Why delhi’s buses are so deadly: an economic analysis
…
Which is why the last thing a Blueline driver ever wants to do is come to a stop. Every move he makes is done with the intent of keeping the bus in motion: slowing just enough so debarking passengers can jump off, then picking up speed as the new passengers run alongside the bus, swinging themselves up and in as the conductor screams at them to hurry.
…
But with an estimated 2,200 Blueline buses careening across Delhi on any given day, it’s no wonder the newspaper reports are almost identical every day. After an accident, the driver tries to flee, an angry mob beats him, the police impound the bus, the driver is thrown in jail, the owner of the bus is not mentioned. Sometimes the driver escapes, in which case the mob finds its release in setting fire to the bus.
This is a good example of looking at problems economically. It also shows the problem with failure to regulate. I am perfectly happy to live with regulation that removes the economic pressure to risk human life.
Related: Failing Infrastructure in the USA – International Development Fair: The Human Factor – China May Take Car Sales Lead from USA in 2009
Health Care: Lessons for America
It switched to a system that separates insurance from employment. Each individual or family is required to buy coverage, and insurers must offer a basic package of benefits to all applicants. They can’t profit from selling basic coverage, but they can from supplemental plans. Premiums are deducted from paychecks; the unemployed and poor are subsidized.
Despite opposition from insurers, drugmakers, and business, the plan passed by a bare majority and went into effect in 1996. Switzerland now spends 11% of its gross domestic product on health care, just as it did before. But everyone is covered, insurers are more profitable than ever, and its high-quality health care has been maintained.
The lesson, as laid out in The Healing of America: A Global Quest for Better, Cheaper, and Fairer Health Care, by T.R. Reid, is that “health-care systems can be changed, even in the face of powerful…interests.”
…
Many Americans boast about having the best health care in the world, even though the U.N. ranks the U.S. system 37th, based on a broad range of measurements
…
At the same time, he learned that almost all countries use one of four health-care models: Germany’s Bismarck system, in which hospitals and insurers are private entities and financing comes from payroll deductions; Britain’s Beveridge Model, with the government providing health care financed by taxes; the Canadian plan, where private doctors and hospitals are paid by the government through taxes; and the out-of-pocket care found in most poor nations, where those who can afford care get it, while the rest suffer or die. Unlike any other country, the U.S. combines all four models
Related: posts on the economics of health care – Broken Health Care System: Self-Employed Insurance – Many Experts Say USA Health-Care System Inefficient, Wasteful – USA Spent $2.2 Trillion, 16.2% of GDP, on Health Care in 2007 – International Health Care System Performance
Mark Mobius is an investment manager with Franklin-Templeton that I have invested with for over a decade (through the Templeton Emerging Markets Trust and Templeton Dragon Fund – they are closed end funds). I believe in Templeton’s emerging market investment team and Mark Mobius and believe his thoughts are worth paying attention to. He recently wrote an overview on Emerging Markets:
…
In Mexico, GDP contracted 10% y-o-y in the second quarter of 2009 as a result of the global economic crisis and swine flu outbreak. In comparison, GDP fell 8% in the first quarter of the year. Declines in the manufacturing, construction and retail sectors had negatively impacted GDP during the period.
…
Since 1995, portfolio inflows into emerging markets have totaled more than US$123 billion. A significant amount, considering it includes the US$49 billion in net outflows in 2008 as a result of the global financial crisis. The recovery in emerging markets and hunt for attractive investment opportunities, however, saw these funds return just as quickly with inflows totaling more than US$44 billion in the first seven months of 2009, nearly 90% of the outflows registered all of last year.
…
Emerging markets account for more than 80% of the world’s population. With economic growth accelerating and population growth decelerating, per capita income is one the rise. In our view, markets such as China, India and Brazil stand at the front of the class.
…
As of end-August 2009, the benchmark MSCI Emerging Markets index had a P/E of 16 times, cheaper than the MSCI World index which was trading at a P/E of 21 times.
There are several issues with economic data, as I have mentioned before. These issues have to be considered when analyzing economic data and being financially literate requires an understanding of the problems with economic data. The political pressures for manipulating the data to appear good exist is every country. The practical difference is the other forces that push for data that is more accurate (businesses, investors, economists… need accurate data to succeed) and practices that have been adopted to provide accurate data.
Foreign Policy magazine takes a look at problems in How China Cooks Its Books
But local and provincial governmental officials are the ones who actually fiddle with the numbers. They retain considerable autonomy and power, and have a self-interested reason to manipulate economic statistics. When they reach or exceed the central government’s economic goals, they get rewarded with better jobs or more money. “The higher [their] GDP [figures], the higher the chance will be for local officials to get promoted,” explained Liu.
…
Last October, Vice Premier Li Keqiang said in a speech after inspecting China’s Statistics Bureau, “China’s foundation for statistics is still very weak, and the quality of statistics is to be further improved” — a brutally harsh assessment coming from a top state official.
…
China’s economy grew at an annualized 6.1 percent rate in the first quarter, and 7.9 percent in the second. Yet electricity usage, a key indicator in industrial growth and a harder metric to manipulate, declined 2.2 percent in the first six months of the year. How could an economy largely dependent on manufacturing grow while its industrial sector shrank? It couldn’t; the numbers don’t add up
My guess is China’s data is highly questionable and still China’s economy is fairly strong. But because the data is so questionable it does make the risks of being wrong on that guess fairly high. Even the US government data is flawed: it is no surprise China’s data is less reliable.
Related: Is China’s Recovery for Real? – Misuse of Statistics – Mania in Financial Markets – Manufacturing Employment Data – 1979 to 2007 – The Long-Term USA Federal Budget Outlook –
Data Shows Subprime Mortgages Were Failing Years Before the Crisis Hit
Welcome to the Curious Cat Investing and Economics Carnival, we hope you enjoy the following posts we share here.
- Does Earning More Trump Frugality? – “Which way is better? I think there’s a different answer for each person, actually. For some people, the bird in the hand is better – if you have a career that isn’t helped by such networking, for example. For others, building your presence might be more valuable than a frugality task.”
- Existing Home Sales Far Worse Than Advertised by Barry Ritholtz – “While the very worst of housing trouble may be behind us, we are still looking at falling prices and increasing foreclosures. The Housing getting worse more slowly camp is ignoring the massive Federal subsidies required to get worse more slowly.”
- Loan Delinquency Rates Increased Dramatically in the 2nd Quarter by John Hunter – “Default rates on commercial (up another 151 basis points) and residential (up 93 basis points) real estate continued to increase dramatically in the second quarter. Credit card default rates increased but only by 20 basis points.”
- Don’t Bet On A V-shaped Economy Recovery – “Banks’ restrictive lending, unemployment, stagnant wages and falling home values resulted in reluctance of households to borrow money for spending. With debt weary US consumers (which accounts for 70% US GDP), the US economy and export markets will not be in a hurry to rush into a V-shaped recovery even as the recession eases.”
- Tips for Managing Your 401k Plan by Patrick – “Max out company match. If your company offers matching contributions, then you should contribute at least the amount of the full company match if you can afford it. The company match is part of your benefits package and is essentially free money.”
- Deciphering the GDP Numbers by Philip – “Federal Spending: Federal Spending grew 10.9%, as compared with a drop of 3% in the previous quarter. This number tells you what a big cushion the economy got from the various stimulus programs that the government ran. Without the stimulus, the numbers would have been much worse than they were”
China’s recovery: Is it for real?
…
Investors don’t need to answer or even be interested in those philosophical questions. But they do need to consider the possibility that China’s huge acceleration in its growth rate is merely an artifact of the way the country keeps its books.
Economic data is often messy and confusing. The data itself often has measurement error. The actual aim is often not exactly what people think. And the data is often delayed so it provides a view of the situation, not today, but in the past and guesses must be made about what that says about today and the future.
And on top of those factors many countries feel significant internal pressures to report numbers that make the current economy look good. This is just another factor investor must consider when looking to make investments and evaluate economic conditions.
It seems to me the Chinese recovery does look real. How strong the economy will be 6 months from now is less clear but right now things look positive to me.
Related: posts on economic data – What Do Unemployment Stats Mean? – China Manufacturing Expands for the Fourth Straight Month (Jun 2009) – A Bull on China
The Greenback Effect by Warren Buffett
…
Because of this gigantic deficit, our country’s “net debt” (that is, the amount held publicly) is mushrooming. During this fiscal year, it will increase more than one percentage point per month, climbing to about 56 percent of G.D.P. from 41 percent. Admittedly, other countries, like Japan and Italy, have far higher ratios and no one can know the precise level of net debt to G.D.P.
…
Legislators will correctly perceive that either raising taxes or cutting expenditures will threaten their re-election. To avoid this fate, they can opt for high rates of inflation, which never require a recorded vote and cannot be attributed to a specific action that any elected official takes.
…
Our immediate problem is to get our country back on its feet and flourishing — “whatever it takes” still makes sense. Once recovery is gained, however, Congress must end the rise in the debt-to-G.D.P. ratio and keep our growth in obligations in line with our growth in resources.
Unchecked carbon emissions will likely cause icebergs to melt. Unchecked greenback emissions will certainly cause the purchasing power of currency to melt. The dollar’s destiny lies with Congress.
Related: Warren Buffett Webcast on the Credit Crisis – The Long-Term USA Federal Budget Outlook – Berkshire Hathaway Annual Meeting 2008 – Federal Reserve to Buy $1.2 Trillion in Bonds, Mortgage-Backed Securities
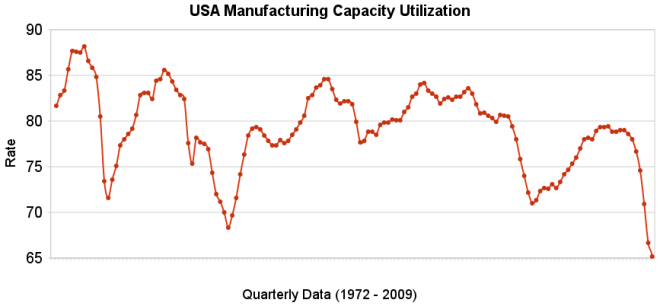 The chart shows the capacity utilization rate in the USA. By Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.
The chart shows the capacity utilization rate in the USA. By Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.Industrial production increased .5% in July and capacity utilization rate increased to 68.5% from an all time low of 68.1%. Capacity utilization has averaged 80.9% from 1972 to today.
Manufacturing output increased 1.0% in July but remained 14.4% lower than its year-earlier level. The factory operating rate rose to 65.4% in July, 70 basis points above the historical low recorded in June; the series begins in 1948. Production in durable goods industries advanced 2.2% in July. In addition to the sharp increase in motor vehicles and parts output, large production gains occurred for nonmetallic mineral products and for primary metals. The indexes for wood products, computer and electronic products, aerospace and miscellaneous transportation equipment, furniture and related products, and miscellaneous goods also rose. The indexes for fabricated metal products, machinery, and electrical equipment declined.
The production of nondurable goods fell 0.1% in July. The indexes for textile and product mills and for printing and support recorded sizable declines; the indexes for food, beverages, and tobacco and for petroleum and coal products also declined. The output of paper, of chemicals, and of plastic and rubber products increased.
The index for other manufacturing, which consists of publishing and logging, was down 0.6% in July.
The output of electric and gas utilities decreased 2.4%, and the operating rate for utilities dropped 21 basis points, to 77.6%. Mining production moved up 0.8%; its utilization rate in July, at 81.7%, was 59 basis points below its 1972-2008 average.
Data from the St. Louis Federal Reserve and Federal Reserve August 14th Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization press release.
Related: Loan Default Rates: 1998-2009 – Government Debt as a Percentage of GDP – USA Spent $2.2 Trillion, 16.2% of GDP, on Health Care in 2007
Read more
The behavior of banks is despicable enough when they are merely trying to trick educated, financially secure people out of their money. Banks charged $38.5 billion in fees last year according to the Financial Times. But that behavior, toward the poor, by banks (paying millions to hundreds of executives for, I guess, getting congress to send the companies billions) is immoral.
The Gates Foundation has decided to go into improving financial services for the poor. The are supporting micro-credit but also micro finance. Saving is key for poor people to get and stay out of poverty. Most already save money informally but want better, safer options. Setting aside money in a safe place will allow poor people to weather setbacks, build assets and financial security, and invest in opportunities for the next generation. Formal savings accounts also help them keep more of what they earn and easily access their money when they need it.
The poor need better banking options in poor countries. But the poor need better banking options in at least one rich country (the only one I know is the USA and banks in the USA provide lousy options for the poor). Credit Unions are much more likely to actually try and provide value to customers. Unfortunately banks in the USA seem to operate on the principle that customer are suckers that exist to pay for Porches for the children of bank executives.
Related: FDIC Study of Bank Overdraft Fees – Microfinancing Entrepreneurs – Incredibly Bad Customer Service from Discover Card – 10 Things Your Bank Won’t Tell You
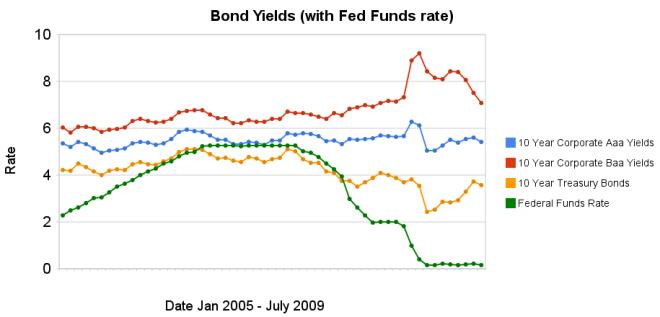 Chart showing corporate and government bond yields by Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.
Chart showing corporate and government bond yields by Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.The changes in bond yields over the last 3 months months indicate a huge increase in investor confidence. The yield spread between corporate Baa 10 year bonds and 10 year treasury bonds increased 304 basis points from July 2008 to December 2008, indicating a huge swing in investor sentiment away from risk and to security (US government securities). From April 2009 to July 2009 the yield spread decreased by 213 basis points showing investors have moved away from government bonds and into Baa corporate bonds.
From April to July 10 year corporate Aaa yields have stayed essentially unchanged (5.39% to 5.41% in July). Baa yields plunged from 8.39% to 7.09%. And 10 year government bond yields increased from 2.93% to 3.56%. federal funds rate remains under .25%.
Investors are now willing to take risk on corporate defaults for a much lower premium (over government bond yields) than just a few months ago. This is a sign the credit crisis has eased quite dramatically, even though it is not yet over.
Data from the federal reserve: corporate Aaa – corporate Baa – ten year treasury – fed funds
Related: Continued Large Spreads Between Corporate and Government Bond Yields (April 2009) – Chart Shows Wild Swings in Bond Yields (Jan 2009) – investing and economic charts