Mortgages Falling to 4% Become Bernanke Housing Focus by Brian Louis and Kathleen M. Howley
…
Conventional mortgages averaged 4.61 percent in 1951, 4 percent when backed by the Veterans Administration, and 4.25 percent by the Federal Housing Administration, according to The Postwar Residential Mortgage Market, a 1961 book written by Saul Klaman and published by Princeton University Press. Rates during the 1930s were as high as 7 percent.
…
Mortgages were cheaper through most of the 1940s, ranging from about 4 percent to 5.7 percent, depending on whether the lender was a life insurer, a commercial bank or a savings and loan. In that era, most loans were for 14 years and less.
…
The central bank has purchased more than $300 billion of mortgage-backed securities in 2009 through the week ended April 8, helping to cut home-loan rates to 4.82 percent last week from 5.1 percent at the start of the year, according to Freddie Mac data.
…
The difference between 30-year mortgage rates and 10-year Treasury yields has narrowed to about 2.2 percent from 3.1 percent in December, which was the widest since 1986. The spread remains almost 0.7 percentage point above the average of the past decade, data compiled by Bloomberg show. Rates for 15-year mortgages are about 1.8 percent above 10-year Treasury yields, compared with an average 1.4 percent since 1999.
Excellent article with interesting historical information. I don’t believe mortgage rates will fall to 4% but differences of opinion about the future is one function of markets. Those that predict correctly can make a profit. I am thinking of refinancing a mortgage and I think I am getting close to pulling the trigger. If I was confident they would keep falling I would wait. It just seems to me the huge increase in federal debt and huge outstanding consumer debt along with very low USA saving will not keep interest rates so low. However, as I have mentioned previously, it is interesting that the Fed is directly targeting mortgage rates and possible they can push them lower. The 10 year bond yield has been increasing lately so the slight fall in mortgage rates over the last month are due to the reduced spread (that I can see decreasing – the biggest question for me is how much that spread can decrease).
Related: Fed to Start Buying Treasury Bonds Today – Federal Reserve to Buy $1.2T in Bonds, Mortgage-Backed Securities – Low Mortgage Rates Not Available to Everyone – what do mortgage terms mean?
Let big banks fail, bailout skeptics say
I must say this is the is how I feel, but I don’t have the time to research all the details – to know all the existing limitations for realistic solutions. But I can’t believe allowing huge, incredibly poorly run financial organizations to remain in place with the same bozos that have looted the treasuries of their companies and then taken huge handouts from the federal government, is good policy. It was a very bad idea to allow such anti-competitive large financial institutions to exist in the first place. Then the extremely bad behavior of thousands of people taking millions from those banks treasuries and imposing huge risks on the financial system certainly should result in government finally doing their job to prevent harm to the economic system.
This sounds like a much more sensible strategy to me. It is certainly much much better than increasing consolidation with moves like having huge financial firms buy other huge firms. Obviously I would not support the selling of pieces of the old broken institution to remaining large organizations. The anti-competitive market power must be sharply reduced.
Related: Treasury Now (1987) Favors Creation of Huge Banks – posts on the credit crisis – Leverage, Complex Deals and Mania – Canadian Banks Avoided Failures Common Elsewhere – There is No Invisible Hand
 photo of Cesar Augusto Santamaría Escoto in his welding workshop, Chinandega, Nicaragua.
photo of Cesar Augusto Santamaría Escoto in his welding workshop, Chinandega, Nicaragua.I made my 100th contribution to a micro-loan through Kiva last week. Participating with Kiva is a great antidote to reading about the unethical “leaders” taking huge sums to run their companies into the ground (or even just taking obscene sums to maintain their company). The opportunity to give real capitalists an chance at a better life is wonderful.
Kiva allows you to lend money to entrepreneur (in increments of $25). The most you get back is the amount you loaned, and if the entrepreneur, does not pay back the loan then you take a loss. This is something you do if you believe if giving people an opportunity to make a better life for themselves through hard work and intelligent economic choices.
I encourage you to join me: let me know if you contribute to Kiva and I will add your Kiva page to our list of Curious Cat Kivans. Also join the Curious Cats Kiva Lending Team.
My loans have been made to in 32 countries including: Ghana, Cambodia, Uganda, Viet Nam, Peru, Ukraine, Mongolia, Ecuador and Tajikistan. Kiva provides sector (but I think this data is a not that accurate – it depends on the Kiva partners that are not that accurate on identifying the sectors (it seems to me). A large number of the loans are in retail, clothing and food. I like making loans that will improve productivity (manufacturing, providing productivity enhancing services…) but can’t find as many of those as I would like (8% of my loans are in manufacturing, 11% agriculture, retail 18%, 23% food, 25% services (very questionable – these are normally really retail or food, it seems to me).
Some examples of the entrepreneurs I have lent to: welding workshop (Nicaragua), expanding generator services business with computer services (Cambodia), food production (Ghana), manufacturing nylon (Nigeria), internet cafe (Lebanon), electronics repair (Benin), new engine for mill (Togo), weaving (Indonesia) and a food market (Mexico).
Related: Financial Thanksgiving – MicroFinance Currency Risk – Creating a World Without Poverty – Provide a Helping Hand
21 of my loans have been paid back in full. 3 have defaulted. Those figure give a distorted picture though (I believe). There was a problem with a Kiva partner (they partner with micro-finance banks around the world) MIFEX, in Ecuador. Kiva discovered that MIFEX (i) improperly inflated the loan amounts it posted for entrepreneurs on the Kiva website and (ii) kept the excess amount of the posted loan to fund its own operational expenses. Kiva does not expect any further payments on these loans. I had 2, so I think those 2 give a fair impression. The 3rd default is from Kenya. That loan was to a business selling bicycle parts. In 2008, in Kenya, the prevailing political crisis deteriorated and businesses have either been destroyed or closed in fear of looters. Technically the loan did default, however, I was paid $71.50 out of $75 loan (so the defaulted amount was very small.
Read more
Home Ownership Shelter, or Burden?
The other area of concentrated distress is subprime mortgages, which increased their share of the American mortgage market from 7% in 2001 to over 20% in 2006. According to the Mortgage Bankers Association, the delinquency rate was 22% in the fourth quarter of 2008, compared with only 5% for prime loans.
…
“Perhaps the most compelling argument for housing as a means of wealth accumulation”, argues Richard Green of the University of Southern California, “is that it gives households a default mechanism for savings.” Because people have to pay off a mortgage, they increase their home equity and save more than they otherwise would. This is indeed a strong argument: social-science research finds that people save more if they do so automatically rather than having to choose to set something aside every month.
Yet there are other ways to create “default savings”, such as companies offering automatic deductions to retirement plans. In any case, some of the financial snake oil peddled at the height of the housing bubble was bad for saving.
The debate over whether home ownership is a wise investment or not, is contentious (more so in the last year than it was several years ago). I believe in most cases it probably is wise, but there are certainly cases where it is not. If you put yourself in too much debt that is often a big problem. I also think you should save a down payment first. If you are going to move (or have good odds you may want to) then renting is often the better option.
The “default saving” feature is one of the large benefits of home ownership. That benefit is destroyed when you take out loans against the rising value of the house. And in fact this can not just remove the benefit but turn into a negative. If you spend money you should have (increasing your debt) that can not only remove you default saving benefit but actual make your debt situation worse than if you never bought.
Related: Your Home as an Investment – Nearly 10% of Mortgages Delinquent or in Foreclosure – Housing Rents Falling in the USA – Ignorance of Many Mortgage Holders
Federal Reserve Beige Book highlights for April 15th. The Beige Book documents comments received from business and other contacts outside the Federal Reserve and is not a commentary on the views of Federal Reserve officials. The book is published eight times a year.
…
Manufacturers’ assessments of future factory activity improved marginally over the survey period as well.
…
Consumer spending remained generally weak. However, several Districts said sales rose slightly or declines moderated compared with the previous survey period.
…
Home prices continued to decline in most Districts, although a few reports noted that prices were unchanged or that the pace of decline had eased. Low mortgage rates were fueling refinancing activity. Outlooks for the housing sector were generally more optimistic than in earlier surveys, with respondents hopeful that increased buyer interest would lead to better sales.
…
Commercial real estate investment activity weakened further.
…
Labor market conditions were weak and reports of layoffs, reductions in work hours, temporary factory shutdowns, branch closures and hiring freezes remained widespread across Districts.
Related: Central Bank Intervention Unprecedented in scale and Scope – Why do we Have a Federal Reserve Board? – Manufacturing Employment Data – 1979 to 2007 – Oil Consumption by Country
It is no surprise that paying politicians lot of money gets you favors: Politicians Change rules for Big Donors – Lobbyists Keep Tax Off Billion Dollar Private Equities Deals (2007) – Congress Eases Bank Laws to Aid Big Donors (1999) – More Government Waste – Monopolies and Oligopolies do not a Free Market Make
Investments Can Yield More on K Street, Study Indicates by Dan Eggen
…
The paper by three Kansas professors examined the impact of a one-time tax break approved by Congress in 2004 that allowed multinational corporations to “repatriate” profits earned overseas, effectively reducing their tax rate on the money from 35 percent to 5.25 percent. More than 800 companies took advantage of the legislation, saving an estimated $100 billion in the process, according to the study.
The largest recipients of tax breaks were concentrated in the pharmaceutical and technology fields, including Pfizer, Merck, Hewlett Packard, Johnson & Johnson and IBM. Pfizer alone repatriated $37 billion, representing 70 percent of its revenue in 2004
…
Mazza added that the results are “troubling” because they show how large companies can distort tax policy to benefit their bottom line.
It’s Now a Renter’s Market by Prashant Gopal
…
Oklahoma City, where people spent just 12% of their income on rent, was the most affordable. Other cheap markets included Indianapolis, Denver, Fort Worth, and Cleveland. The least affordable market was New York, where people spent 57% of their income on rent.
Rental markets are driven largely by 2 factors, vacancy rates and jobs. If jobs in a metropolitan area are increasing rents usually increase. If more new apartments are added to the market than jobs (which then increases vacancy rates) this will push down rates. Other factors influence vacancy rates (such as people moving back in with parent, people sharing apartments…). Those factors often are largely influenced by losing jobs in an area.
D.C. apartment market remains strong
…
Rent increases over the past 12 months for all investment grade apartments kept under the long-term average of 4.2 percent per annum, at 0.5 percent since March 2008.
Related: Housing Rents Falling in the USA – Home Values and Rental Rates – Real estate investing articles – Urban Planning – Longer Commutes Translate to Larger Housing Price Declines
Read more
This Time, Old Hands Are Keeping Their Jobs
That’s a big change from the last serious recession, in 1990-91, when older workers, especially in manufacturing, were hard-hit. Today’s pattern is closer to that of the mild 2001 recession, when older workers did reasonably well.
…
Boeing’s buyouts in the 1990s encouraged workers near retirement to jump ship. “We’ve learned from that,” says Hartnett. While Boeing says it doesn’t look at age in making cuts, it and others want to save the most productive workers—often employees whom companies have invested in most and who have “demonstrated track records,” says Chicago lawyer Gerald L. Maatman Jr., who recently advised 10 companies on downsizing. Such workers “tend to be more experienced and are often older.”
Related: Keeping Older Workers – Our Only Hope: Retiring Later – Focus on Customers and Employees – People are Our Most Important Asset
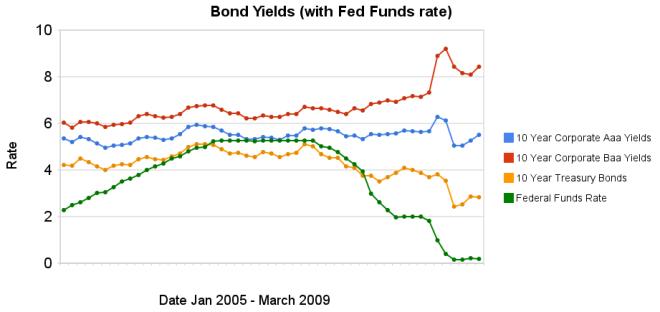 Chart showing corporate and government bond yields by Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.
Chart showing corporate and government bond yields by Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.The federal funds rate remains under .25%. The large spread between government bonds and corporate bonds remains very large. In the last 3 months the yields on Aaa corporate bonds have increased 45 basis points, Baa corporate bond yields have decreased 1 basis points, while treasury bond yields have increased 40 basis points.
The spread between 10 year Aaa corporate bond yields and 10 year government bond yields is now 268 basis points. In January, 2008 the spread was 159 points. The larger the spread the more people demand in interest, to compensate for the increased risk. The spread between government bonds and Baa corporate bonds decreased to a still very large 566 basis points, the spread was 280 basis point in January 2008, and 362 basis points in September 2008.
Data from the federal reserve: corporate Aaa – corporate Baa – ten year treasury – fed funds
Related: Chart Shows Wild Swings in Bond Yields – Fed to Start Buying Treasury Bonds Today – Corporate and Government Bond Rates Graph (Oct 2008) – investing and economic charts
William Black wrote The Best Way to Rob a Bank Is to Own One: How Corporate Executives and Politicians Looted the S&L. I think he a bit off on the “owning one,” being the best way to loot. The looters are not owners, they are executives that loot from owners, taxpayers, customers… And those looters pay politicians a great deal of money to help them. He appeared on Bill Moneys Journal discussing the huge mess we know are in and how little is being done to hold those responsible for the enormous crisis created by them.
…
The FBI publicly warned, in September 2004 that there was an epidemic of mortgage fraud, that if it was allowed to continue it would produce a crisis at least as large as the Savings and Loan debacle. And that they were going to make sure that they didn’t let that happen. So what goes wrong? After 9/11, the attacks, the Justice Department transfers 500 white-collar specialists in the FBI to national terrorism. Well, we can all understand that. But then, the Bush administration refused to replace the missing 500 agents. So even today, again, as you say, this crisis is 1000 times worse, perhaps, certainly 100 times worse, than the Savings and Loan crisis. There are one-fifth as many FBI agents as worked the Savings and Loan crisis.
…
Well, certainly in the financial sphere, I am. I think, first, the policies are substantively bad. Second, I think they completely lack integrity. Third, they violate the rule of law. This is being done just like Secretary Paulson did it. In violation of the law. We adopted a law after the Savings and Loan crisis, called the Prompt Corrective Action Law. And it requires them to close these institutions. And they’re refusing to obey the law.
…
In the Savings and Loan debacle, we developed excellent ways for dealing with the frauds, and for dealing with the failed institutions. And for 15 years after the Savings and Loan crisis, didn’t matter which party was in power, the U.S. Treasury Secretary would fly over to Tokyo and tell the Japanese, “You ought to do things the way we did in the Savings and Loan crisis, because it worked really well. Instead you’re covering up the bank losses, because you know, you say you need confidence. And so, we have to lie to the people to create confidence. And it doesn’t work. You will cause your recession to continue and continue.”
…
And their ideologies, which swept away regulation. So, in the example, regulation means that cheaters don’t prosper. So, instead of being bad for capitalism, it’s what saves capitalism. “Honest purveyors prosper” is what we want. And you need regulation and law enforcement to be able to do this. The tragedy of this crisis is it didn’t need to happen at all.
Related: Fed Continues Wall Street Welfare – Credit Crisis the Result of Planned Looting of the World Economy – Lobbyists Keep Tax Off Billion Dollar Private Equities Deals – Poll: 60% say Depression Likely – Canadian Banks Avoid Failures Common Elsewhere – Too Big to Fail – Why Pay Taxes or be Honest