the U.S. unemployment rate of 8.9 percent is the highest since 1983. As more consumers fall behind on bills, settlement companies often end up adding to the debt burden rather than offering a cost-saving solution, said Gail Cunningham, a spokeswoman for the National Foundation for Credit Counseling in Silver Spring, Maryland.
…
New York Attorney General Andrew Cuomo has begun a national investigation of settlement companies, and has sued two for fraud and false advertising. Illinois Attorney General Lisa Madigan has also filed two lawsuits against debt-settlement companies, alleging they “engage in deceptive marketing practices” and “do little or nothing to improve consumers’ financial standings.” Texas Attorney General Greg Abbott sued a debt settlement company in March, saying it engaged in “deceptive and misleading acts,” according to court documents.
It is much better to avoid this problem by taking wise personal finance actions – don’t take on personal debt for minor purchases (for a mortgage then debt is fine, probably fine for a car – though avoid debt if you can). The “secret” is not very secret. Just don’t buy what you can’t pay for. It is very simple, many people just don’t want to follow that simple strategy. Also save money in an emergency fund, so when some emergency comes along you don’t go into debt. You just use your emergency fund.
Once you are stuck in a bad situation with more debt than you can afford to pay back you have bad choices. Obviously many try to take advantage of you. Frankly they realize many that are stuck in bad financial position make bad financial decisions. Therefor it is a good place for those trying to rip people off to find people to take advantage of. The best way to deal with this is not to try and find the best debt negotiators it is to manage you finances well and not get in trouble.
Related: Personal Saving and Personal Debt in the USA – How to Use a Credit Card Successfully – Credit Card Companies Willing to Deal Over Debt – Where to Keep Your Emergency Funds? – Americans are Drowning in Debt
Growing Crude Storage in China
…
Bernstein estimates that the amount of crude entering the SPR ports in China—the world’s second biggest oil consumer after the U.S.–has increased by around 400,000 barrels a day since November, based on its assessment using the satellite imaging services of Google, the search engine company.
…
There’s likely more to come. Bernstein says satellite images show a marked increase in oil-storage construction over the past few years and estimates that China’s number of days of forward demand–a gauge of oil storage–amount to just 28 days of imports and 14 days of total demand.
China is targeting storage capacity that will hold demand cover of around 90 days. (The U.S. currently has storage for about 62 days of oil imports.) In other words, there’s a lot more oil still to be packed away in China now and in the coming years as more facilities are built.
This is another smart move by China, in my opinion. With the huge amount of cash they are holding, I would rather hold more of it as crude than dollars. And stockpiling the crude also protects the domestic demand from supply shocks. I would also take other steps they are taking, like investing heavily in adding wind power capacity.
Related: I Wouldn’t Sell Oil at These Prices – Who Will Buy All the USA’s Debt? – Oil Consumption by Country – South Korea To Invest $22 Billion in Overseas Energy Projects
John Bogle was the founder of Vanguard Group and a well respected investment mind. He has written several good books including: The Little Book of Common Sense Investing, Common Sense on Mutual Funds and Bogle on Mutual Funds. This interview from 2006 discusses the state of the retirement system, before the credit crisis.
Frontline: How do they get away with that? Don’t they have to fund them?
John Bogle: No, they don’t, because a lot of it is based on assumptions. Our corporations are now assuming that future returns in their pension plan will be about 8.5 percent per year, and that’s not going to happen. The future returns in the bond market will be about 4.5 percent, and maybe if we’re lucky 7.5 percent on stocks. Call it a 6 percent return — before you deduct the cost of investing all that money, the turnover cost, the management fees. So maybe a 5 percent return is going to be possible, in my judgment, and they are estimating 8.5 percent.
Why? Because when they do it that way, corporation earnings become greatly overstated, and all the executives get nice, big bonuses. They are using pension plan assumptions as a way to manage corporate earnings and meet the expectations of Wall Street.
Frontline: So if a company overstates the value of its pension plan assets, it makes the company look better to Wall Street, so there’s an incentive to kind of exaggerate, if not cheat.
John Bogle: That is precisely correct. And let me clear on the cheating: It’s legal cheating; it’s not illegal cheating. In other words, you can change any reasonable set of numbers — and corporations have done this, have raised the pension assumption from 7 percent to 8.5 percent — and all of a sudden that corporation will report an earnings gain for the year rather than an earnings loss that they would otherwise have. Simple, legal.
The entire PBS series (from 2006) on 401(k)s (including interviews with Elizabeth Warren, David Wray and Alicia Munnell) is worth reading.
In February of 2009 he spoke to the House of Representatives committee exploring retirement security.
Read more
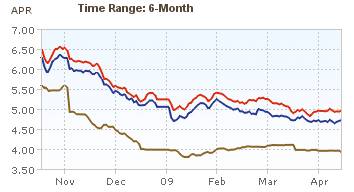 Showing mortgage rates over the last 6 months. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate.
Showing mortgage rates over the last 6 months. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate.
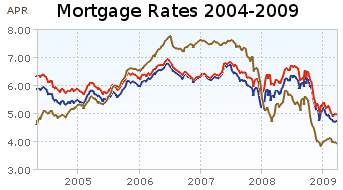 Showing mortgage rates over the last 5 years. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate. From Yahoo Finance, for conventional loans in Virginia.
Showing mortgage rates over the last 5 years. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate. From Yahoo Finance, for conventional loans in Virginia.
The 6 month chart shows that mortgage rates have been declining ever so slightly. Rates on a 1 year adjustable mortgage fell from 5.5 to 4% and have stayed near 4% for all of 2009. 30 and 15 year rates (15 year rates staying about 25 basis points cheaper) have declined from 6.5%, 6 months ago to about 5% at the start of the year and have moved around slightly since. This is while the yield 10 year government treasuries have been rising (normally 30 year fixed rate mortgages track moves in the 10 year government bond). The federal reserve has been buying bonds in order to push down the yield (and stimulate mortgage financing and other borrowing).
Mortgage rates certainly could fall further but the current rates are extremely attractive and I just locked in a mortgage refinance for myself. I am getting a 20 year fixed rate mortgage; I didn’t want to extend the mortgage period by getting another 30 year fixed rate mortgage. For me, the risk of increasing rates outweigh the benefits of picking up a bit lower rate given the current economic conditions. But I can certainly understand the decision to hold out a bit longer in the hopes of getting a better rate. If I had to guess I would say rates will be lower during the next 3 months, but I am not confident enough to hold off, and so I decided to move now.
Related: Mortgage Rates Falling on Fed Housing Focus – posts on mortgages – 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates and the Fed Funds Rate – Continued Large Spreads Between Corporate and Government Bond Yields – Lowest 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates in 37 Years –
Consumer borrowing falls in March at fastest pace in over 18 years, Americans saving more
In dollar terms, consumer borrowing plunged by $11.1 billion. That’s the largest dollar amount on records dating to 1943, and more than three times the $3.5 billion drop that economists expected. The borrowing category that includes credit cards dropped 6.8 percent in March after a 12.1 percent plunge in February. The category that includes auto loans fell 4.2 percent after rising by 1.2 percent in February.
The Commerce Department last week said that the personal savings rate edged up to 4.2 percent in March, marking the first time in a decade that the savings rate has been above 4 percent for three straight months.
Good. Consumer debt is far to large and should be paid down. This is a start but a small start, but a much larger reduction in outstanding consumer debt is needed before we have reached a healthy level of debt. The continued improvement in that debt level signifies a stronger economy. Far too many financial journalists instead of pointing out the benefits of such improvement note that this reduces current consumption (and thus, effectively, will lower current GDP – compared to what it would be if we continued to spend beyond our means). You cannot spend money your don’t have forever.
Having more stuff in your house (along with an increased outstanding credit card balance) does not make you economically more successful. And the same holds true for the economy. Having more stuff sitting in people’s house and an increasing debt load is not the sign of a stronger economy (even if it is a route to a higher current GDP). Increased saving and reducing debt will strengthen the economy and improve our economic success over the long term.
Related: Will Americans Actually Save and Worsen the Recession? – Proper credit card use – Personal Saving and Personal Debt in the USA – Americans are Drowning in Debt – Buying Stuff to Feel Powerful