Total health expenditures in the USA in 2010 reached $2.6 trillion, $8,402 per person or 17.9% percent of GDP. All these are all time highs. Every year, for decades, health care costs have taken a larger and larger portion of the economic value created in the USA. The costs have risen much more rapidly than the costs in the rest of world. This creates a burden that slows the USA economy – it acts as a friction dragging everything else down. We not only need to slow down how fast we are getting worse (which we have done the last 2 years) but actually start making up for all the ground lost in the last few decades. We haven’t even started on that. The amount of work to do in getting our health system back to mediocre and reasonably priced is enormous (currently we have mediocre performance and extremely highly priced – twice as costly as other rich countries).
In 2009 the USA Spent Record $2.5 Trillion, $8,086 per person 17.6% of GDP on Medical Care.
USA health care spending grew 3.9% in 2010 following an increase of 3.8% in 2009. While those are the two slowest rates of growth in the 51 year history of the National Health Expenditure Accounts, they still outpaced both inflation and GDP growth. So yet again the health system expenses are taking a bigger portion of overall spending.
As a result of failing to address this issue for decades the problem is huge and will likely take decades to bring back just to a level where the burden on those in the USA, due to their broken health care system, is equal to the burden of other rich countries. Over 2 decades ago the failure in the health care system reached epidemic proportions but little has been done to deal with the systemic failures. Dr. Deming pointed to excessive health care cost, back then, as one of 7 deadly diseases facing American business. The fact that every year costs have increased more than GDP growth and outcome measures are no better than other rich countries shows the performance has been very poor. The disease is doing even more harm today.
Related: USA Heath Care System Needs Reform – USA Spends Record $2.3 trillion ($7,681 Per Person) on Health Care in 2008 – Systemic Health Care Failure: Small Business Coverage – Measuring the Health of Nations – How to improve the health care system performance – Management Improvement in Healthcare – USA Spent $2.2 Trillion, 16.2% of GDP, on Health Care in 2007
I decided to take a look at some historical economic data to see if some of my beliefs were accurate (largely about how well Singapore has done) and learn a bit more while I was at it.
| country |
|
1970** |
|
2010*** |
|
% increase |
| Korea | 1,320 | 20,200 | 1,430 | |||
| China | 325 | 4,280 | 1,217 | |||
| Singapore | 4260 | 42,650 | 901 | |||
| Indonesia | 460 | 2,960 | 543 | |||
| Brazil | 1900 | 10,500 | 453 | |||
| Thailand | 850 | 4,600 | 441 | |||
| Portugal | 3,970 | 21,000 | 429 | |||
| Japan | 9,000 | 42,300 | 370 | |||
| Malaysia | 1,900 | 7,755 | 308 | |||
| Germany | 11,550 | 40,500 | 251 | |||
| UK | 10,400 | 36,300 | 249 | |||
| France | 13,600 | 40,600 | 199 | |||
| Mexico | 4,160 | 9,200 | 121 | |||
| Panama | 3,480 | 7,700 | 121 | |||
| India | 555 | 1,180 | 113 | |||
| USA | 23,350 | 47,100 | 102 | |||
| South Africa | 3,930 | 7,100 | 81 | |||
| Venezuela | 8,280 | 9,770 | 18 |
I just picked countries that interested me and seemed worth looking at. I looked for some around the starting position of Singapore and close to Singapore geographically. And looked at Panama as the closest match to Singapore (for Singapore’s main 1970 asset, convenient for shipping lanes, and very close for GDP per capita).
Malaysia and Singapore were 1 country after independence (from 1963-1965).
I can’t imagine more than a couple countries could reasonably be argued to have had better economic performance from 1970 to 2010 than Singapore (Korea? China? Who else?). Singapore had very little going for it in 1970. They had a good location for shipping and that is about it macro-economically. No natural resources. No huge storage of wealth. No preeminence in science, technology or business.
It seems to me that Singapore actually did have 1 other thing. A government that was to preside over a fantastic economic growth success. You won’t find many textbooks talking about the way to economic success is a very well run government. And there is good reason for that, I believe. Relying on a very well run government will nearly always fail. In some ways Singapore was like Japan but with significantly more government influence on the way economic development played out.
I was surprised how poorly the USA has faired. It isn’t so surprising that we lagged. People forget how rich the USA was in 1970. The USA is still very rich but bunched together with lots of other rich countries instead of way out ahead as they were in 1970. And in 1970 the lead was already contracting, for what it had been earlier. But even knowing the relative performance of the USA had lagged, I was surprised by how much it under-performed.
I was also surprised with India. I knew they have done poorly but I didn’t realize it had been this poor. The failures to greatly improve infrastructure, education and the stifling effect of their bureaucracy have been causing them great harm. They have been doing some good things in the last 10 years especially but still have a long way to go. Their premier education is actually pretty decent. The problem is the other 90% of the education is often poor and many people (especially women) hardly have any education at all. It is very hard to get ahead when you fail to take advantage of the talents of so many of your people.
Related: Singapore and Iskandar Malaysia – Chart of Largest Petroleum Consuming Countries from 1980 to 2010 – Chart of Nuclear Power Production by Country from 1985-2009 – Top Countries For Renewable Energy Capacity
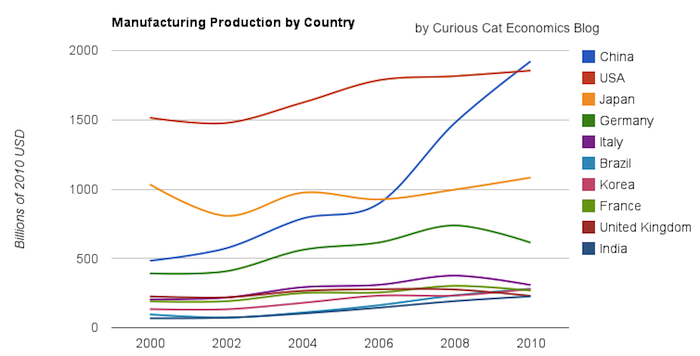
Chart of manufacturing production by the top 10 manufacturing countries (2000 to 2010). The chart was created by the Curious Cat Economics Blog. You may use the chart with attribution. All data is shown in 2010 USD (United States Dollar).
In my last post I looked at the output of the top 10 manufacturing countries with a focus on 1980 to 2010. Here I take a closer look at the last 10 years.
In 2010, China took the lead as the world’s leading manufacturing country from the USA. In 1995 the USA was actually very close to losing the lead to Japan (though you wouldn’t think it looking at the recent data). I believe China will be different, I believe China is going to build on their lead. As I discussed in the last post the data doesn’t support any decline in Chinese manufacturing (or significant moves away from China toward other South-East Asian countries). Indonesia has grown quickly (and have the most manufacturing production, of those discussed), but their total manufacturing output is less than China grew by per year for the last 5 years.
The four largest countries are pretty solidly in their positions now: the order will likely be China, USA, Japan, Germany for 10 years (or longer): though I could always be surprised. In the last decade China relentlessly moved past the other 3, to move from 4th to 1st. Other than that though, those 3 only strengthened their position against their nearest competitors. Brazil, Korea or India would need to increase production quite rapidly to catch Germany sooner. After the first 4 though the situation is very fluid.
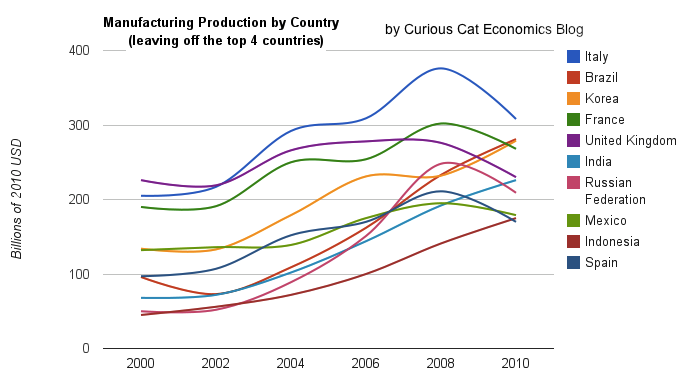
Taking a closure look at the large group of countries after top 4. Chart of manufacturing production from 2000-2010.
Chart of manufacturing production by the leading manufacturing countries (2000 to 2010). The top 4 countries are left off to look more closely at history of the next group. The chart was created by the Curious Cat Economics Blog based on UN data. You may use the chart with attribution.
Removing the top 4 to take a close look at the data on the other largest manufacturing countries we see that there are many countries bunched together. It is still hard to see, but if you look closely, you can make out that some countries are growing well, for example: Brazil, India and Indonesia. Other countries (most in Europe, as well as Mexico) did not fare well in the last decade.
The UK had a particularly bad decade, moving from first place in this group (5th in the world) to 5th in this group and likely to be passed by India in 2011. Europe has 4 countries in this list (if you exclude Russia) and they do not appear likely to do particularly well in the next decade, in my opinion. I would certainly expect Brazil, India, Korea and Indonesia to out produce Italy, France, UK and Spain in 2020. In 2010 the total was $976 billion by the European 4 to $961 billion by the non-European 4. In 2000 it was $718 billion for the European 4 to $343 billion (remember all the data is in 2010 USD).
There is an increasing trend to move from the USA to another country to work and live. This is not surprising to me. Recently this has picked up quite a bit; I am surprised by the velocity at which this interest in moving (I figured it would be a long term mega trend but not so drastic, so quickly). Economic changes are often quite surprising in how rapidly they move forward.
An interesting survey shows USA investors have become much more interested in relocating in the last two years (the data they show though has tremendous volatility over time, so I am not really sure this means much). I wonder how much of it can be explained by investors wanting to get a deep understanding of very promising markets. I wouldn’t image the actual number that do this is huge, but maybe the number considering it is significant. Billionaire investor, Jim Rodgers moved to Asia because he sees Asia as key to the future. One of the reasons I moved to Malaysia this year was to get a in depth understanding of what South East Asia is like (it is not a deciding reason, at all but maybe the 4th or 5th reason).
I believe the globalization of the employment market is a long term trend that will continue – especially for “knowledge workers.” The USA rested on the post WW II economic domination for nearly 50 years. The policies also helped this continue: investing in science and engineering, favoring entrepreneurship… But other countries have realized the value of these things (and the USA is slipping – not investing nearly as much in science and engineering and favoring large corporations that give politicians large amounts of cash over innovation – see things like the incredibly outdated “intellectual property” system, SOPA, favoring huge financial institutions…
The combination of long term policy weakness, the inevitable decline in the USA to world ratio of economic wealth, and the financial crisis caused by the policy weaknesses have seemingly greatly accelerated the trend. The next 2 or 3 years will determine if that is a permanent acceleration or if we go back to a slower pace – but on the same path. My guess is that we will stay on this path but the pace will not follow the level surveys might indicate (showing interest in such a big change is far different from actually moving).
There don’t seem to be any decent estimates of Americans living abroad. The US State Department claims releasing their estimates would be a national security risk? And the Census bureau says it would cost too much to try. Wild guesses seem to be between 4 and 6 million.
Related: I want out (subreddit) – Why Investing is Safer Overseas – USA Heath Care System Needs Reform – Copywrong
 Chart by Curious Cat Economics Blog using data from the Wind Energy Association. 2011 data is for the capacity on June 30, 2011. Chart may be used with attribution as specified here.
Chart by Curious Cat Economics Blog using data from the Wind Energy Association. 2011 data is for the capacity on June 30, 2011. Chart may be used with attribution as specified here._________________________
In 2007 wind energy capacity reached 1% of global electricity needs. In just 4 years wind energy capacity has grown to reach 2.5% of global electricity demand. And by the end of 2011 it will be close to 3%.
By the end of 2011 globally wind energy capacity will exceed 240,000 MW of capacity. As of June 30, 2011 capacity stood at 215,000. And at the end of 2010 it was 196,000.
As the chart shows Chinese wind energy capacity has been exploding. From the end of 2005 through the end of 2011 they increased capacity by over 3,400%. Global capacity increased by 233% in that period. The 8 countries shown in the chart made up 79% of wind energy capacity in 2005 and 82% at the end of 2010. So obviously many of other countries are managing to add capacity nearly as quickly as the leading countries.
USA capacity grew 339% from 2005 through 2010 (far below China but above the global increase). Germany and Spain were leaders in building capacity early; from 2005 to 2010 Germany only increased 48% and Spain just 106%. Japan is an obvious omission from this list; given the size of their economy. Obviously they have relied heavily on nuclear energy. It will be interesting to see if Japan attempts to add significant wind and solar energy capacity in the near future.
Related: Nuclear Power Production by Country from 1985-2009 – Top Countries For Renewable Energy Capacity – Wind Power Capacity Up 170% Worldwide from 2005-2009 – USA Wind Power Installed Capacity 1981 to 2005 – Oil Consumption by Country 1990-2009
The unemployment rate fell from 9.0% to 8.6% in November, however that is not an accurate representation of employment in the USA. The news is good, but very mildly good, while a decrease in the unemployment rate by 40 basis points would lead you to believe the improvement was dramatic. Nonfarm payroll employment rose by 120,000 which is about the number needed to keep up with population growth each month. Employment continued to trend up in retail trade, leisure and hospitality, professional and business services, and health care. Government employment continued to trend down.
The change in total nonfarm payroll employment for September was revised from +158,000 to +210,000, and the change for October was revised from +80,000 to +100,000. This means this report shows an increase of 192,000 jobs which is pretty good news (especially for those that think the economy has been in a recession – it has not).
One year ago the unemployment rate stood at 9.6%.
The number of unemployed persons, at 13.3 million, was down by 594,000 in November. The labor force, which is the sum of the unemployed and employed, was down by a little more than half that amount. What this means is the reduction in the unemployment rate was largely due to the decrease in those actively looking for jobs.
Among the major worker groups, the unemployment rate for adult men fell to 8.3% in November. The jobless rate rates for adult women (7.8%), teenagers (23.7%), African-Americans (15.5%), and Hispanics (11.4%) showed little or no change. The jobless rate for Asians was 6.5%.
The number of long-term unemployed (those jobless for 27 weeks and over) was little changed at 5.7 million and accounted for 43.0% of the unemployed. This is one of the numbers that has to come down drastically for the job situation to really show good improvement.
Related: Jobs News in the USA is not Good, Unemployment Remains at 9.1% (Aug 2011) – USA Economy Adds 151,000 Jobs in October, Unemployment Rate Steady at 9.6% (Oct 2010) – Unemployment Rate Reached 10.2% (Oct 2009) – Over 500,000 Jobs Disappeared in November (2008)
I try to find global economic data on manufacturing and manufacturing jobs, but it isn’t easy. This is one of the areas I will be working on with the time I have freed up by moving to Malaysia (and taking a “sabbatical” [it isn't really a sabbatical, I guess, just me studying and working on what I want to instead of what someone pays me to]).
I found some interesting data from the USA census bureau on manufacturing employment in several countries (it would be interesting to see the data for more countries but for now I am limited to this data). Sadly they just use indexed data (I would rather see raw data). This data for example lets you see the changes in countries but I don’t see any way to compare the absolute values between countries – all you can compare is the changes between countries.
The data is all indexed at 2002 = 100. Interestingly the USA has increased output per hour much more than any other country since 2002. The USA index stands at 146, the next highest is Sweden at 127 then the UK at 120. Italy is the only country tracked that fell since 2002, to 94. Japan (the 3rd largest manufacturer and 2nd largest of the countries include, China isn’t included) only increased to 113. Germany (4th and 3rd) increased to 111.
The data also lets you look back from 1990 to 2002 and again the USA has increased productivity very well (2nd most) – the value in 1990 was 58. Sweden actually had the largest gain from 1990-2002, rising from 49. In 1990 Japan stood at 71 and Germany 70.
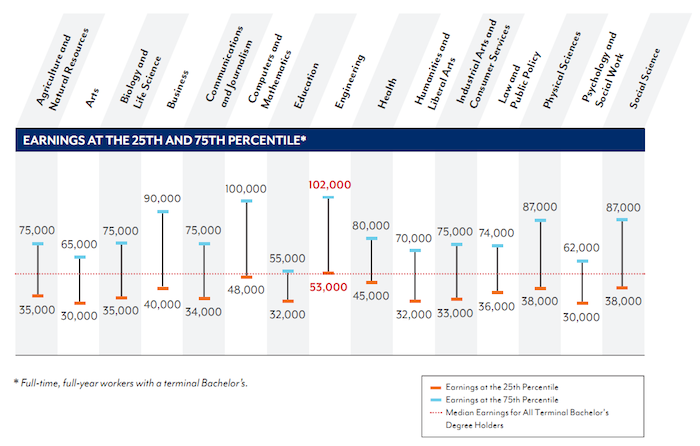
Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce has produced a new report looking at the value of different college degrees in the USA. I have seen a great increase in discussions of the “bubble” in education. Those articles often say a college degree doesn’t assure the success it used to. The data I review seems to show extremely large benefits for those with a college degree (higher salaries but, much more importantly, in my opinion, they also have much lower unemployment rates).
Those benefits are greatest for several majors including science, math and engineering. The problem I see is not so much that significant benefits are lacking for college degrees but the huge increases in costs of getting a degree are so large that for some majors the cost is just so large that even with the benefits it is arguable whether it is worth the cost (while a few decades ago the benefits were universal and so large the economic benefit was not debatable).
The authors of the report found that all undergraduate majors are worthwhile, even taking into account the cost of college and lost earnings. However, the lifetime advantage ranges from $1,090,000 for Engineering majors to $241,000 for Education majors. As I have written frequently on the Curious Cat Science and Engineering blog, engineering degrees are very financially rewarding.
The top 10 majors with the highest median earnings for new graduates are:
- Petroleum Engineer ($120,000)
- Pharmacy/pharmaceutical Sciences and Administration ($105,000)
- Mathematics and Computer Sciences ($98,000)
- Aerospace Engineering ($87,000)
- Chemical Engineering ($86,000)
- Electrical Engineering ($85,000)
- Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering ($82,000)
- Mechanical Engineering, Metallurgical Engineering and Mining and Mineral Engineering (each with median earnings of $80,000)
Related: 10 Jobs That Provide a Great Return on Investment – Mathematicians Top List of Best Occupations – New Graduates Should Live Frugally
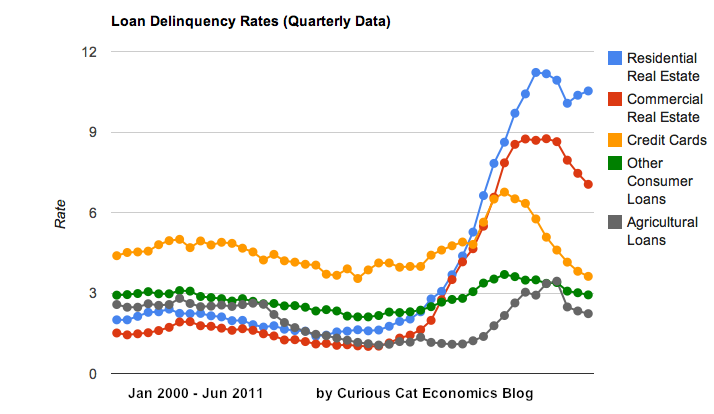
Chart showing loan delinquency rates from 2000-2011, shows seasonally adjusted data for all banks for consumer and real estate loans. The chart is available for use with attribution. Data from the Federal Reserve.
Residential real estate delinquency rates increased in the first half of 2011 in the USA. Other debt delinquency rates decreased. Credit card delinquency rates have actually reached a 17 year low.
While the job market remains poor and the serious long term problems created by governments spending beyond their means (for decades) and allowing too big to fail institutions to destroy economic wealth and create great risk for world economic stability the USA economy does exhibit positive signs. The economy continues to grow – slowly but still growing. And the reduction in delinquency rates is a good sign. Though the residential and business real estate rates are far far too high.
Related: Consumer and Real Estate Loan Delinquency Rates 2000-2010 – Real Estate and Consumer Loan Delinquency Rates 1998-2009 – Government Debt as Percent of GDP 1998-2010 for OECD
After World War II essentially the only significantly large industrial base was in the USA. The USA was emerging as a national power in the early 1900′s. The wake of World War I and World War II left a very odd situation. You had many formerly very rich countries that were devastated and one rich country that wasn’t. Devastation is not easy to overcome in even 20 years. So for a good 2 decades the USA got wealthier and wealthier even while other formerly rich countries were re-developing there countries rapidly.
This made the USA even richer as selling to all those around the world was pretty easy, just creating enough stuff was the hardest part. Almost none of the current emerging markets were doing much of anything economically. This resulted in the USA being able to live incredibly well and generate enormous wealth.
The main legacy of this is a huge benefit to the USA – enormous wealth and experience. However, it seems to have left people thinking the USA is just suppose to be enormously wealthy always no matter if we throw away hundreds of billions a year on a broken health care system, provide huge benefits to political donors (farmers or bankers or phone oligopolists or robbers of the public domain [preventing innovation through repressive, outdated "intellectual property" regimes]), spending many hundreds of billions yearly on military expenditures far beyond those of any other country… It doesn’t work that way.
You can waste huge amounts of economic benefit when you are the dominant economic power globally. And when you were as rich as the USA was in the 1950s and 1960s more and more people felt they deserved to be favored with economic gifts. So for a a few decades the USA used the excess wealth to pay off all sorts of special interests and still do very well economically. The only thing surprising is how long we have been able to keep this up.
It isn’t rational to base expectations on periods when we were granted economic wealth largely by virtue of the world industrial production, other than ours, being destroyed. This isn’t the only reason we were wealthy, we do many things very well (compared to other countries) entrepreneurship, less corruption (still way too much but less than average), from 1950 to about 1990 an equitable distribution of economic gains, until recently a good advanced education system, a brilliant system to turn science and engineering breakthroughs into economic profit (that in the last few decades other countries are starting to do, but they are still way behind)…
From 1970s until say the 2000s we could use our accumulate wealth to live off and not allow huge inefficiencies to continue (lousy job of regulating banks, lousy job of subsidizing farming, lousy job of subsidizing lousy food [making it cheap to eat unhealthy food and expensive to eat healthy food], lousy job of controlling the costs of higher education, lousy job of getting people to realize they cannot expect to live far beyond most everyone else in the world just because they were born in the USA…
Read more