The New Paradigm for Financial Markets is George Soros‘ newest book. Here is an interview with him in May of this year, on PBS, Financial World Shifts Gears Amid Economic Tumult, about the ideas in the book and the current crisis.
GEORGE SOROS: I think this is the most serious crisis of our lifetime. It’s not just a housing crisis, but a crisis of the financial system.
…
GEORGE SOROS: The regulators have failed to regulate, and they really have to — they left it to the market. That was this market fundamentalist philosophy, that markets will take care of themselves.
…
And I contend that there’s been what I call a super bubble that has been growing over the last 25 years at least, which basically consisted of an extension in credit, increasing use of leverage. That was the trend in reality.
And the misconception that credit is that markets can be left to their own devices. Now, in fact, they are given to excesses, and occasionally they create crises, but each time the authorities intervene and bail out the failing institutions, provide fiscal stimulus, monetary stimulus.
So it seems like the market corrects itself, but it’s actually the intervention of the authorities that saves the market.
Related: Soros on the Financial Market Collapse – Jim Rogers on the Financial Market Mess – Leverage, Complex Deals and Mania
FDIC Details Plan To Alter Mortgages
…
Agency officials estimated the cost to the government at $22.4 billion.
…
The mortgage industry is concerned that any new modification plan will persuade some people to stop making mortgage payments in addition to helping people who already have stopped making payments. The industry argues this will translate into higher interest rates because investors will demand compensation for the increased risk of loan defaults. That, in turn, would limit the number of people who can afford mortgage loans.
…
FDIC estimates that 1.4 million borrowers with such loans are at least two months late on their payments, and another 3 million borrowers will miss at least two payments by the end of next year. The agency estimates that half those borrowers, or about 2.2 million people, would receive a loan modification under the program, and that about 1.5 million will successfully avoid foreclosure.
Under the terms of the proposed FDIC program, lenders would reduce monthly payments primarily by cutting the borrower’s interest rate to a minimum rate of 3 percent. If necessary, the company could also extend the repayment period on the loan beyond 30 years, reducing each monthly payment. Finally, in some cases, companies could defer repayment of some principal. The borrower still would be on the hook for the full value of the loan.
Officials said their experience at IndyMac showed that principal reductions were not necessary. So far, FDIC has modified about 20,000 IndyMac loans. In 70 percent of the cases, FDIC was able to create an affordable payment solely by reducing the interest rate. In 21 percent of the cases, the agency also extended the life of the loan. In 9 percent of the cases, it delayed repayment of some principal.
An interesting proposal I would support. Ideally this type of action would not be necessary but since banks were allowed to degrade their standards so far and allowed to grow so large their failures threaten the economy some radical actions are being taken. Compared to many others this is sensible.
Related: How Much Worse Can the Mortgage Crisis Get? – JPMorgan Chase Freezes Mortgage Foreclosures – Fed Plans To Curb Mortgage Excesses (Dec 2007)
It doesn’t take much effort to notice the economic news is increasingly dire. And this is not just a few alarmist reports, the economy is in serious trouble. The decades of spending beyond their means (for consumers and those the consumers elected to run government) are creating a very difficult situation. And the credit crisis precipitating the current slide has brought to light many failures to properly regulate the economy. U.S. Slump May Be Longest in Decades as Growth Fell Off ‘Cliff’
The implosion of credit markets last month will cause the economy to shrink at a 3 percent annual rate in the fourth quarter and decline at a 1.5 percent pace in the first three months of 2009, according to the median estimate of 59 economists surveyed Nov. 3 to Nov. 11. Following last quarter’s 0.3 percent drop, the slump would be the longest since 1974-75.
…
Falling demand will cause an even bigger increase in unemployment than projected last month. Economists surveyed forecast the jobless rate will rise to 7 percent in the first quarter of 2009, up from last month’s forecast of 6.6 percent. The rate will climb to 7.7 percent by the end of 2009, the highest level since 1992, the survey showed.
The jobless rate rose to 6.5 percent in October, the highest since 1994
There is little doubt the economy is in for serious trouble. What investment moves are wise now is less obvious. I have been buying during the decline and continue to do so. I bought some Google yesterday at the same price I first bought Google for several years ago. I think in 10 years that will pay off quite well, but time will tell. My purchases of Google earlier this year would obviously have been better if I had made them yesterday than when I did.
I discussed the Economic Crisis on my Curious Cat Management Blog last month:
One of the challenges with personal financial matters is they are by nature long term issues. What you did over the last 5 years cannot be fixed in a few weeks, most likely it takes years.
Related: Stock Market Decline – Bad News on Jobs
Consumer debt gets bailout attention
…
“Approximately 40 percent of U.S. consumer credit is provided through securitization of credit card receivables, auto loans and student loans and similar products. This market, which is vital for lending and growth, has for all practical purposes ground to a halt.”
The Next Meltdown: Credit-Card Debt
…
Innovest estimates that credit-card issuers will take a $41 billion hit from rotten debt this year and a $96 billion blow in 2009.
…
Risky borrowers with low credit scores account for roughly 30% of outstanding credit-card debt, compared with 11% of mortgage debt. More than 45% of Washington Mutual’s credit-card portfolio is subprime, according to Innovest.
Related: Americans are Drowning in Debt – How to Use Your Credit Card – Credit Crisis (Aug 2007) – Curious Cat Economics Search Engine
Singapore is again ranked first for Ease of Doing Business by the World Bank. For some reason they call the report issued in any given year as the report for the next year (which makes no sense to me). The data shown below is for the year they released the report.
| Country | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| New Zealand | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| United States | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Hong Kong | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Denmark | 5 | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| United Kingdom | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 |
| Ireland | 7 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
| Canada | 8 | 7 | 4 | 4 |
| other countries of interest | ||||
| Japan | 12 | 12 | 11 | 12 |
| Germany | 25 | 20 | 21 | 21 |
| France | 31 | 31 | 35 | 47 |
| Korea | 23 | 30 | 23 | 23 |
| Mexico | 56 | 44 | 43 | 62 |
| China | 83 | 83 | 93 | 108 |
| India | 122 | 120 | 134 | 138 |
| Brazil | 125 | 122 | 121 | 122 |
The rankings include ranking of various aspects of running a business. Some rankings for 2008: starting a business (New Zealand 1st, Singapore 10th, USA 6th, Japan 64th), Dealing with Construction Permits (St. Vincent and the Grenadines 1st, Singapore and New Zealand 2nd, USA 26th, China 176th), Employing Workers (Singapore and the USA 1st, Germany 142, Korea 152), protecting investors (New Zealand 1st, Singapore 2nd, Hong Kong 3rd, Malaysia 4th, USA 5th), enforcing contracts (Singapore 1, Hong Kong 2, USA 6, China 18), getting credit (Malaysia 1; UK and Hong Kong 2; Singapore, New Zealand and USA 5th), paying taxes (Maldives 1, Hong Kong 3, USA 46, Japan 112, China 132).
These rankings are not the final word on exactly where each country truly ranks but they do provide a valuable source of information. With this type of data there is plenty of room for judgment and issues with the data. Several of my posts, from my other blogs, that I recommend on this topic: The Future is Engineering, Science and Engineering in Global Economics Read more
So few economists foresaw the current credit disaster, New York Times interview of James Galbraith.
Dr. Galbraith: Ten or 12 would be closer than two or three.
NYT: What does that say about the field of economics, which claims to be a science?
Dr. Galbraith: It’s an enormous blot on the reputation of the profession. There are thousands of economists. Most of them teach. And most of them teach a theoretical framework that has been shown to be fundamentally useless.
NYT: You’re referring to the Washington-based conservative philosophy that rejects government regulation in favor of free-market worship?
Dr. Galbraith: Reagan’s economists worshiped the market, but Bush didn’t worship the market. Bush simply turned over regulatory authority to his friends. It enabled all the shady operators and card sharks in the system to come to dominate how we finance.
Related: Rodgers on the US and Chinese Economies – Greenspan Says He Was Wrong On Regulation – Leverage, Complex Deals and Mania – What is Economics?
In a recent article in Business Week Michael E. Porter makes some excellent points – Why America Needs an Economic Strategy:
Second, U.S. entrepreneurship has been fed by a science, technology, and innovation machine that remains by far the best in the world. While other countries increase their spending on research and development, the U.S. remains uniquely good at coaxing innovation out of its research and translating those innovations into commercial products.
…
Third, the U.S. has the world’s best institutions for higher learning, and they are getting stronger. They equip students with highly advanced skills and act as magnets for global talent, while playing a critical role in innovation and spinning off new businesses.
Fourth, America has been the country with the strongest commitment to competition and free markets.
…
An inadequate rate of reinvestment in science and technology is hampering America’s feeder system for entrepreneurship. Research and development as a share of GDP has actually declined, while it has risen in many other countries.
…
A creeping relaxation of antitrust enforcement has allowed mergers to dominate markets. Ironically, these mergers are often justified by “free market” rhetoric. The U.S. is seeing more intervention in competition, with protectionism and favoritism on the rise. Few Americans know that the U.S. ranks only 20th among countries in openness to capital flows, 21st on low trade barriers, and 35th on absence of distortions from taxes and subsidies
I have discussed similar idea in this blog and the Curious Cat Science and Engineering Blog: The Future is Engineering – Engineering the Future Economy – Science Gap – Not Understanding Capitalism
More dramatic evidence that changing in the federal funds rate do not lead to similar changes in 30 year fixed mortgage rates. It is true the last few months are very unusual times for the credit market. However, the current lack of correlation is not the exception, the graph clearly shows there is very little correlation between changes in the two interest rates.
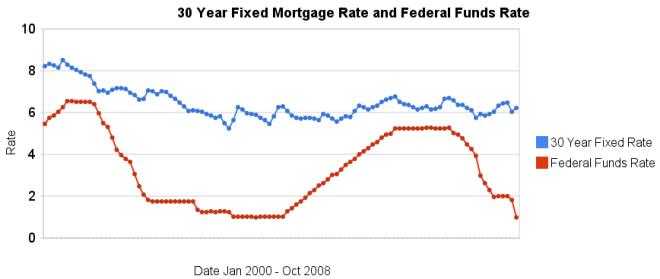
Related: historical comparison of 30 year fixed mortgage rates and the federal funds rate – Affect of Fed Funds Rates Changes on Mortgage Rates – posts on financial literacy – Jumbo v. Regular Fixed Mortgage Rates: by Credit Score
For more data, see graphs of the federal funds rate versus mortgage rates for 1980-1999. Source data: federal funds rates – 30 year mortgage rates
As many as 10,000 corrupt government officials have fled China with $100 billion.
More unexpected, however, was the heavy press coverage that Yang’s walkabout attracted in a country where the government is generally reluctant to wash its dirty linens in public. That suggests that “the government is sending a signal” that it regards “the number of officials fleeing as a very important problem which needs to be solved,” says Mao Zhaohui, director of anticorruption studies at Beijing’s Renmin University.
Corruption is pervasive at almost every level of the government, and it is a major factor eroding faith in the ruling Communist Party. Earlier this year, after thousands of schoolchildren died in the Sichuan earthquake, the Internet was ablaze with accusations that local officials had taken bribes to approve substandard materials for school construction.
Chinese President Hu Jintao has repeatedly declared that the fight against fraud is a top government priority and courts have handed down heavy sentences against prominent offenders. Last year, the former head of the Chinese Food and Drug Administration, Zheng Xiaoyu, was executed after being found guilty of taking bribes to approve thousands of new drugs.
China has many strong winds for economic growth. Corruption is an anchor holding back their progress.
Related: Capitalism in China – Not Understanding Capitalism – Oil Consumption by Country – Data on Leading Manufacturing Countries – Curious Cat Economics Search Engine
The USA national debt decreased almost $1 billion yesterday. If it decreased by $1 billion dollars a day in just 10,526 days the USA government would be out of debt. That is just under 29 years, that doesn’t seem so bad. Unfortunately the decrease yesterday is not likely the start of a new trend (it is just daily variation).
In the last month the debt is up over $580 Billion. At that rate, well lets just say if that rate continued long we would be in even more serious trouble than we have been placed in by the amazingly irresponsible behavior of the politicians increasing taxes on our grandchildren (with massive spending they chose to fund by huge tax increases on our grandchildren) have been doing the last 5 years. In the last year they have spent $1.46 Trillion more than they paid for (which will have to be paid for by future taxes – although the recent decision to purchase $125 billion in bank stocks perhaps opens another option for the the government to start buying companies and use profits they make to pay off the debt they are taking on).
The current debt stands at $10,525,823,144,117. That is a bit over $10.5 Trillion.
Related: True Level of USA Federal Deficit – USA Federal Debt Now $516,348 Per Household – Washington Paying Out Money it Doesn’t Have