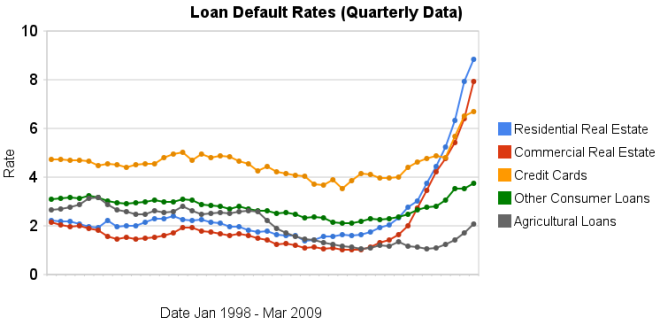
 Chart showing loan delinquency rates for real estate, consumer and agricultural loans for 1998 to 2009 by the Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.
Chart showing loan delinquency rates for real estate, consumer and agricultural loans for 1998 to 2009 by the Curious Cat Investing Economics Blog, Creative Commons Attribution, data from the Federal Reserve.Delinquency rates on commercial (up another 151 basis points) and residential (93 basis points) real estate continued to increase dramatically in the second quarter. Credit card delinquency rates increased but only by 20 basis points.
Real estate delinquency rates exploded in 2008. In the 4th quarter of 2007 residential delinquency rates were 3.02% by the 4th quarter of 2008 they were 6.34% and in the 2nd quarter of this year they were 8.84% (582 basis points above the 4th quarter of 2007). Commercial real estate delinquency rates were at 2.74% in the 4th quarter of 2007, 5.43% in the fourth quarter of 2008 and 7.91% in the 2nd quarter of 2009 (a 517 basis point increase).
Credit card delinquency rates were much higher than real estate default rates for the last 10 years (the 4-5% range while real estate hovered above or below 2%). Now they are over 200 and 300 basis points bellow residential and commercial delinquency rates respectively. From 4.8% in the 3rd quarter 2008 to 5.66% in the 4th and 6.5% in the 1st quarter of 2009.
The delinquency rate on other consumer loans and agricultural loan delinquency rates are up but nowhere near the amounts of real estate or credit cards.
As I wrote recently bond yields in the last few months show a dramatic increase in investor confidence for corporate bonds.
Related: Loan Delinquency Rates: 1998-2009 – The Impact of Credit Scores and Jumbo Size on Mortgage Rates – 30 Year Mortgage Rate and Federal Funds Rate Chart
Debt Negotiators May Give Little Relief to Consumers
Credit-card delinquencies are at record highs, according to Fitch Ratings, and the U.S. unemployment rate of 8.9 percent is the highest since 1983. As more consumers fall behind on bills, settlement companies often end up adding to the debt burden rather than offering a cost-saving solution, said Gail Cunningham, a spokeswoman for the National Foundation for Credit Counseling in Silver Spring, Maryland.
…
New York Attorney General Andrew Cuomo has begun a national investigation of settlement companies, and has sued two for fraud and false advertising. Illinois Attorney General Lisa Madigan has also filed two lawsuits against debt-settlement companies, alleging they “engage in deceptive marketing practices” and “do little or nothing to improve consumers’ financial standings.” Texas Attorney General Greg Abbott sued a debt settlement company in March, saying it engaged in “deceptive and misleading acts,” according to court documents.
It is much better to avoid this problem by taking wise personal finance actions – don’t take on personal debt for minor purchases (for a mortgage then debt is fine, probably fine for a car – though avoid debt if you can). The “secret” is not very secret. Just don’t buy what you can’t pay for. It is very simple, many people just don’t want to follow that simple strategy. Also save money in an emergency fund, so when some emergency comes along you don’t go into debt. You just use your emergency fund.
Once you are stuck in a bad situation with more debt than you can afford to pay back you have bad choices. Obviously many try to take advantage of you. Frankly they realize many that are stuck in bad financial position make bad financial decisions. Therefor it is a good place for those trying to rip people off to find people to take advantage of. The best way to deal with this is not to try and find the best debt negotiators it is to manage you finances well and not get in trouble.
Related: Personal Saving and Personal Debt in the USA – How to Use a Credit Card Successfully – Credit Card Companies Willing to Deal Over Debt – Where to Keep Your Emergency Funds? – Americans are Drowning in Debt
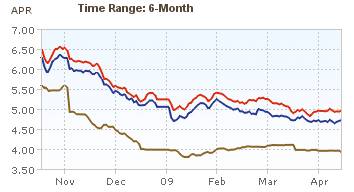 Showing mortgage rates over the last 6 months. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate.
Showing mortgage rates over the last 6 months. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate.
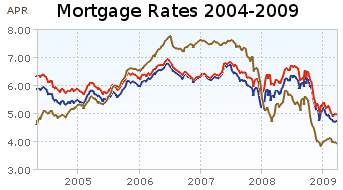 Showing mortgage rates over the last 5 years. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate. From Yahoo Finance, for conventional loans in Virginia.
Showing mortgage rates over the last 5 years. Red: 30 year fixed rate. Blue: 15 year fixed rate. Tan: 1 year adjustable rate. From Yahoo Finance, for conventional loans in Virginia.
The 6 month chart shows that mortgage rates have been declining ever so slightly. Rates on a 1 year adjustable mortgage fell from 5.5 to 4% and have stayed near 4% for all of 2009. 30 and 15 year rates (15 year rates staying about 25 basis points cheaper) have declined from 6.5%, 6 months ago to about 5% at the start of the year and have moved around slightly since. This is while the yield 10 year government treasuries have been rising (normally 30 year fixed rate mortgages track moves in the 10 year government bond). The federal reserve has been buying bonds in order to push down the yield (and stimulate mortgage financing and other borrowing).
Mortgage rates certainly could fall further but the current rates are extremely attractive and I just locked in a mortgage refinance for myself. I am getting a 20 year fixed rate mortgage; I didn’t want to extend the mortgage period by getting another 30 year fixed rate mortgage. For me, the risk of increasing rates outweigh the benefits of picking up a bit lower rate given the current economic conditions. But I can certainly understand the decision to hold out a bit longer in the hopes of getting a better rate. If I had to guess I would say rates will be lower during the next 3 months, but I am not confident enough to hold off, and so I decided to move now.
Related: Mortgage Rates Falling on Fed Housing Focus – posts on mortgages – 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates and the Fed Funds Rate – Continued Large Spreads Between Corporate and Government Bond Yields – Lowest 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates in 37 Years –
Then came a shocker: Amid one of the most reckless lending sprees in history, regulators focused on the one bank that refused to play along. Beal’s moves confused and worried them, and so they began to probe him with questions. “What are you doing?” he recalls them asking. “You’re shrinking yet you’re raising capital?”
Says Beal about the scrutiny, “I just didn’t fit into any box.” One regulator, the former head of the Texas Savings & Loan Department, Charles Danny Payne, says, “I was skeptical at first, but I’ve gained a lot of confidence over the years,” adding that Beal has an “uncanny ability to sniff out deals.”
Next, the credit rating agencies started pestering him about his dwindling loan portfolio. They never downgraded him but scolded him for seeming not to have a “sustainable” business model. This while their colleagues were signing off on $32 billion of bum collateralized debt obligations issued by Merrill Lynch.
…
He thinks the government is going to be “disappointed” by its various programs to revive lending. He says Treasury Secretary Timothy Geithner’s new plan to guarantee loans to buyers of toxic assets won’t lead to many sales because the problem isn’t liquidity but price. They are not low enough. Half the country’s banks–4,000 in all–would be bust, he says, if they marked their loans to what the loans would fetch in an auction. He says banks are fooling themselves by refusing to mark busted assets down.
“Banks are on a prayer mission that somehow prices will come back and they won’t have to face reality,” Beal says. And that reality, according to Beal, is going to get a lot worse. “Unemployment is going over 10%, commercial real estate hasn’t even begun collapsing and corporate credit defaults are just getting started,” he says. His prediction: depression, without bread lines this time, thanks to the government safety net, but with equal cost to society.
There are some (very few) who succeeded in not acting like lemmings. I wish someone would explain to me why people are worthy of millions in bonuses when they just do what every single other person in their position did that was also getting millions in bonuses. Obviously they were just practicing bankruptcy for profit (which worked out incredibly well for them) and still we seem to think the only solution is to support these moral bankrupt (and now commercially bankrupt) organizations and individuals.
Related: What the Bailout and Stimulus Are and Are Not – Sound Canadian Banking System – More on Failed Executives – Jim Rogers on the Financial Market Mess
Fed to start buying T-bonds today, hoping to move rates
The yield on the 10-year T-note plunged to 2.53% on March 18 from 3% the previous day, the biggest one-day drop in decades. But since then, Treasury bond yields have been creeping higher. The 10-year T-note ended Tuesday at 2.65%. Conventional mortgage rates have flattened or inched up, although they remain historically low, in the range of 4.75% to 5%.
…
On Tuesday the Treasury sold $40 billion of new two-year T-notes at a yield of 0.95%, which was lower than expected, indicating healthy investor demand. The government will auction $34 billion in five-year notes today and $24 billion in seven-year notes on Thursday. Against numbers like those in just one week, the Fed’s commitment to buy $300 billion of Treasuries over six months doesn’t look like much.
…
there’s nothing to stop the Fed from suddenly announcing that its $300-billion commitment will get substantially bigger: The central bank can, in effect, print as much money as it wants to buy bonds — at least, until the day that global investors stop wanting dollars.
The original announcement caused a dramatic move but since then yields have been drifting up, every day, including today. Rates are already very low. And the huge amount of increased federal borrowing is a potential serious problem for lowering rates. And potentially an even more serious problem is foreign investors deciding the yield does not provide a good investment given the risks of inflation (I know that is how I feel). It will be interesting to see what happens with rates.
Related: Who Will Buy All the USA’s Debt? – Lowest 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates in 37 Years – mortgage terms
The economy has structural problems. The solution at this time is not to convince people that everything is fine and just go spend money you don’t have. Personal debt is much to high. The practices that allowed huge anti-competitive and economy endangering institutions to threaten the economy have not been addressed. Hundreds of billions of dollars have been given to those who caused the credit crisis. Making the federal debt problem even worse.
Some suggest we need to regain consumer confidence. Unfortunately that fixes nothing. That “strategy” is just to convince people problems don’t exist and buying what you can’t afford is fine. Just convince people to go spend more money, run up their credit card debt, borrow against their house, as long as everyone believes it can continue. That can work for awhile but it then fails due to structural issues. And the solution becomes more and more difficult the longer such a strategy is used. The same way a ponzi scheme eventually implodes.
If you could convince those in a ponzi scheme (and new investors) that they should just be optimistic it can continue. But eventually people ask for their money to buy something and none exists and the scheme fails.
With an economy, after structural problems are addressed then you need to convince people to be less fearful and to be more optimistic. Because often by that time people have become so fearful that they are not taking even reasonable steps. They don’t buy even though they have the money in the bank and have a real need for the purchase. When this happens, convincing people that the economy is stable is important. However, cheerleading and convincing people to just continue to run up their debts to spend more is not wise when the economy is already far to in debt is not wise (though it is politically expedient).
The USA needs to stop living beyond its means. That is the most important factor to long term economic strength. But the focus doesn’t seem to be on doing this, instead it seems to be on printing money to paper over the problems. There are many great strengths of the economy and those have allowed huge federal deficits, huge personal debt, monopolistic practices, destabilizing financial risks taking… Even with that things have been quite good. But those areas need to be addressed over the long term.
Related: Let the Good Times Roll (using Credit) – Families Shouldn’t Finance Everyday Purchases on Credit – Living on Less
A documentary of the mortgage crisis by CNBC: House of Cards. It is a bit slow and simple but still for people that don’t really understand the basics of what happened it is interesting.
Related: Nearly 10% of Mortgages Delinquent or in Foreclosure – Ignorance of Many Mortgage Holders (2007) – How Not to Convert Equity – mortgage terms
Low Mortgage Rates a Mirage as Fees Climb, Eligibility Tightens
…
“A score of 700 was once near perfect,” said Gwen Muse Evans, vice president of credit policy at Fannie Mae, the government-controlled company that helps set lending standards. “Today, a 700 performs more like a 660 did. We have updated our policy to take into account the drift in credit scores.”
Consumer credit scores, called FICOs after creator Fair Isaac Corp., range from 300 to 850. The average FICO score on mortgages bought by Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae rose to 747.5 in the fourth quarter of last year from 722.3 in 2005, according to Inside Mortgage Finance.
Accunet’s Wickert said that a 660 FICO score would have qualified most borrowers for loans with no upfront fees in the past. Now, someone trying to borrow $200,000 with a 660 score would have to pay a 2.8 percent fee, or $5,600, he said. Even someone with a 719 score would have to pay $1,750 in cash.
The low mortgage rates are attractive but a decision to re-finance (or buy) must consider the long term implications. Also if you are re-financing to take advantage of the low rates consider a 20 year or 15 year loan if you are already well into your 30 year loan. A fixed rate loan is the most sensible option at this time.
Related: Low Mortgage Rates Not Available to Everyone – 30 Year Fixed Mortgage Rates and the Fed Funds Rate Chart – Ignorance of Many Mortgage Holders – Fed Plans To Curb Mortgage Excesses – How Not to Convert Home Equity
Who Will Buy All the USA’s Debt? That is a question worth thinking about. The USA is a huge net borrower. The government can’t borrow from consumers because they are hugely in debt themselves. Over the last few decades huge investments from Japan, China and the Middle East in USA government debt have allowed the huge amount of federal debt to continue to grow rapidly. But who is going to buy the increasing amounts of debt; in the next few years, and the next few decades?
China is right to have doubts about who will buy all America’s debt
…
The other area of concern for China is the value of its Treasuries. Given the US borrowing requirement and its lax monetary policy, Treasury bond yields could well rise sharply, causing a corresponding price decline. If China’s holdings match Treasuries’ average 48-month duration, then a 5pc rise in yields, from 1.72pc on the 5-year note to 6.72pc, would lose China 17.5pc of its holdings’ value, or $119bn.
Foreign buyers have absorbed a little over $200bn of Treasuries annually, a useful contribution to financing the $459bn 2008 deficit, but only a modest help towards the $1.35 trillion minimum average deficit forecast for 2009 and 2010.
Unless that changes substantially, there will be $1 trillion annually to be raised by the Treasury from domestic sources, more than double the previous record from domestic and foreign sources together, plus whatever is needed to bail out the banks.
Even if the US savings rate were to rise from zero to its long-term average of 8% of disposable personal income, that would create only an additional $830bn of savings — not enough to fund the domestic share of the deficit. Interest rates would probably have to rise substantially to pull in more foreign investors.
Very true. Anyone buying government debt at these rates has reason to question the wisdom of doing so. Exporters to the USA have macro-economic reasons for buying debt (to keep the value of the dollar from collapsing) but the investing reasons for buying USA debt I find very questionable (I wouldn’t be buying it as an investment, if I were them).
Related: Personal Saving and Personal Debt in the USA – Americans are Drowning in Debt – USA Federal Debt Now $516,348 Per Household – Is the USA Broke?
President Barack Obama’s Inaugural Address
That sounds nice I believe however, it is fairly irrelevant. Economic demand is what is down, not production capacity. We are “no less productive than when this crisis began.” Ok, that is probably true. So what. That implies that the crisis has something to do with productivity. If we say the color of our eyes is the same as when the crisis began it is obvious that is a non-sequitur. Well so is the quote by the new President, though that is less obvious.
Our demand was definitely over stimulated using massive federal government budget deficits, massive trade deficits, massive amounts of consumer debt, massive amounts of unjustified mortgage debt and massive amounts of leverage. None of those things has anything to do with capacity in the implied sense – capacity to produce. They have to do with the capacity to consume. And while our capacity to consume has not declined. The funding that allows that consumption (foreign lending, high leverage, junk mortgages…) has decreased.
Read more