Canada’s banking system kept high and dry by strict regulation: Flaherty
…
Some of the fundamentals credited with keeping Canada’s banks in the safe zone were put in place nearly a decade ago by the Liberal government of Jean Chretien, including a refusal to approve any Canadian bank mergers.
…
The finance minister said Canada is in a strong position to deal with the global crisis, with a strong banking system, a stable housing market and a federal budget surplus. “Other countries have been increasing their deposit standards, but they’re still for the most part below the high Canadian standard,” he said.
Related: Monopolies and Oligopolies do not a Free Market Make – Too Big to Fail – What Should You Do With Your Government “Stimulus” Check? – The Budget Deficit, the Current Account Deficit and the Saving Deficit – 2nd Largest Bank Failure in USA History
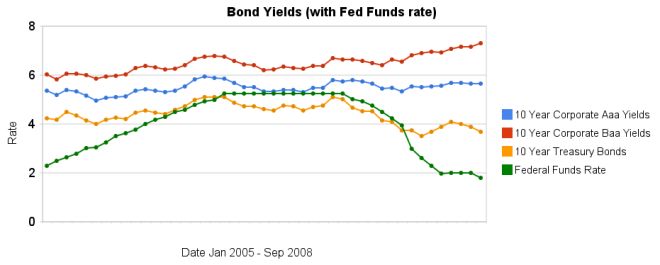
Over the last 3 months the yields on corporate bonds have increased while treasury bonds have decreased. The chart shows the move away from lower quality bonds to higher quality though probably not as dramatically as actually has taken place as it is just an average for each month (and in September the flight to quality became extreme at the end of the month). While the Fed did not announce a formal cut in the discount rate, the average rate for overnight loans from the Fed last month was 1.81%.
The spread between 10 year Aaa corporate bond yields and 10 year government bonds increased to 196 basis points. In January, 2008 the spread was 159 points. The larger the spread the more people demand in interest, to compensate for the increased risk. The spread between government bonds and Baa corporate bonds increased to 362 basis points, the spread was 280 basis point in January. The rate on government bonds has barely change (decreasing from 3.74% in January to 3.69% now) so the change has nearly all been in increased corporate bond rates.
Data from the federal reserve – corporate Aaa – corporate Baa – ten year treasury – fed funds
Related: Bond Yields 2005 to June 2008 – 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates versus the Fed Funds Rate – Curious Cat Investing and Economics Search – posts on interest rates
I would say the chance of a depression in the next 5 years is very unlikely. The last 2 years have been full of bad economic news but a depression is still not likely, in my opinion. However, much of the public, seems to think it is likely – Poll: 60% say depression ‘likely’
* 25% unemployment rate
* Widespread bank failures
* Millions of Americans homeless and unable to feed their families
In response, 21% of those polled say that a depression is very likely and another 38% say it is somewhat likely. The poll also found that 29% feel a depression is not very likely, while 13% believe it is not likely at all.
…
The economists surveyed by CNNMoney.com said they saw a drop of 2% to 4% in a worst case scenario.
I must say I don’t think those polled don’t really hold their belief very firmly. If you actually see a depression as likely you have to take drastic steps with your finances. I really doubt many of them are and instead think they are casually saying they think it is likely without really thinking about what that would mean.
I don’t see it as likely and don’t see any need to change significantly what made good personal financial sense 2 years ago. The biggest change I see (over the last couple of months) is the importance of taking smart person finance actions has increased dramatically. The smart moves are pretty much the same but the risks to failing to create an emergency fund, abusing your credit card, losing a job… have increased dramatically.
Related: Uncertain Economic Times – Personal Finance Basics: Health Insurance – Financial Illiteracy Credit Trap
Warren Buffett quotes from the interview:
|
- “AIG would be doing fine today if they never heard of derivatives… I said they were possibly financial weapons of mass destruction and they have been, I mean they destroyed AIG, they certainly contributed to the destruction of Bear Stearns and Lehman”
- The biggest single cause was that we had an incredible residential real estate bubble.
- [on consuming more than we are producing] I don’t think it is the most pressing problem at all. We are trading away a little bit of our country all the time for the excess consumption that we have, over what we produce. That is not good. I think it is terrible over time.
Related: Warren Buffett related posts – Credit Crisis Continues – Credit Crisis (August 2007)
The FDIC limit has been raised to $250,000 which is a good thing. The increased limit is only a temporary measure (through Dec 31, 2009) but hopefully it will be extended before it expires. I don’t see anything magical about $250,000 but something like $200,000 (or more) seems reasonable to me. The coverage level was increased to $100,000 in 1980.
What does federal deposit insurance cover?
FDIC insurance covers funds in deposit accounts, including checking and savings accounts, money market deposit accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs). FDIC insurance does not, however, cover other financial products and services that insured banks may offer, such as stocks, bonds, mutual fund shares, life insurance policies, annuities or municipal securities.
Joint accounts are covered for $250,000 per co-owner. The limit is per person, per institution, so all your accounts at one institution are added together. If you have $200,000 in CDs and $100,000 in savings you would have $50,000 that is not covered.
FDIC is an excellent example of good government in action. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) was created in 1933 and serves to stabilize banking by eliminating the need to get ahead of any panic about whether the bank you have funds in is in trouble (which then leads to people creating a run on the bank…)
From an FDIC September 25 2008 news release: the current FDIC balance is $45 billion (that is after a decrease of $7.6 billion in the second quarter). The FDIC is 100% paid for by fees on banks. The FDIC can raise the fees charged banks if the insurance fund needs to get increased funds.
Read more
Anyone involved in finance should understand mania in the markets. It is not a shock that financial markets do irrational things. They do so very frequently. Anyone who has not read, Manias, Panics, and Crashes: A History of Financial Crises, should do so. Leverage often is a catalyst that turns bad investments into panics that damage the economy. A previous post on this topic: Misuse of Statistics – Mania in Financial Markets.
Enron was the pit canary, but its death went unheeded
As for the lessons we’ve forgotten, how about this one: financial statements aren’t supposed to be fairytales.
…
when all was booming, Wall Streeters said they deserved their pay because the market said they were worth it. But now things are falling apart, they say the market doesn’t work, and we need to stop short-selling, and taxpayers need to pony up. If there is a tiny bit of good in all this, it’s that Wall Street, although it was complicit in the Enron mess, managed to walk away relatively unscathed. This time, Wall Street has brought itself down.
I think the odds that Wall Street has brought itself down is very low. Even that the ludicrous excesses of Wall Street are at risk is very unlikely. Perhaps for a few years their might be some restraints put on excesses. But most likely politicians will respond to huge payments by arranging favors for those that want to bring excesses back. If this can be prevented that would be great, but I doubt it will.
Related: Investing books – Tilting at Ludicrous CEO Pay – Losses Covered Up to Protect Bonuses
I give more credence to Warren Buffett’s thoughts on this than anyone else, though, of course, he could be wrong. Buffett: My fix for the economy
Buffett, the chairman and CEO of Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.A), called the problems facing world markets “unprecedented” and warned of a “disaster” if Congress does not move faster to shore up the economy.
…
Under Buffett’s plan, Treasury would lend hedge funds, Wall Street firms or any other investors 80% of the price for distressed assets. Investors would benefit from borrowing at lower rates available to the Treasury. But the government would get first claim on the sale of those assets, which means it would get its loan back plus interest and possibly turn a profit. Only then would investors see a penny.
“Now you have someone with 20% skin in the game,” explained Buffett. “Believe me, I won’t be overpaying if I’m buying with that kind of leverage. And you have someone [the investors] to manage the assets to the extent they need to be managed.”
Buffett also noted that the presence of the government in the transactions would raise the price of assets above the absolute firesale levels for which they could now be sold. That would benefit the banks trying to unload them.
It is a mess. And politicians should be held accountable for eliminating regulation (through law changes, political appointees that were chosen specifically to not enforce regulations, restricting money for enforcement…) to reward those that paid them a lot of money. But they won’t be, so there you go. I would love to be wrong about that but I don’t think I will.
Related: 2005 annual meeting with Buffett and Munger – Misuse of Statistics, Mania in Financial Markets – General Air Travel Taxes Subsidizing Private Plane Airports – Central Bank Intervention Unprecedented in scale and Scope (March 2008)
Since the S&P/Case-Shiller 20 city home price index peaked in June 2006 it has fallen 19.5%. In the year ending July 2008 the decline was 16.3%. That is a record drop. In that year Las Vegas declined 29.9%, Phoenix 29.3% and Miami 28.2%. For the largest cities: New York City declined 7.4%, Los Angeles 26.2%, Chicago 10% and Dallas 2.5% (the second lowest decline – Charlotte declined 1.8%); Houston and Philadelphia, the 4th and 5th largest cities are not included in the 20 city index.
Only one city shows a decline in housing values since January, 2000: Detroit is down nearly 7%. Washington is up 95% since January, 2000 (even with a 15.8% decline in the last year), Los Angels and New York are tied for second at 93% increases. The 20 city index is up 66% from January 2000 to July 2008.
The S&P/Case-Shiller Composite of 20 Home Price Index is a value-weighted average of the 20 metro area indices for single family homes.
Source: Record Home Price Declines (pdf)
Related: Housing Prices Post Record Declines – Home Price Declines Exceeding 10% Seen for 20% of Housing Markets – Fourteen Fold Increase in 31 Years – The Ever Expanding House – Coming Collapse in Housing?
I have had difficulty finding good economic data on manufacturing jobs. I have posted about this previously but have trouble finding much worth posting about: Worldwide Manufacturing Job Data – Manufacturing Jobs. The Unites States Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics has published some interesting data and so here is a look at some of that data.
The table shows average annual productivity gains (output per hour, in USA dollars – I think it is not clear) – the 2007 output totals are from the United Nations data I posted about last week (Data on Top Manufacturing Countries).
| Average Annual Manufacturing Productivity Gains by Country | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | 1979-1990 | 1990-1995 | 1995-2000 | 2000-2007 | 1979-2007 | 2007 Output $USA billion |
| Taiwan | 6.1 | 4.7 | 5.6 | 6.4 | 5.9 | |
| Korea | NA | 9.4 | 10.8 | 7.6 | NA | 241 |
| USA | 2.8 | 3.7 | 5.6 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 1,831 |
| France | 3.8 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 296 |
| Japan | 3.8 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 926 |
| United Kingdom | 4.1 | 2.8 | 2.7 | 3.9 | 3.6 | 342 |
| Germany | 2.1 | 2.9 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.0 | 670 |
| Spain | 3.3 | 3.1 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 208 |
| Canada | 2.1 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 218 |
| Italy | 3.4 | 3.8 | 1.4 | -.2 | 2.2 | 345 |
The countries that were part of the study but are not included in the table above: Australia, Belgium, Denmark, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden.
Manufacturing productivity increased in 14 of 16 countries in 2007, according to the study. The United States of America increase of 4.1 was the fourth largest among the 16 economies and was slightly above the 3.9 percent U.S. average annual increase since 1979. 15 of the 16 countries increased manufacturing output in 2007.
9 countries increased manufacturing hours worked in 2007, the USA increased 2.3% (below their average increase since 1979). Hours worked decreased for all countries in the period of 2000-2007 (UK has had the largest decrease 3.9% annual average decrease, the USA in next at 3.1%).
Manufacturing employment increased in 10 countries in 2007. From 2000-2007 the USA has experienced average annual declines of 3% in manufacturing employment (the second sharpest drop to the UK which has fallen 4%). From 1979-2007 the USA annual declines averaged 1.2% (only Taiwan.9% and Spain .1% showed increases). From 2000-2007 four countries show slight average annual increases: Spain .5%, Korea .4%, Taiwan .2% and Italy .2%. From 2000-2007 only 3 countries showed annual average decreases in output: Canada -.3%, Italy -.2% and UK – .1%.
Hourly manufacturing compensation has increased in all countries for the period 1979-2007 (data shown for this item is in each national currency: USA 4.6% average annual increases, Spain up 7.2% annually, Taiwan up 7%, UK 6.8%, Germany 4.4%, Japan 4.2%.
via: Canada’s Manufacturing Crisis in International Perspective
Related: posts on employment – Top 10 Manufacturing Countries 2006
re: New Rule: If your company is to big to fail, your company is too big to exist. The next Prez. needs to split up huge companies like we did with AT&T.
Exactly right. Companies too big to fail have massive negative externalities that should be managed through regulation. And the discussion (see link) of this claiming that the huge, anti-capitalist, companies that exist now are not monopolies and therefore anti-trust laws should not be used makes no sense. Anti-trust laws are not for monopolies. Trusts were huge anti-competitive organizations that sought to eliminate the free market and extract benefits by distorting the market. Those laws were adopted not to regulate monopolies but to regulate anti-competitive behavior.
The free market theory formulated by Adam Smith et.al. was based on perfect competition where no one entity could influence the market. In reality that is not possible but approximations of it can exist (we are far from such a state today, however). Fine, the anti-capitalist large corporations are not monopolies – they are oligopolistic that can still extract profits through their ability to distort the free market. Is the fact they are not a monopoly really that relevant?
Enforcing rules that prevent businesses from using their size and power to extract outsized profits is the right thing to do. Anti-trust laws are the proper tool. when politicians are paid lots of money by people with the gold to allow them to cripple the free market and create large corporations that profit, not by competing in a free market, but by manipulating the market that is a bad practice. It won’t change until people stop electing politicians that reward those that pay them for favors. And that is unlikely to happen anytime soon.
What we can hope is that there is some limit on how egregious the favors politicians grant those paying them money are. Maybe this latest escapade (and the costs of those favors to bankers) will cause a reduction in the favors granted. I don’t have high expectations for the changes though.
Read more