The behavior of banks is despicable enough when they are merely trying to trick educated, financially secure people out of their money. Banks charged $38.5 billion in fees last year according to the Financial Times. But that behavior, toward the poor, by banks (paying millions to hundreds of executives for, I guess, getting congress to send the companies billions) is immoral.
The Gates Foundation has decided to go into improving financial services for the poor. The are supporting micro-credit but also micro finance. Saving is key for poor people to get and stay out of poverty. Most already save money informally but want better, safer options. Setting aside money in a safe place will allow poor people to weather setbacks, build assets and financial security, and invest in opportunities for the next generation. Formal savings accounts also help them keep more of what they earn and easily access their money when they need it.
The poor need better banking options in poor countries. But the poor need better banking options in at least one rich country (the only one I know is the USA and banks in the USA provide lousy options for the poor). Credit Unions are much more likely to actually try and provide value to customers. Unfortunately banks in the USA seem to operate on the principle that customer are suckers that exist to pay for Porches for the children of bank executives.
Related: FDIC Study of Bank Overdraft Fees – Microfinancing Entrepreneurs – Incredibly Bad Customer Service from Discover Card – 10 Things Your Bank Won’t Tell You
Fed Focusing on Real-Estate Recession as Bernanke Convenes FOMC
…
Commercial property is “certainly going to be a significant drag” on growth, said Dean Maki, a former Fed researcher who is now chief U.S. economist in New York at Barclays Capital Inc., the investment-banking division of London-based Barclays Plc. “The bigger risk from it would be if it causes unexpected losses to financial firms that lead to another financial crisis.”
…
Any sales of mortgage-backed bonds would be the first new issues in the $700 billion U.S. market for commercial-mortgage- backed securities since it was shut down by the credit freeze in 2008. About $3 billion are in the pipeline, and the success of these sales may foster as much as $25 billion in total deals in the next six months
…
Forty-seven percent of loans at the 7,000-plus smaller U.S. lenders are in commercial real estate, compared with 17 percent for the biggest banks…
Related: Data Shows Subprime Mortgages Were Failing Years Before the Crisis Hit – Home Values and Rental Rates – Record Home Price Declines (Sep 2008)
The USA unemployment rate dropped slightly to 9.4%. The economy lost 247,000 jobs which is both a sign the economy is not strong and also that it is improving (job losses from November through April were 645,000/month and 331,000/month from May through July). The job losses for May and June were both revised to show 20,000 fewer job losses each in the press release from the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
The number of long-term unemployed (those jobless for 27 weeks or more) rose by 584,000 over the month to 5.0 million. In July, 1 in 3 unemployed persons were jobless for 27 weeks or more.
The employment-population ratio, at 59.4%, was little changed over the month but has declined by 330 basis points since the recession began in December 2007. About 2.3 million persons were marginally attached to the labor force in July, 709,000 more than a year earlier (The data are not seasonally adjusted). These individuals, who were not in the labor force, wanted and were available for work and had looked for a job sometime in the prior 12 months. They were not counted as unemployed because they had not searched for work in the 4 weeks preceding the survey.
In July, the average workweek of production and nonsupervisory workers on private nonfarm payrolls edged up by 0.1 hour to 33.1 hours. The manufacturing workweek increased by 0.3 hour to 39.8 hours. Factory overtime was unchanged at 2.9 hours.
This news supports the increasing livelihood of a weak recovery taking hold during 2009 – which is frankly pretty amazing in my opinion. The economy could certainly have taken longer to recover. Still, more job losses and an increasing unemployment rate are likely before the end of 2009.
Related: Another 450,000 Jobs Lost in June – USA Unemployment Rate Jumps to 9.4% (May 2009) – USA Unemployment Rate Rises to 8.1%, Highest Level Since 1983 (March 2009)
Read more
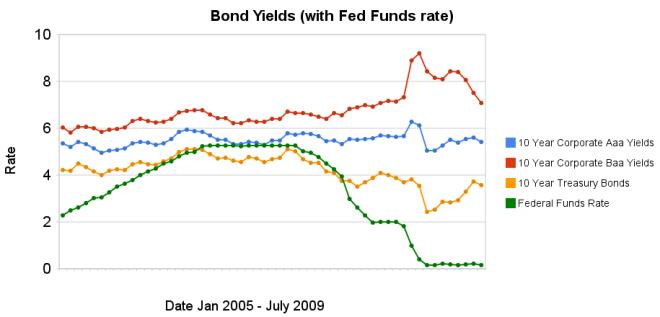 Chart showing corporate and government bond yields by Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.
Chart showing corporate and government bond yields by Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.The changes in bond yields over the last 3 months months indicate a huge increase in investor confidence. The yield spread between corporate Baa 10 year bonds and 10 year treasury bonds increased 304 basis points from July 2008 to December 2008, indicating a huge swing in investor sentiment away from risk and to security (US government securities). From April 2009 to July 2009 the yield spread decreased by 213 basis points showing investors have moved away from government bonds and into Baa corporate bonds.
From April to July 10 year corporate Aaa yields have stayed essentially unchanged (5.39% to 5.41% in July). Baa yields plunged from 8.39% to 7.09%. And 10 year government bond yields increased from 2.93% to 3.56%. federal funds rate remains under .25%.
Investors are now willing to take risk on corporate defaults for a much lower premium (over government bond yields) than just a few months ago. This is a sign the credit crisis has eased quite dramatically, even though it is not yet over.
Data from the federal reserve: corporate Aaa – corporate Baa – ten year treasury – fed funds
Related: Continued Large Spreads Between Corporate and Government Bond Yields (April 2009) – Chart Shows Wild Swings in Bond Yields (Jan 2009) – investing and economic charts
Apartment Vacancy at 22-Year High in U.S.
…
Asking rents for apartments fell 0.6 percent in the second quarter from the first, Reis said. That matched the rate of change in the first quarter, the biggest drop since Reis began reporting such data in 1999.
…
New York had the lowest vacancy rate in the second quarter, at 2.9 percent, followed by New Haven, home to Yale University; Central New Jersey; New York’s Long Island; and Syracuse, New York, according to Reis.
Related: Housing Rents Falling in the USA – Rent Controls are Unwise – It’s Now a Renter’s Market – articles on investing and real estate
The decisions over the past 30 years to pass huge huge tax bills to those in the future is unsustainable. Saying you cut taxes when all you actually do is postpone them is dishonest. However, many people go along with such false statements so politicians have learned to buy votes today by raising taxes on the future. Since the public keeps voting for such people when the facts are clear the only explanation is they support raising taxes, not today, but in the future (or, I suppose, they are not able to understand the clear implications of what they vote for). The Long-Term Budget Outlook
…
For decades, spending on Medicare and Medicaid has been growing faster than the economy. CBO projects that if current laws do not change, federal spending on Medicare and Medicaid combined will grow from roughly 5 percent of GDP today to almost 10 percent by 2035. By 2080, the government would be spending almost as much, as a share of the economy, on just its two major health care programs as it has spent on all of its programs and services in recent years.
…
CBO projects that Social Security spending will increase from less than 5 percent of GDP today to about 6 percent in 2035 and then roughly stabilize at that level.
…
Federal interest payments already amount to more than 1 percent of GDP; unless current law changes, that share would rise to 2.5 percent by 2020.
The cost of paying for a dysfunctional medical system has been a huge drain on the USA economy for decades. But that is nothing compared to what the future holds if we don’t adopted sensible strategies that reduce the huge extra costs we pay and the worse performance we receive for that cost.
Social security is not the huge problem many think it is. Still I would support reducing the payout to wealthy individuals and bringing the age limits more in line with the changes in life expectancy. 12.4% of pay for low and middle wage workers (high income earners stop paying social security taxes so in effect marginal tax rates decrease by 12% for any income above $106,800). Medicare taxes add 2.9% bringing the total social security and Medicare taxes to 15.1% (including both the amount paid directly by the employee and the amount paid for the employee by the employer).
Related: True Level of USA Federal Deficit – USA Federal Debt Now $516,348 Per Household – quotations about economics – articles on improving the health care system – USA Spent $2.2 Trillion, 16.2% of GDP, on Health Care in 2007
Two Professors Argue About the Invisible Hand – And Both Get it Wrong too
…
He used the term not in his discussion and analysis of markets (Book I and II of Wealth Of Nations), but in a discussion of the choice of export/importing versus investing in domestic businesses (Book IV of Wealth Of Nations on his critique of mercantile political economy). It had nothing to do with ‘regulating’.
…
It was a metaphor Smith used only three times and he never said “that when this invisible hand exists, when we all pursue our own interest, we end up promoting the public good, and often more effectively than if we had actually and directly intended to do so.” That is a modern construction placed on the metaphor and has next to nothing to do Adam Smith
…
The invisible hand was never in Adam Smith’s world in the form invented in mid-20th century by some economists who created the Chicago version of Adam Smith, while ignoring the Adam Smith born in Kirkcaldy, Scotland in 1723.
Related: There is No Invisible Hand – Myths About Adam Smith Ideas v. His Ideas – Not Understanding Capitalism
Mobius Says Derivatives, Stimulus to Spark New Crisis
“Political pressure from investment banks and all the people that make money in derivatives” will prevent adequate regulation, said Mobius, who oversees $25 billion as executive chairman of Templeton in Singapore. “Definitely we’re going to have another crisis coming down,”
…
A “very bad” crisis may emerge within five to seven years as stimulus money adds to financial volatility, Mobius said. Governments have pledged about $2 trillion in stimulus spending.
…
“Banks have lobbied hard against any changes that would make them unable to take the kind of risks they took some time ago,” said Venkatraman Anantha-Nageswaran, global chief investment officer at Bank Julius Baer & Co. in Singapore. “Regulators are not winning the battle yet and I’m not sure if they are making a strong case yet for such changes.”
Mobius also predicted a number of short, “dramatic” corrections in stock markets in the short term, saying that “a 15 to 20 percent correction is nothing when people are nervous.” Emerging-market stocks “aren’t expensive” and will continue to climb
I share this concern for those we bailed out using the money we paid them to pay politicians for more favors. Those paying our politicians like very much paying themselves extremely well and then being bailed out by the taxpayers when their business fails. They are going to try to retain the system they have in place. And they are likely to win – politicians are more likely to provide favors to those giving them large amounts of money than they are to learn about proper management of an economy.
Related: Congress Eases Bank Laws for Big Donors (1999) – Lobbyists Keep Tax Off Billion Dollar Private Equities Deals and On For Our Grandchildren – General Air Travel Taxes Subsidizing Private Plane Airports – CEOs Plundering Corporate Coffers
Welcome to the Curious Cat Investing and Economics Carnival, we hope you enjoy the following posts we share here.
- Warren Buffet On An Investment News Channel by Robin Bal – “I could see that the mere mention of a time scale like three to five years had derailed the interviewer’s thought process. Coming as she did from a world where three to five hours or at most three to five days is the standard unit of time, the idea of an investor talking in years seemed to have thrown a spanner in her works.”
- Loan Default Rates: 1998-2009 by John Hunter – “In the 4th quarter of 2007 residential real estate default rates were 3.02% by the 4th quarter of 2008 they were 6.34% and in the 1st quarter of this year they were 7.91%”
- Key Factors Affecting Long-Term Growth in Federal Spending by Douglas Elmendorf – “Two factors underlie the projected increase in federal spending on Medicare, Medicaid, and Social Security as a share of GDP: rapid growth in health care costs and an aging population.”
- Will the Chinese Keep Saving? by Rachel Ziemba – “Should export-oriented ’surplus’ countries like China keep saving and keep trying to export demand, the reduction in imbalances could actually exacerbate the global economic contraction or contribute to a more sluggish recovery. “
- Use Your Health Insurance! by David Weliver – “So if you’re worried about losing your job (and insurance) or anticipate making a life change that will leave you uninsured, get in to see a doctor while you are still covered.”
- Where is the externality here? by Matt Nolan – “They are paid less because their marginal product is lower, and they are willing to be paid less because the benefit they receive from consuming alcohol is sufficient compensation – this is a completely internalised decision for the drinker isn’t it, so where is the social cost.”
- Quibbles With Quants – “What the models failed to capture was that humans don’t behave in simple, predictable and uncorrelated ways. It’s impossible to overstate the importance of the way these models cope with correlation of peoples’ psychology. To sum it up: they don’t. Let me know if that’s too complex an analysis for the mathematical masters of the universe.”
- Goldman’s Back, and Why We Should Be Worried by Robert Reich – “The decision to bail out AIG resulted in a $13 billion giveaway to Goldman because Goldman was an AIG counterparty. Indeed, Goldman executives and alumni have played crucial roles in guiding the Wall Street bailout from the start. So the fact that Goldman has reverted to its old ways in the market suggests it has every reason to believe it can revert to its old ways in politics, should its market strategies backfire once again — leaving the rest of us once again to pick up the pieces.”
Here is a good blog post showing one great feature of the blogosphere (that term seems to have fallen out of use hasn’t it): interaction. It also shows that you have to think critically. You can’t just accept what you read (you never can, but that is even more true with blogs than it is with newspapers that at least have some standards normally). I tend to agree with this posts look at the data, though I have not examined the issue closely.
Bad Math, Bad Statistics: Trying to get a blogger to admit a mistake
1981: 229465714 * 8476.0 = 1.944 trillion
1992: 255029699 * 14847.0 = 3.786 trillion (94% gain)
2005: 292892127 * 25036.0 = 7.332 trillion (93.6% gain)
Er, doesn’t look like a lag to me. In fact, it looks like it’s doubling every 12-13 years just as much as GDP is. I also looked up total income statistics for the US, and found the following figures (source). (Note these figures are different. More on that later.)
1981: $2,580,600,000 (2.58 / 3.1 = 83% of GDP)
1992: $5,349,384,000 (more than double!) (5.34 / 6.2 = 86% of GDP)
2005: $10,252,973,000 (another double!) (10.25 / 12.4 = 82% of GDP)
Anyway it is a much more interesting argument than I would hear when I listened to TV “pundits” years ago spout meaningless talking points at each other. Granted they argument is not going to be studied as a wonderful example of how we should debate. Still it is much above what passes for debate from our politicians (yes this is more a sad commentary on how failed our politicians are than a statement of how marvelous the argument on the GDP issue is between the two bloggers).
Here is a math question for you, what has a bigger impact moving from 15 to 18 mpg or 50 to 100 mpg?
Related: Government Debt as a Percentage of GDP – USA Consumers Paying Down Debt – Is Productivity Growth Bad? – Americans are Drowning in Debt