Predatory Lenders’ Partner in Crime by Eliot Spitzer
In 2003, during the height of the predatory lending crisis, the OCC invoked a clause from the 1863 National Bank Act to issue formal opinions preempting all state predatory lending laws, thereby rendering them inoperative. The OCC also promulgated new rules that prevented states from enforcing any of their own consumer protection laws against national banks. The federal government’s actions were so egregious and so unprecedented that all 50 state attorneys general, and all 50 state banking superintendents, actively fought the new rules.
But the unanimous opposition of the 50 states did not deter, or even slow, the Bush administration in its goal of protecting the banks. In fact, when my office opened an investigation of possible discrimination in mortgage lending by a number of banks, the OCC filed a federal lawsuit to stop the investigation.
It is unfortunate when the federal government chooses to strip states of the ability to protect citizens.
Related: Credit Freeze Stops Identity Theft Cold – Investor Protection Needed
Data from the Commonwealth fund report, Toward Higher-Performance Health Systems: Adults’ Health Care Experiences in Seven Countries, 2007:
| Australia | Canada | Germany | Netherlands | New Zealand | UK | USA | |
| National health spending – Percent of GDP | 9.5% | 9.8% | 10.7% | 9.2% | 9.0% | 8.3% | 16.0% |
| Percent uninsured | 0 | 0 | <1 | <2 | 0 | 0 | 16 |
| Last time you were sick or needed care, how quickly could you get an appointment to see a doctor? | |||||||
| Same day | 42 | 22 | 55 | 49 | 53 | 41 | 30 |
| Next day | 20 | 14 | 10 | 21 | 22 | 17 | 19 |
| 2-5 days | 26 | 26 | 10 | 17 | 17 | 26 | 25 |
| 6 or more days | 10 | 30 | 20 | 5 | 4 | 12 | 20 |
| Overall health system views | |||||||
| Only minor changes needed, system works well | 24 | 26 | 20 | 42 | 26 | 26 | 16 |
| Fundamental changes needed | 55 | 60 | 51 | 49 | 56 | 57 | 48 |
| Rebuild completely | 18 | 12 | 28 | 9 | 17 | 15 | 34 |
Related: Measuring the Health of Nations – USA Paying More for Health Care – Traveling for Health Care – resources for improvement health system performance
Jimmy Rodgers is one of the most successful investors ever. He and George Soros were partners during the amazing run with Quantum Fund (up over 4000% in 10 years) and he has been successful since. This interview provides his current thoughts – ‘It’s going to be much worse’
Rogers looks at the Fed’s willingness to add liquidity to an already inflationary environment and sees the history of the 1970s repeating itself. Does that mean stagflation? “It is a real danger and, in fact, a probability.”
One smart investor, no matter how smart, will have many wrong guesses about the future. Still he is someone worth listening to.
Related: Investment Biker – Charge It to My Kids – Buffett’s 2007 Letter to Shareholders
I have update my article showing the historical comparison of 30 year fixed mortgage rates and the federal funds rate. When deciding whether to lock in a rate for a 30 year fixed rate mortgage (when refinancing or buying a new home) some believe moves in the federal reserve discount rate will raise or lower that mortgage rate directly. This is not the case, in general. The effect of federal reserve discount rates on other mortgage rates (such as adjustable rate mortgages is not the same and can be predictably affected by fed fund rate moves).
The chart shows the federal funds rate and the 30 year fixed rate mortgage rate from January 2000 through December 2007 (for more details see the article).
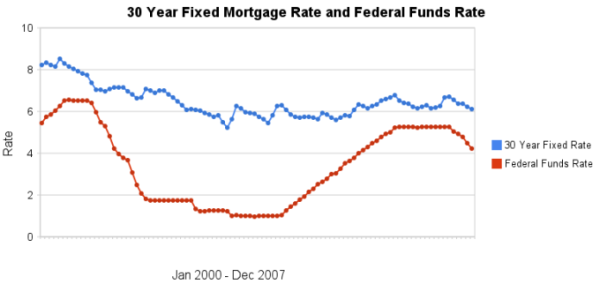
There is not a significant correlation between moves in federal funds rate and 30 year mortgage rates that can be used for those looking to determine short term (over a few days, weeks or months) moves in the 30 year fixed mortgage rates. For example if 30 year rates are at 6% and the federal reserve drops the federal funds rate 50 basis points that tells you little about what the 30 year rate will do. No matter how often those that should know better repeat the belief that there is such a correlation you can look at the actual data in the graph above to see that it is not the case.
Read more
Here is updated data from the UN on manufacturing output by country. China continues to grow amazingly moving into second place for 2006. UN Data, in billions of current US dollars:
| Country | 1990 | 2000 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 1,040 | 1,543 | 1,545 | 1,629 | 1,725 | |
| China | 143 | 484 | 788 | 939 | 1096 | |
| Japan | 808 | 1,033 | 962 | 954 | 929 | |
| Germany | 437 | 392 | 559 | 584 | 620 | |
| Italy | 240 | 206 | 295 | 291 | 313 | |
| United Kingdom | 207 | 230 | 283 | 283 | 308 | |
| France | 223 | 190 | 256 | 253 | 275 | |
| Brazil | 117 | 120 | 130 | 172 | 231 | |
| Korea | 65 | 134 | 173 | 199 | 216 | |
| Canada | 92 | 129 | 165 | 188 | 213 | |
| Additional countries of interest – not the next largest | ||||||
| Mexico | 50 | 107 | 111 | 122 | 136 | |
| India | 50 | 67 | 100 | 118 | 130 | |
| Indonesia | 29 | 46 | 72 | 79 | 103 | |
| Turkey | 33 | 38 | 75 | 92 | 100 | |
So yet again everyone in Washington DC wants to raise taxes on your children and grandchildren to spend money today. We might be going into a recession because the bubble of financing real estate led to people spending money they couldn’t pay back. So now home construction is decreasing, banks are having trouble meeting within capitalization requirement without huge inflows of capital from abroad, excess housing supply…
The government has been spending huge amounts of money it doesn’t have for a long time. So what great ideas do our leaders have: put more burden on the children and grandchildren to pay for our spending today. What a sad state of affairs. And almost no-one seems to question this behavior.
Is the idea that we would go into a recession so remote these leaders never imagined it could happen? No, of course they new it would happen. So what should a country, company, individual do if they know they have some expected event in the future they might want to spend money on? This isn’t really tricky. I would guess many 8 years olds understand the concept. You put the money in the piggy bank for when you will want to spend it.
If you decide to spend not only all the money you have but borrow huge amounts that will tax your future earnings to pay back your current spending that is your choice (as long as you can find someone to lend you money). But as many parents have told their kids you have to live with the decisions you make. You don’t get to spend your money today. Spend tomorrows money today. Spend your kids money today. And then when, tomorrow comes, just spend all that money all over again. How can a country allow leaders to so transparently tax the future of the country?
It is a sad state of affairs. The country chooses not to sent aside funds for obvious future needs. Then instead of accepting the hole they have dug for themselves decides to tax their children even more to continue the spendthrift ways. I think we not only need to have politicians actually read the bills before they vote (they refuse to pass such a law) they need to read about the ant and the grasshopper.
I have no problem with the country choosing to set aside funds to use when they want to try and stave off a recessions (to pay for tax cuts or more spending). I do have a problem with: running enormous deficits every year, raising taxes on our children and grandchildren year after year, and then deciding to raise taxes even more on the future when the obvious happens and perfectly predictable desired expenditures present themselves. The get another credit card school of financial management (that everyone in Washington DC seems to practice) is not workable for a country over the long term. As anyone that has used that strategy personally will tell you – it works for awhile but eventually there are serious consequences.
Read more
Warren Buffett and Bill Gates are two of the richest people on the planet (though many are gaining on them recently). Both have pledged to give away nearly all (over 99%) of the money they have earned to charity. Both have spoken out against the harm to children and society (and the capitalist system) when huge wealth is provided by lottery of birth to a few instead of provided to those who earn the money.
…
Melinda and Bill will very likely give away more than $100 billion in their lifetimes. Already the foundation has disbursed $14.4 billion – more than the Rockefeller Foundation has distributed since its creation in 1913 (even adjusted for inflation).
…
Bill, who is nine years older than Melinda, plans to spend more than 40 hours a week on philanthropy, leaving 15 or so for his duties as chairman of Microsoft.
…
Early on she and Bill agreed to focus on a few areas of giving, choosing where to place their money by asking two questions: Which problems affect the most people? And which have been neglected in the past? While many philanthropists take the same tack, the Gateses, who love puzzles, apply particular rigor. “We literally go down the chart of the greatest inequities and give where we can effect the greatest change,” Melinda says. So while they don’t give to the American Cancer Society, they have pumped billions into the world’s deadliest diseases – most importantly AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis – and failing public high schools in the U.S.
Charity is important. As is understanding that capitalism is about people earning their wealth not getting it from Mom and Dad. Unfortunately many politicians don’t know what capitalism is and think that providing huge inheritances to some kids of rich people is capitalism. Providing resources to those that didn’t earn them is the opposite of capitalism. They need to learn. If they oppose capitalism and would rather assure the kids of the rich get huge inheritances that is fine, they just shouldn’t get away with claiming they support capitalism.
Related: Estate Tax Repeal (a very bad idea) – Helping Capitalism Make the World Better – charity links – Multi-millionaires giving to charity not creating later day idle nobility
It is not your parents world. In case you hadn’t noticed the economic power in the world has been changing quickly. Many are missing the magnitude of these changes. One visible example is explored by the Economist in Emerging-market Multinationals:
…
By 2006 foreign direct investment (including mergers and acquisitions) from developing economies had reached $174 billion, 14% of the world’s total, giving such countries a 13% share (worth $1.6 trillion) of the stock of global FDI. In 1990 emerging economies accounted for just 5% of the flow and 8% of the stock.
This is just one visible sign of shifting economic power. And it shows no sign of slowing down. Our 12 Stocks for 10 Years portfolio is heavily invested for overseas growth. Close to 20% directly in emerging markets (through Templeton funds). PetroChina, Google, Toyota and Tesco all are very well positioned to grow quickly in emerging markets. And other stocks are likely do do well too – I am not clear on how well Pfizer, Amazon and Dell are positioned at this time.
Emerging stock markets will continue to be very volatile I believe. However looking decades out and at a pool of 20 countries it is hard to imagine they won’t do very well: China, Singapore, Mexico, India, Thailand, Brazil, South Africa, Vietnam, etc.
Related: Growing Size of non-USA Economies – Why Investing is Safer Overseas – South Korea To Invest $22 Billion in Overseas Energy Projects – Changing Economic Clout and Science Research
One way to evaluate the real estate market is to compare rental rates to home values. This can provide a comparison of an approximate cost of buying a house versus the cost to rent. As the ratio of monthly rent to home price increases, at least on this measure or real estate value, the market can be seen as becoming more expensive.
Several points to keep in mind:
- This does not take into account things like tax rates (in higher tax areas the rents will be higher [since the owners will pass on that cost that is not reflected in the home price] – the ratio lower)
- This is only a comparison measure – it can be that rents also experience a bubble. So if rents experience a bubble then the ratio could stay low and fail to indicate an “expensive” market.
- Don’t rely on one measure – this is one useful measure there are plenty of others that matter for real estate prices (income levels, job growth, interest rates, zoning regulations…)
The Rent-Price Ratio for the Aggregate Stock of Owner-Occupied Housing
likely would have to fall considerably.
This paper is well worth reading. I would like to point out another factor here though. When those investing in real estate were focused largely on capital gains (say a few years ago) there could well have been an increased demand for rental property (which increased prices). That effect also moved extra supply into the rental market (that previously would have been sold to owners that would live there instead of investors). Those investors were more concerned with capital gains and it seems to me could well have been willing to accept lower rents just to have some cash coming in to help pay the expenses.
As those investors no longer believe they will receive large capital gains in the short term it is possible they will be more focused on cash flow – and seek increased rents. I will not be surprised that rent prices increase as investors focus more on cash flow and stop assuming such large capital gains will be where their profits are made. Thus the ratio will close both by real estate value declines and rental price increases.
Related: Explaining Rent-Home Price Ratios – True Rent-to-Price Ratio for Housing – articles on the real estate market – Real Estate Median Prices Down 1.5% in the Last Year – Rent Controls are Unwise
I have noticed that many of the stories I read and heard lately, about economists work, is not exactly what you would expect: Randomization in Sports, Violent Films May Drive Down Crime Rate, Study ties dropouts to violent crime rate, Seat Belts Still Best Hedge Against Injury.
I understand that it is possible to see the economic interest in almost everything (though things like randomization in sports it gets pretty hard). It seems to me lately there has been an increase in economist studying interesting areas that really are not about the economy. It seems like the knowledge and skill to examine complex data sets and draw conclusions is really defining what some economists are becoming (instead of the study of economic matters specifically). While the majority of economists still examine traditional economy related data some others are increasingly studying other areas. But this may just be my perception.
Some economics definitions:
- Princeton WordNet – “the branch of social science that deals with the production and distribution and consumption of goods and services and their management”
- Illinois State Water Survey – “The study of choice and decision-making in a world with limited resources”
- American Economic Association – “Economics is the study of how people choose to use resources.”
Related: Curious Cat Economics Dictionary – articles on economics – economics related blog posts